![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MOA of Heparin
|
Activates Antithrombin which decreases thrombin and factor Xa
|
|
|
Clinical use of Heperin?
Monitor using what? |
Can be used for just about any acute issue (MI, DVT, PE, acute coronary syndrome)
Very short half life (IV). Must be monitored with PTT! |
|
|
Treatment for Heperin overdose?
|
Protamine sulfate (positevly charged molecule which binds to the negatively charged heparin)
|
|
|
SE of Heparin
|
Bleeding
Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Osteoporosis |
|
|
What is Heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
|
Develop IgG antibodies against platelet factor 4 (activates platelets).
IgG + Hep + PF4 activate many platelets leading to thrombosis but you use them up leading to thrombocytopenia |
|
|
What is the IgG made against in Heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
|
IgG against platelet factor 4
|
|
|
What is enoxaparin and dalteparin?
|
Low molecular weight heparin?
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of low molecular weight heparin (Enoxaparin and Dalteparin)
|
Mainly work on Factor Xa.
Longer half life and can be used orally. Do not require intense laboratory monitor. Not reversible though. |
|
|
Lepirudin, bivalirudin, desaruin and argatroban
MOA? |
Inhibit thrombin (come from leeches)
Used as a alternative to Heparin |
|
|
These drugs are used as a replacement for heparin especially in HIT patients
|
Lepirudin, Bivalirudin, Desarudin, Argatroban
|
|
|
Warfarin aka Coumadin
MOA? What is the normal role of Vitamin K? |
Inhibits epoxide reductase which activates VItamin K
The normal role of Vitamin K in the body is to carboxylate factors C, S, 2,7, 9, 10 |
|
|
What factors are carboxylated/activated by Vitamin K?
|
1972 + C + S
(10, 9, 7, 2) |
|
|
How do you monitor Warfarin?
What is the worldwide recognized name? |
PT (it should increase) aka for EXTRINSIC pathway
INR |
|
|
Clinical use of Warfarin
|
Used for many long term things:
prevent stroke in A-fib pt., venous thromboembolosim prophylaxis |
|
|
Which can you use in pregnancy warfarn or Heparin?
|
HEPARIN!!
Warfarin crosses the placenta and causes a mess!! |
|
|
Warfarin has many DDI b/c it is metabolized in the ________________ (what organ)?
|
Liver's P450 enzyme.
IMPORTANT! |
|
|
SE of Warfarin
|
Bleeding
Teratogenic DDI |
|
|
Treatment for warfarin overdose?
|
Vitamin K and fresh frozen plasma (b/c Vitamin K doesn't work right away)
|
|
|
69 year old female has A-fib but we can't cardiovert her right away b/c we are scared to blow the clot to her brain. Thus she is started on warfarin therapy. Heparin is also started with it. WHY?
|
Warfarin initially inhibits C+s first. Thus you will form CLOTS! Thus heparin given until Warfarin can work fully
|
|
|
Name some thrombylytics
|
Alteplase (tPA)
reteplase (rPA) Tenecteplase (TNK-tPA) |
|
|
alteplase, reteplase, tenecteplase
MOA |
Aid in conversion of Plasminogen to plasmin (CLUT BUSTER!)
Both will Increase PTT and PT |
|
|
Clinical use of thrombolytics
|
Early MI, early stroke, early PE
TIME IS VERY IMPORTANT! |
|
|
What is the bad part about thrombolytics?
|
Time restraint (must use it intially in disease).
Else you risk the patients bleeding out. Risk outweigh the benefits a lot of the times |
|
|
What are the SE of Thrombolytics?
|
BLEEDING!
