![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocrine organs have __________ capillaries |
Fenestrated |
|
|
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) development |
Rathke's Pouch (Roof of oropharynx) |
|
|
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) development |
Floor of diencephalon |
|
|
Pars Intermedia development |
Remnants of rathke's pouch |
|
|
Adenohypohysis components |
Pars tuberalis, pars distalis |
|
|
Neurohypophysis components |
Median eminence, infundibulum, pars nervosa |
|
|
How does posterior pituitary stain and why? |
Pale because of unmyelinated axons, neuroglial cells and no fibers |
|
|
Describe anterior pituitary appearance on a slide |
Very cellular with distinct boundaries |
|
|
Pars distalis (adenohypophysis/anterior pituitary) cells |
Chromophobes and chromophils |
|
|
Chromophobes (50%) |
-Clear cells -Function unknown |
|
|
Chromophils (50%) |
40% acidophils 10% basophils |
|
|
Acidophils |
-Somatotropes --> GH -Mammotropes/Lactotropes --> PRL
Make PEPTIDES Pale staining |
|
|
Basophils |
B-FLAT
-FSH (Gonadotrope) -LH (Gonadotrope) -ACTH -TSH
These act on other organs (*Tropic Effect*) Make GLYCOPROTEINS |
|
|
What does Pars Intermedia release? |
MSH |
|
|
What type of chromophils does Pars Tuberalis have? |
Basophils --> mainly gonadotropes |
|
|
Where do the unmyelinated axons from Pars Nervosa descend from? |
Supraoptic nuclei and Paraventricular nuclei in hypothalamus |
|
|
Herring bodies |
Axonal dilations that store oxytocin and ADH and contain neurosecretory granules |
|
|
What does supraoptic nucleus synthesize? |
ADH |
|
|
What does paraventricular nucleus synthesize? |
Oxytocin |
|
|
Pituicytes |
Supportive neuroglial cells of posterior pituitary |
|
|
2 Pineal gland cells |
Astrocytes and pinealocytes |
|
|
What do pinealocytes secrete? |
Melatonin and serotonin |
|
|
What are astrocytes' function on pineal gland? |
Supportive cell |
|
|
Pineal gland histological marker |
Corpora arancea --> "brain sand" |
|
|
Corpora Arancea |
Deposits of calcium in pineal gland stroma |
|
|
2 cells of thyroid gland |
Follicular (principle) cells and Parafollicular (C) cells |
|
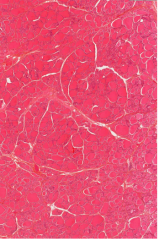
Identify |
Thyroid gland |
|
|
Parafollicular cells (C cells) |
-Secrete calcitonin --> lowers blood calcium -Not controlled by pituitary |
|
|
Follicular (Principle) cells |
-Secretes T3 and T4 -Controlled by pituitary |
|
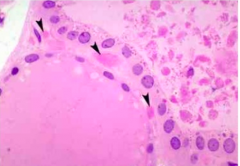
Identify |
Thyroid gland (Notice flattened inactive follicular cells and cuboidal follicular cells) |
|
|
Grave's Disease |
Hyperplasia of follicular cells |
|
|
Simple goiter |
Insufficient iodine intake |
|
|
Cretinism |
Hypothyroidism in fetal life |
|
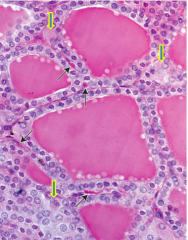
Identify |
Thyroid |
|
|
Thyroid epithelium |
Simple cuboidal |
|
|
Parathyroid gland cells |
Oxyphil and Chief cells |
|
|
Oxyphils cells (of parathyroid gland) |
Large acidophilic cells Unknown function Numerous mitochondria |
|
|
Chief Cells (of parathyroid gland) |
Secrete PTH --> increases blood calcium, decreases blood phosphate |
|
|
Adrenal cortex development |
Mesoderm |
|
|
Adrenal medulla development |
Neural crest |
|
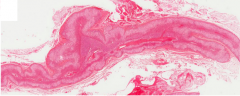
Identify |
Adrenal gland |
|
|
Zona glomerulosa |
Mineralocorticoids --> aldosterone |
|
|
Zona fasciculata |
-Glucocorticoids --> cortisol -Pale staining |
|
|
Zona reticulata |
Androgens |
|
|
Addison's Disease |
Antibodies against adrenal cortex |
|
|
Cushing's Disease |
Increase glucocorticoids |
|
|
Adrenal medulla cell types |
Chromaffin cells and ganglion cells |
|
|
Chromaffin cells |
-Modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons -Store and secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine |
|
|
Pheochromocytoma |
Tumor of chromaffin cells |

