![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
133 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
when does the Moro (startle) reflex disappear in kids
|
Moro reflex disappears by 5th month
|
|
|
|
when does a babinski sign disappear
|
1 year
|
|
|
|
when does the grasp reflex disappear
|
4 months
|
|
|
|
when does an infant have head and neck control
|
2 months
|
|
|
|
when does a baby crawl (up on all fours)
|
3-5 months
|
|
|
|
when does a baby creep
|
7-9 months
|
|
|
|
when does a baby stand
|
9-14 months
|
|
|
|
list the progression of knee position from birth to age 60
|
Birth: varum (bow)
1-3:straight 3-6:knock 7-14:straight 14-18: knock over 18: straight over 60: knock Multiples of 6; 0-3,6,12,18,24 sksksk |
|
|
|
at what age is heel varus (10 degrees) normal until
|
-from birth to 6 yo
-then normal is 2-5 degrees varus |
|
|
|
list 4 diff hip tests for infants
|
-Ortoloni: adduction of thigh creates clicking for dislocation
-Barlow: like Ortoloni, but abduction -Anchor sign: difference in number of gluteal folds when baby is on stomach -Galezzi: lower knee position on affected side, knees and hips flexed with baby on back |
|
|
|
most common congenital pediatric deformity
|
-calcaneovalgus
-dorsal foot is in contact with the anterior surface of the leg -prime cause of flexible flatfoot deformity |
|
|
|
TX for calcaneovalgus
|
-manipulation and casting
-equinus with PF of first met and adduction of FF to align TN joint |
|
|
|
rocker bottom deformity in peds
|
vertical talus (rigid flat foot)
|
|
|
|
when should surgery be chosed for vertical talus
|
-when casting fails or the TN dislocation isnt reducible
|
|
|
|
surgery in MA in pediatrics should be postponed until age 3; what are non surgical tx options
|
-manipulation
-Wheaton brace(plastic AFO brace, alternative to casting). serial casts with calc in neutral, abduction FF |
|
|
|
Talipes equinovarus (TEV) signs
|
-clubfoot
-inversion od FF and RF -adduction of the FF -Simons rule: Kites (T-C) angle <15degrees, talo first > 15 -CI 17 (N=45) |
|
|
|
what if equinus is corrected first in clubfoot (TEV)
|
-rocker bottom deformity, flat topped talus
|
|
|
|
when do sesamoids appear
|
12 yo
|
|
|
|
when dose calcaneal apopkysis appear
|
7 yo
|
|
|
|
1st bone to ossify AFTER birth
|
-lateral cuneiform (3 months)
-Look Mom! -medial cune (2 yo) -intermediate cune (2+ yo) -navi is the last bone to ossify AFTER birth (3-4 yo) |
|
|
|
what is the LAST bone to ossify BEFORE birth
|
-cuboid
-so it may be absent in a premature baby |
|
|
|
osteochondrosis (disorder of primary or secondayr ossification centers by vascular disturbance) of the tibial tubercle
|
-Osgood Schlatters
-caused by the patellar tendon on the tibial tubercle |
|
|
|
at what age do kids get Kohlers dz
|
-navi
3-6 yo (navi ossifies at 3 yo) |
|
|
|
when is Severs dz seen, and with what foot type is it MC
|
-age 10-11 with a cavus foot type
|
|
|
|
how much ROM at the hip at 1 yo and 5 yo
|
1 yo: twice as much external
5 yo: internal = external |
|
|
|
what can internal femoral torsion cause
|
in toe gait
-low tibial torsion also causes in toe gait -external femoral torsion causes out toe gait |
|
|
|
normal malleolar position at birth and 6 yo (tibial torsion = malleolar torsion + 5 degrees)