CI in active bleeding, or ppl with history of bleeding or recent surgeries or severe HTN |
|
|
Aminocaproic acid
|
Given to patients who you expect will bleed a lot in surgery
It can treat thrombolytics These STOP bleeding |
|
|
ADP recetor inhibitors
(Clopidogrel, ticlopidine, prasugrel, ticagrelor) MOA? |
Block ADP receptor thus prevent aggregation
|
|
|
Clinical use of clopidogrel, ticlopidine, prasugrel, ticagrelor
|
Used to prevent clots in patients who have had MI or stroke or any other vessel disorders in which you don't want clots
|
|
|
SE of Ticlopidine
|
Neutropenia
|
|
|
What kind of drugs are Cilostazol and dipyridamole
|
Phosphodiesterase III inhibitor
Will increase cAMP in platelets thus inhibiting platelet aggregation. Also a vasodilator |
|
|
Clinical use of Cilostazol and dipyridamole
|
Will open up vessels and prevent clotting. (thus has many uses)
Main uses involve: intermitten claudication |
|
|
SE of Cilostazol and dipyridamole
|
Nausea, HA, flushing, hypotension, abdominal pain
(mainly associated with the vasodilatoin) |
|
|
Abciximab, eptifibatide, tirofiban
MOA? |
GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors
Prevent aggregation |
|
|
Clinical use
|
Decrease clotting thus many uses (just like the other ones)
Main uses: percutaenous transluminal coronary angioplasty (eg. STENT) |
|
|
Toxicity of GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors
|
Bleeding and thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
ASPIRIN
|
STUDY THAT ON YOUR OWN.
|
|
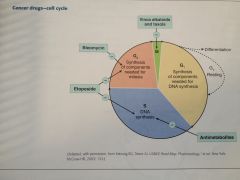
|
Overview
|
|
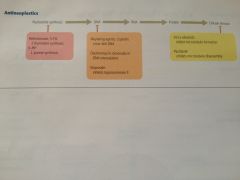
|
Overview
|
|
|
SE of Cancer drugs
|
GI, hair, blood cells most common toxicity issues.
Bone marrow suppression is key Toxicity with lots of these drugs (thus easier to remember which DON’T target BM) |
|
|
Methotrexate
MOA |
Folic acid analog
Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (converts inactive DHF to active THF which is needed in aiding Thymidylate synthase to convert dUMP to dTMP); thus decrease DNA synthesis |
|
|
Methotrexate
Clinical use |
Leukemias, lymphomas, choriocarcinoma, sarcomas (nothing specific)
ectopic pregnancy, RA, psoriasis |
|
|
methotrexate
SE |
BM toxicity (dose limiting)
GI ulcers, Teratogenic* Macrovesicular fatty change in liver |
|
|
What can you use to treat overdose of Methotrexate?
|
Leucovorin
|
|
|
5-flurouracil
MOA |
Pyrimidine analog
Inhibits Thymidylate synthase (dUMP --> dTMP) Thus decrease DNA synthesis |
|
|
5-fluorouracil (5-FU)
Clinical use |
Colon Ca
Basal cell carcinoma (topical) |
|
|
SE of 5-FU
|
BM suppression (dose limiting)
Photosensitivity |
|
|
What can you treat overdose of 5-FU with?
|
Thymidine
|
|
|
Cytarabine
MOA |
Pyrimidine analog
Inhibits DNA polymerase |
|
|
Cytarabine
Clinical use |
Leukemias and lymphomas
|
|
|
Cytarabine
SE |
BMD - dose limiting
Cerebellar toxicity (ATAXIA)* |
|
|
Azathioprine
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) 6-thioguanine (6-TG) MOA |
Purine analogs which decrease de novo purine synthesis
Activated by HGPRT |
|
|
What enzyme metabolizes Azathioprine, 6MP, 6TG?
|
Xanthine oxidase
Thus be careful when giving allopurinol! |
|
|
Clinical use of azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, 6-thioguanine
|
Leukemias
|
|
|
Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, 6-thioguanine
SE |
BM
Hepatotoxicty Increased toxicity with allopurinol |
|
|
Dactinomycin
MOA |
Binds and intercalates into DNA (stops replication and transcription)
|
|
|
Dactinomycin
Clinical use |
KIDS TUMORS!
(Wilm's tumor, Ewing's sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma) |
|
|
Dactinomyocin
SE |
BM
|
|
|
Doxorubicin and daunorubicin
MOA |
Intercalates into DNA
Generate free radicals Inhibits topoisomerase II (know 3 ways) |
|
|
Doxorubicin and daunorubicin
Clinical use |
SOlid tumors, leukemias, lymphomas
|
|
|
Doxarubicin, daunorubicin
SE |
CARDIOTOXICITY*
(dilated cardiomyopathy) due to free radicals BM |
|
|
What drug is given with Doxorubicin and daunorubicin to prevent the cardiotoxicty?
