![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
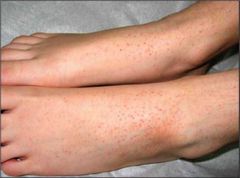
Pinpoint, non blanching hemorrhages as in the picture are called |
Petechiae |
|
|
Petechiae denotes what? |
Decreased platelet number |
|
|
Pseudothrombocytopenia |
Due to hypocalcemia because of ETDA in CBC tubes. Mechanism: Platelet agglutination via antibodies |
|
|
Most common cause of Thrombocytopenia |
Non prescription drugs and herbals. |
|
|
Most common non-iatrogenic causes of Thrombocytopenia |
Infections (bacterial and viral) - decreases production and survival. |
|
|
Examples of immuneediated thrombocytopenia |
Infectious mononucleosis. Early HIV (In Late HIV - decreased production). Infection associtaed ITP in children. |
|
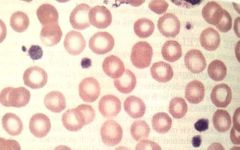
What is it? What are the DDs? |
Macro-thrombocytopenia DIfferentials : May hegglin anomaly Sebastian syndrome Epstein's syndrome Fechter syndrome |
|
|
Evan's syndrome |
AIHA + ITP |
|
|
Examples of X linked inherited thrombocytopenia syndromes X linked Thrombocytopenia |
Wiskott Aldrich syndrome Dyshematopoietic syndrome from GATA1 mutation WAS GATA |
|
|
A R thrombocytopenias |
CAT (congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenias) Thrombocytopenia with absent radii Bernard Soulier syndrome A B CAT |
|
|
Mortality rate in TTP without plasma exchange? |
85-100% without treatment to 10-30% with plasma exchange |
|
|
What is Upshaw Schulman syndrome? |
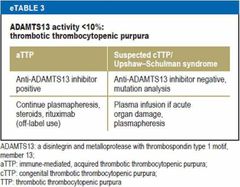
Inherited TTP |
|
|
Pathogenesis of idiopathic TTP |
Antibodies to ADAMTS13 (Enzyme level < 10% are clearly associated) |
|
|
People predisposed to TTP |
Pregnancy. HIV |
|
|
Drug induced TTP |
Antibody formation: Toclopidine, Clopidogrel. Endothelial injury: Cyclosporine Mitomycin C CNI Quinine (Decreasing doses in the second group decreases microangiopathy) |
|
|
True or False. Idiopathic TTP is more common in men. |
False. Idiopathic TTP is related to antibodies to ADAMTS13. It is more common with women. |
|
|
In a patient presenting with new thrombocytopenia (with or without other features of TTP), how will you evaluate? |
Lab data to ruleout DIC and evaluate for MAHA. Findings in favour of TTP diagnosis: Increased LDH Indirect bilirubin Low haptoglobulin High Retic count With Coombs negativity. Peripheral smear for schistiocytes. |
|
|
True or false. Immature RBCs in peripheral blood in TTP is due to hemolysis and infarction of small vasculature in marrow. |
True |
|
|
Duration of plasma exchange in TTP |
Until platelet count normalising or signs of hemolysis resolving for 2 days |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Gluco corticoids can be used in TTP. |
True. |
|
|
Other agents that can be used in TTP |
Rituximab Vincristine Cyclophosphamide Splenectomy |
|
|
Relapse rate in TTP |
25-50% early relapse in 30 days. Relapse correlates with severity of ADAMTS13. |
|
|
Need for dialysis in children with typical HUS |
40%, atleast for some period. |
|
|
Overall mortality in typical HUS |
< 5 % |
|
|
Overall mortality in patients with aHUS |
25% |
|
|
True or flase. aHUS is a diagnosis of exclusion. |
True |
|
|
Treatment for aHUS. |
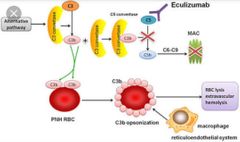
Eculizumab |
|
|
Reason behind HUS. |
Shiga like toxin form EHEC O157:H7. |
|
|
Reason behind aHUS. |
Chronic complement activation. |
|
|
Reason behind TTP. |
ADAMTS 13 deficiency |
|
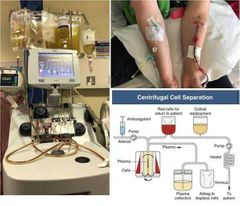
True or false.
Plasma exchange is useful in aHUS and so plasma exchange is done.
|
False. aHUS may be initially treated with plasma exchange until ADAMTS13 levels are obtained and the diagnosis more clear. (ie TTP rules out)
Plasma exchange has no benefit in clinical outcomes. |
|
|
DIfferentials for Thrombocytosis |
Iron deficiency. Reactive Thrombocytosis (inflammation, cancer or infection). MPNs. Rarely, 5q deletion MDS |
|
|
Enzymes inportant for metabolism and regeneration of vitamin K |
ɣ glutamyl carboxylase (GGCX) Epoxide reductase (VKORC1) |