|
Birth: 0-5
6 yo: 13-18 -less than 13-18 degrees gives in toe gait |
|
|
|
list possibles causes of in toe gait
|
-internal femoral torsion
-low exteral torsion of the tibia -talar neck adductus -clubfoot -talipes varus -met adductus -genu varum -tibia varum |
|
|
|
when should you treat in-toeing and with what
|
-when in toed more than 8 degrees
-tx with manipulation, gait plates, D-B bar or Ganley splint |

|
|
|
when is sx (ORIF) indicated in SH injuries
|
Type 3,4
-otherwise NWB cast |
|
|
|
which SH causes growth disturbances
|
SH 4
-extends from the joint surface to the epiphysis and plate and through the metaphysis |
|
|
|
which SH causes angulation deformities
|
SH 5
-severe crush injruy and compression of the plate |
|
|
|
which SH causes shortening and angular deformoty
|
SH 6
-brusing of growth plate |
|
|
|
Summary of SH injuries
|
-the younger the pt, the greater the risk of deformity
-compression fx has worse prognosis -reduction should be done in 10 days -helaing of epiphyseal injusries takes 3 weeks, as compared to 4-6 for bone injuries -f/u for growth defomrity should be 3 years |
SH 4 - growth disturbances SH 5- angulation issues SH 6- both shortening and angulation
|
|
|
what does a shoulder drop in a child signify
|
- short limb on that side
-in contrast adult has a shoulder drop on the opposite side of the short limb |
|
|
|
if a child has an adducted gait, and patellar position is internally rotated - where can the deformity be coming from , what if the patellar position is normal
|
-if patella is internally rotated and foot is adducted, part of the problem is the femur
-if the patella is straight, the problem must be with the knee, tibia or foot |
|
|
|
a childs calc is normally everted until what age
|
6-7 yo
- it should reduce by 1 degree every year -a child with calcaneal eversion of 7 degrees should reduce to perpendicular by age 7 |
|
|
|
what is the normal amt of int and ext knee ROM
|
-equal amounts of internal and external
|
|
|
|
At birth there is no tibial torsion (malleolar position) present,but gradually increases to a position of...
|
13-18 degrees by age 7-8 yo
|
|
|
|
at what age does a propulsive gait start
|
age 3
-so a functional orthoses is not useful prior to this |
|
|
|
list a peds deformity that will NOT be outgrown
|
forefoot varus or valgus
-therfore you should support this deformity to prevent abnormal compensation |
|
|
|
can tibial torsion be treated with casting
|
-YES FROM TOES TO MID THIGH WITH MILD EQIUNUS AND KNEE FLEXION
|
|
|
|
what will a gastroc soleus muscle equinus cause in a child
|
-toe walking
|
|
|
|
Flat navicular on xray, pain, limp
|
-Kohlers dz
-called Mueller Weiss in adults and requires surgical fusion -No surgery for peds in osteochondroses |
|
|
|
what is APGAR score based on
|
-HR, respiratory, muscle tone, reflex to nasal cathter, skin color
-score of 0,1, or 2 -max 10 |
|
|
|
the femur has 30 degrees of internal torsion at birth, this gradually starts to unwind by 5-6 yo; what if this doesnt happen or happens more slowly
|
-intoeing
-90% will out grow this unless there is a familial tendency |
|
|
|
kids have knock knees at ages 3-6 and out grow knock knees by...