|
Dexrazoxane (iron chelating agent)
Used to prevent cardiotoxicity |
|
|
Bleomycin
MOA |
Binds to DNA
Forms radical causing DNA damage |
|
|
Clinical use of Bleomycin
|
Testicular cancer
Hodgkin's lymphoma |
|
|
Bleomycin
SE |
Pulmonary fibrosis*
Significant cutaneous toxicity* MINIMAL BM (one of the few to have such low effect thus used a lot) |
|
|
Cyclophosphamide,
ifosfamide MOA |
Crosslink DNA at guanine N-7
Require activation by LIVER* |
|
|
Cycophosphamide SE
|
BM
Hemorrhagic cystitis* |
|
|
How can you prevent the hemorrhagic cystitis?
|
Mesna and NAC
|
|
|
Nitrosoureas (carmustine, lomustine, semustine)
MOA |
Crosslink DNA
Can enter the BRAIN******* |
|
|
Clinical use of Nitrosoureas (eg. Carmustine, lomustine)
|
Brain tumors**
|
|
|
Nitrosureas
SE |
CNS toxicity (ataxia, dizziness)
BM Hits many many organs thus use limited |
|
|
Busulfan
MOA |
Alkylates DNA
|
|
|
Busulfan
Clinical use |
CML**
Used to ablate BM before transplantation |
|
|
Busulfan
SE |
Pulmonary fibrosis
hyperpigmentation BM |
|
|
Vincristine, Vinblastine
MOA |
Bind to tubulin in M phase. Block polymerization thus the miotic spindles can't form
|
|
|
Vincristine and vinblastine
Clinical use |
SOlid tumors, leukemias, and lymphomas
|
|
|
Vincristine and Vinblastine
SE |
Vincristin -- CNS (peripheral neuritis, autonomic, cranial nerves)
Vinblastin - BM |
|
|
Paclitaxel (+other taxols)
MOA |
Hyperstabalize the polymerized microtubules phase that the the spindle can't break down (can't move onto anaphase)
|
|
|
Paclitaxel
Clinical use |
Ovarian and breast carcinomas
|
|
|
Paclitaxel
SE |
BM
|
|
|
Cisplastin and carboplatin
MOA and clinical use |
Cross link DNA
Testicular, bladder, ovary carcinomas |
|
|
Cisplastin and carboplatin
SE* |
Nephrotoxicity and acoustic nerve damage*
|
|
|
How can you prevent the nephrotoxicity with Cisplatin and carboplatin?
|
Amifostine (free radical scavenger)
Drink plenty of water and stay hydrated |
|
|
Etoposide and teniposide
MOA and clinical use |
Inhibit topoisomerase II (increase DNA degradation)
Testicular and SCC of lungs |
|
|
Teoposide and teniposide
SE |
BM
|
|
|
Hydroxyurea
MOA |
Inhibits ribonucleatide reductase (enzyme which converts ribonucleotides to deoxynucleotides which are required for DNA synthesis)
|
|
|
Hydroxyurea
Clinical use and SE |
Melanoma, CML, sickle cell dz (increases HbF)
SE: BM |
|
|
Tamoxifene and Raloxifene
MOA |
Both work as AGONIST IN BONE and ANTAGONIST in BREAST
Tamoxifene: agonist in endometrium |
|
|
Tamoxifene and Raloxifene
Clinical use |
Breast cancer treatment and prevention
And osteoporosis |
|
|
Which increases the risk of endometrial cancer and has hot flashes as a SE?
|
Tamoxifene b/c it works on the endometrium
|
|
|
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
Moa + Clinical use |
AB against HER-2 (tyrosine kinase)
Helps treat HER-2 positive breast cancer |
|
|
Trastuzumab
SE |
Cardiotoxicity
|
|
|
Imatinib
MOA + Clinical use |
Philadelphia chromosome bcr-abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Tx: CML* |
|
|
Imatinib
SE |
Fluid retention
|
|
|
Rituximab
MOA and clinical use |
Monoclonal AB against CD20, which is found on most B-cell neoplasms
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, RA |
|
|
Vemurafenib
MOA + Clinical use |
Small molecular inhibitor of forms of the B-Raf kinase with the V600E mutation
Tx: Metatstatic melanoma |
|
|
Bevacizumab
Clinical use + MOA |
Monloclonal AB against VGEF. Inhibits angiogenesis
Tx: Any SOLID tumors |

