![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
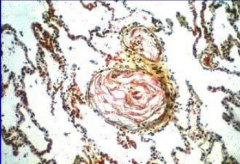
Amniotic fluid embolism - occurs when the placenta is delivered and ruptures open the maternal sinuses, allowing for amniotic fluid to enter maternal circulation and cause DIC
|
|
|
Arterial embolism - most arise from mural thrombi in the heart that travel to lower extremities
|
|
|
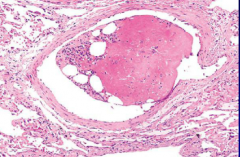
Bone marrow embolism - result from fractures that release bone marrow into circulation (common with overly enthusiastic CPR)
|
|
|
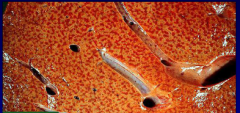
"Nutmeg Liver" aka chronic passive congestion of the liver due to heart failure - causes hepatic sinuses to fill with blood (red dots)
|
|
|
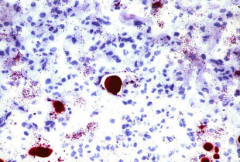
fat embolism - similar bone marrow embolism
|
|
|
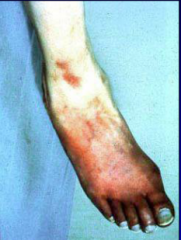
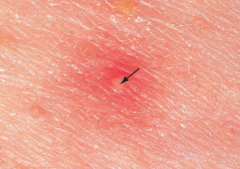
Folliculitis - tiny pus-filled abscess surround by hyperemia due to inflammatory dilation of arterioles
|
|
|
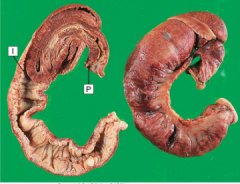
intussception - invagination of the bowel. Causes congestive infarct (dark area) due to compression of venous outflow
|
|
|
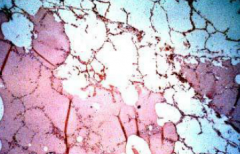
pulmonary edema - notice how there is NO inflammatory cells. Pink stained area is albumin
|
|
|
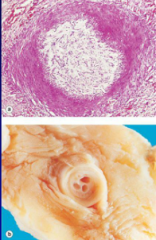
Recanalization - occurs when a scar forms in a blood vessel and a series of small holes are formed to retain blood flow. Lumen will never be as wide as it originally was.
|
|
|
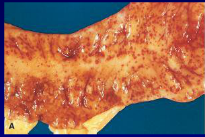
Petichiae - pinpoint hemorrhages causes by leaky capillary walls (which can be due to increased hydrostatic pressure, thrombocytopenia, or poor basement membrane formation)
|
|
|
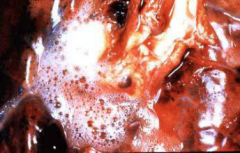
pulmonary edema
|
|
|
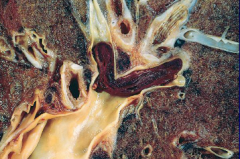
pulmonary thromboembolsim - notice the lines in the clot ("lines of Zahn") that indicate that this is a pre-mortem clot
|
|
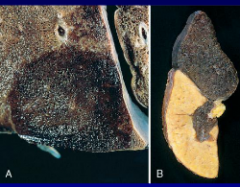
|
A - red infarct = caused by venous occlusion, often in loose tissue with double circulation (ex: lung). B - white infarct = caused by occlusion of arterial supply, often in solid organs
|
|
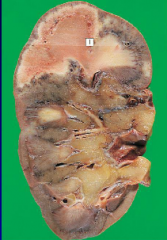
|
renal infarct - notice the characteristic wedge shape, pale necrotic area surrounded by a rim of hyperemia. This will eventually form a scar
|
|
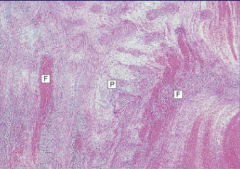
|
Lines of Zahn in a thrombus - lines of organized fibrin ("F") with interwoven platelets ("P")
|