|
age 8
-may again reappear at 12-14 yo esp females |
0-3 s, 6 k, 12 s, 18 k, 21 s
|
|
|
Differentiate Vertical Talus (VT) from Talocalc valgus (TCV)
|
VT: foot is 90 degrees to the leg(equinus), calc is in equinus TCV: foot is DF and contacts the leg, calc is DF, heel valgus
|
|
|
|
TCV can be treated with stretch and casting in younger child, tx options for older or un responsive foot
|
Evans with ST release and tendon lengthening
|
|
|
|
Pes Valgus in peds: heel valgus, FF abduction, ankle equinus; compensation occurs with early heel off and collapse of medial column; what happens with the TN and CC joints
|
TN and CC joints become divergent and their axes become parallel
|
|
|
|
Pediatric flatfoot can be structural (rigid) or functional; list causes of each type
|
Structural (CVT and tarsal coaltions), Functional (ligament dz, accessory navi, os tibiale externum, compensatory for hip or knee, neuropathy)
|
|
|
|
List 2 soft tissue procedures for correction of pes valgus
|
Kidner, Young procedures
|
|
|
|
Describe the Kidner procedure for flat foot
|
resect the accessory navi, move TP insertion to underside of navi
|
|
|
|
Describe the Young procedure for flat foot
|
lengthen the Achilles, re-route the TA through a slot in the navi w/o detaching the tendon, move the TP to underside of navi
|
|
|
|
List osseous medial column procedures for flat foot
|
Hoke arthrodesis, TN fusion, STJ fusion
|
|
|
|
Describe the Hoke procedure for flat foot
|
navi to medial and intermediate cuneiforms with TAL, this procedure has fallen out of use
|
|
|
|
When a TN fusion is used for flat foot, how much of the Midtarsal joint and STJ motion is restricted
|
all the MTJ motion and most of the STJ
|
|
|
|
What is the procedure of choice for transverse plane flat foot
|
Evans
|
|
|
|
Frontal plane dominance flat foot is least common, what bone procedures are best with this type
|
posterior osteotomies (Dwyer, Silver)
|
|
|
|
List some extra-articular osteotomies STJ
|
Chambers, Selakovich, Grice
|
|
|
|
Chambers procedure
|
bone graft into the sinus tarsi
|
|
|
|
Swlakovisch procedure
|
open wedge osteot of the sus tali
|
|
|
|
What is the location of the osteot for an Evans
|
parallel to the CCJ, 1.5 cm proximal to it, with 1 cm bone graft inserted
|
|
|
|
What is a Dwyer
|
for frontal plane dominance, calc medial closing (MC) or lateral opening wedge. - lateral closing will tx varus
|
|
|
|
What is a silver
|
for frontal plane dominance flatfoot, calc lateral open wedge with graft
|
|
|
|
When is a triple AD used for flatfoot
|
3 plane deformity with pain, paralytic deformity, intra articular tarsal coaltions, rupture of TP tendon
|
|
|
|
Presents as a rigid, rocker bottom deformity
|
vertical talus (this is a very rare condition)
|
|
|
|
What is the hallmark of rigid vertical talus
|
dorsal dislocation of the navicular on the talar head and neck, navi rigidly articulates with dorsal cortex of the talus
|
|
|
|
What are some synonyms for vertical talus
|
1.congential valgus flatfoot with TN dislocation 2. Congenital rigid rocker bottom foot 3. Congential convex pes valgus 4. Reverse clubfoot
|
|
|
|
Radiographic findings of congential vertical talus (CVT)
|
AP; there is no TC articulation anteriorly, inc TC angle (kites), FF abduction Lateral: equinus calc, dorsal displacement of FF on talus, vertical talus, rocker bottom
|
|
|
|
What views should be obtained for CVT
|
lateral PF view (irreducibility of the deformity by forced PF distiguisehes this condition from flexible PF talar deformities), lateral DF view (this allows to assess the degree of fixed equinus of the calcaneus)
|
|
|
|
What is the Eyre-Brook test for CVT
|
a forced lateral PF xray, distinguishes rigid PF talus from flexible PF talus
|
|
|
|
Can CVT be treated conservatively
|
rarely, if it fails by 3 months of ago, resort to surgical tx bc bone adaption will start to occur making surgical correction more difficult
|
|
|
|
List surgical tx for CVT at 6-12 months of age, at 2-6 yo, >6 yo
|
6-12 months: Cinnicnnati incision w/post capsultomy and releases, pinning of TC, TN. 2-6 years: grice-green STJ AD. >6 yo: triple AD
|
|
|
|
What plane(s) does met adductus occur in
|
flexible transverse plane only deformity at lisfranc level
|
|
|
|
Bleck grading system of Met adductus
|
based on where the heel bisector bisects the toes. Normal is when the heel bisector passes b/w digits 2/3. Mild: through 3rd toe, moderate through the 4th toe, severe through the 5th toe
|
|
|
|
What is the normal met adductus angle
|
N=15 degrees, 15-20 is mild, 20-25 is moderate, >25 is severe
|
|
|
|
How does MA differ from TEV
|
MA has navi LATERAL, inc Kites angle (>24), Clubfoot (TEV) has navi MEDIAL, dec kites angle (<15). Both feet are turned in.
