![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for in regards to the hair?
|
Quality, distribution, texture, and pattern of loss.
Examples: alopecia & pediculosis |
|
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for in regards to the scalp?
|
scaling, nevi, masses, or other lesions
Examples: psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, cysts |
|
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for in regards to the skull?
|
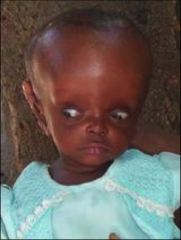
The size and contour including deformities, depressions, lumps, or tenderness.
Examples: hydrocephalus (picture) & plagocephaly |
|
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for in regards to the face?
|

Note symmetry, facial expression, and contour of face. Not involuntary movements, edema, and masses.
Examples: bells palsy, cushings disease, nephrotic syndrome, parkinsons (picture). |
|
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for in regards to the skin?
|
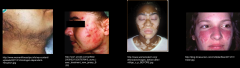
Color, pigmentation, texture, thickness, hair distribution and lesions.
Example: hirsutism, acne, vitaligo, lupus mallor butterfly rash |
|
|
What are you inspecting and palpating for at the tempomandibular joint?
|
Swelling and feeling for clicking, popping, or encumbrance to freedom of motion.
|
|
|
What are you feeling for during lymph node palpation?
|
Size, shape, delimitate, mobility, consistency, and tenderness.
|
|
|
What kind of abnormality is ptosis?
|
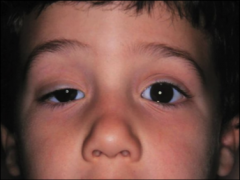
eyelid abnormality due to oculomotor nerve damage
|
|
|
What kind of abnormality is lid retraction & exophthalmos?
|
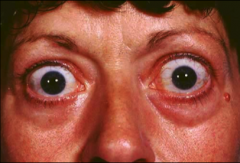
Eyelid abnormality due to hyperthyroidism.
|
|
|
What kind of abnormality is entropion?
|
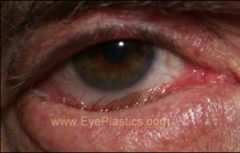
eyelid abnormality seen in geriatric patients where the lower or upper lid retracts and lashes rub up against sclera.
|
|
|
What kind of disorder is ectropion?
|
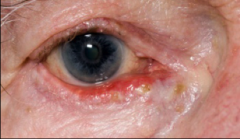
eyelid abnormality where eyelids fall outward. Very common to get dry eye.
|
|
|
What is the typical presentation of conjunctivitis?
|
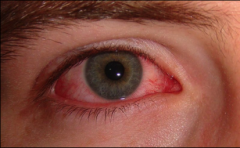
Pink or red eye that can be unilateral or bilateral.
|
|
|
What will a subconjunctival hemorrhage look like and when situations can cause it?
|
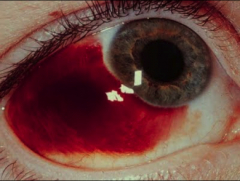
Looks like the picture. Blood in the conjunctiva. Caused by trauma, vomitting, forceful coughing especially if on blood thinners. Takes time to heal.
|
|
|
What is pinguecula and why do you get it?
|
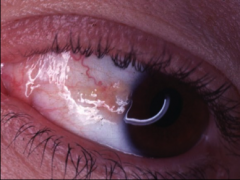
A triangular area of yellow tissue in the eye that is due to constant dry eyes.
|
|
|
What is episcleritis?
|
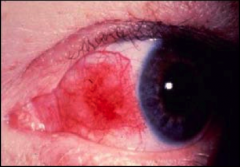
Redness or inflammation on medial cantus side of eye.
|
|
|
What is a hordeolum and what is it caused by?
|
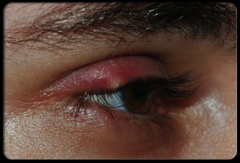
This is a sty (on lid margin) that can have warmth to it and is caused by a virus
|
|
|
What is a chalazion and what can it be caused by?
|
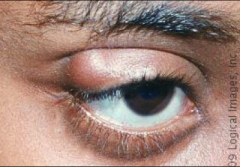
It is a lump or cyst under the eyelid (NOT on the margin) that can be caused by recurrent sty's.
|
|
|
What is xanthelasma and what causes it?
|
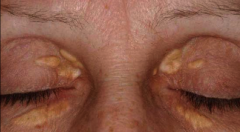
This is plaque like growth on the eyes caused by hyperlipideamia.
|
|
|
What is arcus senilis and what can cause it?
|
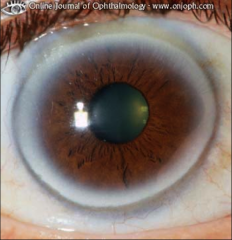
This is a light coloring (halo) around cornea. Can be caused by hyperlipidemia.
|
|
|
What is the test for visual acuity and what cranial nerve does it test?
|
The snellen eye chart, cranial nerve II
|
|
|
What cranial nerve do the extra ocular eye movements test for and what is the method of testing?
|
Tests cranial nerves III,IV,VI.
Method is testing the 6 cardinal directions of gaze. |
|
|
how far away do you hold the visual acuity chart? What about the handheld chart?
|
20ft, 14 in for handheld
|
|
|
What is a normal visual acuity?
What does the first number and second number indicate? |
20/20
1st number: indicates distance of patient from chart 2nd number: indicate distance at which a normal eye can read numbers |
|
|
What visual acuity is considered legally blind?
|
20/200
|
|
|
What problem does a central visual field defect indicate?
|
optic disc or nerve problem
|
|
|
What is a scotoma?
|
area of partial alteration in the field of vision
|
|
|
What are the causes of central visual field defects?
|

Optic neuropathy, macular degeneration, macular hole, cone dystrophies, Best’s disease, Stargardt’s disease, achromatopsia
|
|

What kind of visual field defect is this and what are its causes?
|
peripheral, have a defect in the visual pathways from the optic chiasm back.
Causes: Retinitis pigmentosa, chorioretinitis, glaucoma, retinal detachment, Leber’s optic atrophy |
|
|
What six muscles are you testing when doing the 6 cardinal directions of gaze test for EOM?
|
Superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique, superior oblique
|

