![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define thermometers |
measuretemperature. - do not measure heat. - contains a liquid of alcohol or mercury within a narrow glass tube. - the liquid expands when heated and contracts when cooled. |
|
|
Define heat |
-form of energy - total energy of all particles within an object. |
|
|
Define temperature |
indicates how hot or cold something is. - a measure of kinetic energy/how quickly the particles inside the object are moving. - hotter substances have particles that move faster than those in cooler substances. - read from a scale equivalent to the expansion and contraction of the liquid in the thermometer. |
|
|
What is temperature measured in? |
Degrees Celsius(°C) Degrees Fahrenheit (°F) Kelvin (K) |
|
|
Conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit |
9/5 x °C + 32 |
|
|
Conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius |
5/9 (°F - 32) |
|
|
How can temperature be measured? |
Receptors in yourskin can tell you how hot or cold something is, but they aren't always correct. A thermometer gives an accurate reading of temperature. |
|
|
Water freezing point in Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin |
- 32 °F - 0 °C - 273 K |
|
|
Water boiling point in Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin |
- 212 °F - 100 °C - 373 K |
|
|
Define heat transfer |
-heat flowing fromareas of higher temperature to those of lower temperature. - the greater the temperature difference, the faster the heat flows from oneobject into another. |
|
|
Ways of heat transfer happening |
-conduction - convection - radiation |
|
|
Define conduction |
- occurs whenmolecules increase in temperature in solids. - therefore, molecules start to vibrate. - this vibration causes the adjacent molecules to vibrate and bump into eachother progressively and, therefore, conduct heat energy. |
|
|
Examples of conduction |
heat flows from thewarmer hands into the ice. heat flows from the hotter cup into the hands. |
|
|
Define conductors |
- substances thattransfer heat easily. - have charges that can flow through easily. - solids are better conductors than liquids. - liquids are better conductors than gases. - gases are poor heat conductors. |
|
|
Examples of conductors |
- metals such asgold and copper (frying pans, pots) - steel - water |
|
|
Define insulators |
- materials thatare poor heat conductors. - some can block heat transfer completely. - charges cannot flow through easily. |
|
|
Why are most insulators light weight? |
- the material is expanded, so large amounts of air particles get trapped. - air is a bad conductor ( a good insulator). |
|
|
Examples of insulators |
- wool (jumpers,sleeping bags, carpet) - plastic - air - cloth - wood (floor) - rubber - handles of saucepans are usually made from insulating materials so we do notget burnt. |
|
|
Define convection |
- the transfer of heat through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by molecular motion. - as air is heated, its particles gain energy and move further apart. - this hot air is less dense than cool air and rises. - the cool air descends. - the air flow causes a convection current. |
|
|
Define convection current |
- the air flow through convection - the hot air rises, the cold air descends. |
|
|
Define fluid |
- liquid or gas - a substance that continuously flows under an applied shear stress. |
|
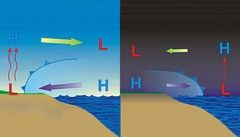
What diagram is this? |
Sea breeze (Ocean Currents) |
|
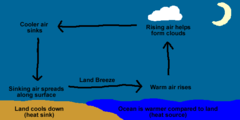
What diagram is this |
Diagram of land breeze (wind currents) |
|
|
Define radiation |
-the movement ofheat waves between the Sun and Earth. - doesn't need particles to transfer heat. - transfers heat as invisible waves (travel at 300,000km per sec). - the hotter something is, the more heat it radiates. |
|
|
Define radiant energy |
- the energy that travels in waves through space and air. - mainly travels by electromagnetic radiation. |
|
|
How do objects respond to radiant heat? |
- the objectsabsorb the heat. |
|
|
What happens when radiated energy hits a surface? |
- the heat can beabsorbed into the surface, reflected from the surface or transmitted throughthe surface. - this accords to the material and its colour. |
|
|
Define transmit |
- to pass somethingfrom one thing/place to another. |
|
|
Define reflect |
- coming out fromthe surface (rebounding). - occurs on shiny surfaces. |
|
|
Define absorb |
- to take in andkeep the part that isn't transmitted or reflected. |
|
|
Why do dark coloured objects heat up more quickly than light-coloured objects? |
- dark-colouredobjects are good radiation absorbers (absorption). - light-coloured objects reflect too much of the radiation. |
|
|
Examples of dark-coloured objects that heat up quickly |
- cars - solar hot water systems use black collection panels. - clothes |
|
|
What is the speed of light |
300,000km |