|
|
|
|
When is surgical tx a choice for met adductus
|
after 2 yo and failed conservative tx. Stretching for less than 3 weeks old, casting for 3 weeks-2 yrs old.
|
|
|
|
Ligamentous releases can be used in MA for 2-5 yrs old (Heyman,Herndon & Strong), why is osseous needed after 6 yrs old
|
metatarsal bases square off
|
|
|
|
What is a Heyman, Herndon & Strong procedure
|
used for 2-6 yo. Complete mobilization of tarsomet and intermet ligaments and fix with K wires, MUST leave the plantar lateral ligs intact to prevent the whole foot from collapsing
|
|
|
|
List and describe osseous procedures for MA
|
Fowler (open wedge of medial cune with graft), Lepird*(closing wedge of 1 and 5 bases, met rotational osteots of 2/3/4
|
|
|
|
What is the one difference between postural clubfoot and congenital rigid clubfoot(TEV)
|
rigid clubfoot has TCN subluxation in addition to the CAVE
|
|
|
|
What is the rule of 15 with respect to clubfoot (TEV)
|
Kites Talo-calc <15 on lateral, talo-1st met >15 on AP
|
|
|
|
Cavus is corrected first with clubfoot Ponseti technique, describe
|
FF is supinated and first met is DF
|
|
|
|
Where is a cinncinnati incision
|
begins medially at the navi, behind the ankle and laterally to 5th met base
|
|
|
|
Where is a Hockey stick incision for clubfoot
|
begins medially at the navi, behind the medial mall and up medial side of the leg
|
|
|
|
Define skewfoot deformity
|
FF adduction, hindfoot valgus; never seen at birth, often a complication of met adductus casting or clubfoot
|
|
|
|
MC short metatarsal
|
4th met
|
|
|
|
TX options for brachy met
|
ex fix, Scarf lengthening osteotomy, bone graft
|
|
|
|
What is the MC polydactyly
|
Post axial (5th met), Pre axial (hallux) is 2nd most common, axis is the 2nd met
|
|
|
|
What more important path should be ruled out with a polydactyly pt
|
atrial septal defect
|
|
|
|
Ectrodactyly
|
cleft foot, claw foot, lobster foot
|
|
|
|
MC coaltion
|
TC, but it is asymptomatic
|
|
|
|
MC symptomatic coaltion
|
CN
|
|
|
|
Pain of TN coaltion appears at
|
3-5 yrs, navi fuses at 3-4 years
|
|
|
|
Pain of CN coaltion appears at
|
8-12 yrs
|
|
|
|
Pain of TC coaltion appears at
|
12-16 yrs
|
|
|
|
Tx algorithm for coalitions
|
fuse if it is: adult, intra articular, assoc DJD
|
|
|
|
Halo sign
|
TC coaltion, increased radio dense underneath the STJ
|
|
|
|
Comma sign, anteater
|
CN coalition
|
|
|
|
MC congential foot malformation
|
calcaneovalgus TCV (DF foot on the anterior tibia)
|
|
|
|
MC short metatarsal
|
4th met
|
|
|
|
TX options for brachy met
|
ex fix, Scarf lengthening osteotomy, bone graft
|
|
|
|
What is the MC polydactyly
|
Post axial (5th met), Pre axial (hallux) is 2nd most common, axis is the 2nd met
|
|
|
|
What more important path should be ruled out with a polydactyly pt
|
atrial septal defect
|
|
|
|
Ectrodactyly
|
cleft foot, claw foot, lobster foot
|
|
|
|
MC coaltion
|
TC, but it is asymptomatic
|
|
|
|
MC symptomatic coaltion
|
CN
|
|
|
|
Pain of TN coaltion appears at
|
3-5 yrs, navi fuses at 3-4 years
|
|
|
|
Pain of CN coaltion appears at
|
8-12 yrs
|
|
|
|
Pain of TC coaltion appears at
|
12-16 yrs
|
|
|
|
Tx algorithm for coalitions
|
fuse if it is: adult, intra articular, assoc DJD
|
|
|
|
Halo sign
|
TC coaltion, increased radio dense underneath the STJ
|
|
|
|
Comma sign, anteater
|
CN coalition
|
|
|
|
MC congential foot malformation
|
calcaneovalgus TCV (DF foot on the anterior tibia)
|
|
|
|
Key features of the Ponsetti method
|
Keep FF supinated(corrects cavus by aligning PF first met with other mets)
Apply lateral pressure to talar neck only. Rotate calc and forefoot around talus, talus head is fulcrum Abduction to 70 |
|
|
|
Pt with hx of clubfoot casting presents with dynamic supination during swing phase...explain
|
Incomplete reduction of navi onto talar head changes TA to supinator instead of a DF
- tx with TA transfer to lateral foot |
|
|
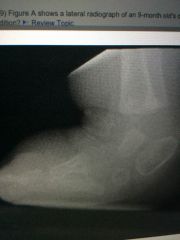
|
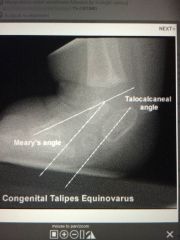
Talus and calc are parallel . A vertical talus wouldn't be parallel to the calc.
|
|
|
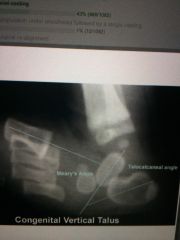
|
Cvt
|
|
|
|
Orthotic for pos Coleman block test cavovarus foot
|
Lateral heel wedge, semi rigid with first ray depression
Cavus feet do not TOL rigid high arch orthotics |
|
|
|
Orthotic for pos Coleman block test cavovarus foot
|
Lateral heel wedge, semi rigid with first ray depression
Cavus feet do not TOL rigid high arch orthotics |
|
|
|
Sx tx for pos Coleman block cavovarus foot
|
TAL, DF first osteotomy, tp transfer to dors for drop foot, rhos augments the weak TA and PL to PB transfer
|
|
|
|
Orthotic for pos Coleman block test cavovarus foot
|
Lateral heel wedge, semi rigid with first ray depression
Cavus feet do not TOL rigid high arch orthotics |
|
|
|
Sx tx for pos Coleman block cavovarus foot
|
TAL, DF first osteotomy, tp transfer to dors for drop foot, rhos augments the weak TA and PL to PB transfer
|
|
|
|
Sx tx for abnormal or neg Coleman block
|
Calc valgus creating osteotomy. Lateral closing
|
|
|
|
Orthotic for pos Coleman block test cavovarus foot
|
Lateral heel wedge, semi rigid with first ray depression
Cavus feet do not TOL rigid high arch orthotics |
|
|
|
Sx tx for pos Coleman block cavovarus foot
|
TAL, DF first osteotomy, tp transfer to dors for drop foot, rhos augments the weak TA and PL to PB transfer
|
|
|
|
Sx tx for abnormal or neg Coleman block
|
Calc valgus creating osteotomy. Lateral closing
|
|
|
|
What muscular imbalance causes cavovarus foot
|
TA and pl, PL over powers
|
|
|

|
CVT. navi will be dorsal to the talus. Use the first met as a navi landmark until age 3 when the navi appears
|
|
|
|
Tx for CVt
|
Rocker bottom
- not reducible with casting, but can help stretch ST before surgery -reduce and pin TN joint and release dorsal lateral tendons. However calcaneovalgus is reducible with stretch and cast |
|
|
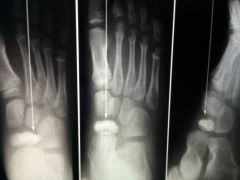
Tx kohlers dz (sclerotic potato chip navi)
|
-occurs bc talus and cune ossify before the navi and compress it
- tx SLC WB for 6-12 weeks usually resolves on its own |
|

