![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In terms of Wigger's Diagram, S1 occurs during:
|
isovolumic contraction
|
|
|
In terms of Wigger's Diagram, S2 occurs during:
|
isovolumic relaxation
|
|
|
S1 is produced by the closing of which two valves?
|
Mitral & Tricuspid
|
|
|
S2 is produced by the closing of which two valves?
|
Aortic & Pulmonic
|
|
|
Which heart sounds occur during ventricular systole?
|
S1
|
|
|
Which heart sounds occur during ventricular diastole?
|
S2, S3, S4
|
|
|
Which heart sounds occur during atrial systole?
|
S4
|
|
|
Which heart sounds occur during rapid ventricular filling?
|
S3
|
|
|
Which heart murmurs are diastolic murmurs?
|
AR
PR MS TS PDA Austin-Flint |
|
|
Which heart murmurs are systolic murmurs?
|
AS
PS ASD HOCM MR TR VSD MVP |
|
|
Name the four mid-systolic murmurs.
|
AS
PS ASD HOCM |
|
|
Name the three Holosystolic murmurs.
|
MR
TR VSD |
|
|
Name the late systolic murmur.
|
MVP
|
|
|
Name the early diastolic murmurs.
|
AR
PR Austin-Flint |
|
|
Name the mid-late diastolic murmurs.
|
MS
TS |
|
|
The mnemonic for sites of auscultation APTM:
|
All Physicians Take Money
|
|
|
Location of the Aortic Area for auscultation.
|
2nd RICS
|
|
|
Location of the Pulmonic Area for auscultation.
|
2nd LICS
|
|
|
Location for the Tricuspid Area for auscultation.
|
Lower Left Sternal Border
|
|
|
Location for the Mitral Area for auscultation.
|
Cardiac apex
|
|
|
Which part of the stethescope is used to detect high-pitched sounds such as S1 & S2?
|
diaphragm
|
|
|
Which part of the stethoscope is used to detect low-pitched sounds?
|
bell
|
|
|
What is the best position for the patient for auscultation of the heart sounds?
|
Supine 45 degrees
|
|
|
What is the best position for the patient for auscultation of the mitral area?
|
left lateral position
|
|
|
Which grades of heart murmur is a loud murmur associated with a thrill?
|
IV, V, VI
|
|
|
A dilated ventricle is associated with which heart sound?
|
S3
|
|
|
A stiff ventricle is associated with which heart sound?
|
S4
|
|
|
What two sounds is S1 composed of?
|
M1 & T1
|
|
|
M1 is best heard at the:
|
apex (may be heard at all sites)
|
|
|
T1 is best heard at the:
|
LLSB
|
|
|
A split S1 occurs when the MV closes significantly before/after the TCV.
|
before
|
|
|
Inspiration delays the closing of which valve in a normal person?
|
TV due to increased venous return.
|
|
|
Which type of bundle branch block is often associated with a split in S1?
|
Right BBB
|
|
|
What two sounds is S2 composed of?
|
A2 & P2
|
|
|
A2 & M1 are normally louder than P2 & T2 because:
|
Left sided pressures are higher.
|
|
|
A2 is loudest at which auscultation site?
|
RUSB
|
|
|
P2 is only heard at which auscultation site?
|
LUSB
|
|
|
A normal physiologic split of S2 occurs during:
|
inhalation
|
|
|
The physiologic split of S2 during inhalation is due to increased:
|
venous return
|
|
|
Increased venous return keeps which valve open longer thus increasing the split of S2.
|
Pulmonic
|
|
|
A paradoxical split of S2 occurs when splitting is heard during:
|
exhalation
|
|
|
A paradoxical split of S2 occurs when the aortic valve closure is delayed as during which cardiac defects?
|
Severe AS
HOCM LBBB |
|
|
A widened S2 split occurs when both A2 & P2 are heard during the entire respiratory cycle although the splitting is greater during:
|
inhalation
|
|
|
A fixed S2 split occurs when there is always a delay in closure of which valve and there is no change with inhalation or exhalation.
|
Pulmonic valve
|
|
|
S3 should disappear when which part of the stethescope is used for auscultation?
|
diaphragm
|
|
|
A split S2 is best heard at which auscultation site?
|
LUSB
|
|
|
What is the best position for the patient to be in for auscultation of S3?
|
left lateral decubitus position
|
|
|
S3 can be an important sign of:
|
systolic heart failure
|
|
|
S3 is called which type of gallop?
|
ventricular
|
|
|
S3 occurs during which phase of the cardiac cycle?
|
early diastole
|
|
|
S3 occurs during which type of ventricular filling?
|
passive
|
|
|
True/False: S3 can be present in athletes, pregnant females and other young healthy individuals.
|
True
|
|
|
S3 requires a very compliant/non-compliant left ventricle.
|
compliant
|
|
|
Regarding pitch, S3 is low/high while S2 is low/high.
|
low
high |
|
|
S4 is best heard at the:
|
cardiac apex
|
|
|
S4 is best heard with the patient in which position?
|
left lateral decubitus position
|
|
|
S4 requires a very compliant/non-compliant left ventricle.
|
non-compliant
|
|
|
S4 is known as which type of gallop?
|
atrial
|
|
|
S4 occurs during which phase of the cardiac cycle?
|
late diastole
|
|
|
S4 occurs during active/passive ventricular filling.
|
active
|
|
|
S4 can be a sign of diastolic/systolic CHF.
|
diastolic
|
|
|
S3 can be a sign of diastolic/systolic heart failure.
|
systolic
|
|
|
This sound frequently indicates a bicuspid aortic valve.
|
systolic ejection click
|
|
|
This sound is mid-systolic and is usually followed by a uniform, high-pitched murmur.
|
MV Prolapse click
|
|
|
This sound caused by increased left atrial opening pressure is present in mitral stenosis.
|
Opening snap
|
|
|
This sound is an early diastolic low-pitched sound just after the S2 and may be followed by a low-pitched diastolic murmur.
|
Tumor Plop
|
|
|
This sound can be present with constrictive pericarditis because early filling of the LV is limited. This sound occurs earlier than the S3 which distinguishes it.
|
Pericardial knock
|
|
|
What are the six distinguishing characteristics of murmur? SCRIPT
|
Site (location)
Configuration (shape) Radiation Intensity Pitch Timing (systolic or diastolic) |
|
|
Draw an Aortic Stenosis murmur.
-systolic -crescendo/decrescendo -ejection click after S1 if calcified bicuspid aortic valve. -best heard RUSB |

|
|
|
Draw an Aortic Insufficiency (regurgitation) murmur.
-diastolic -decrescendo -best heard LLSB |

|
|
|
Draw a Pulmonic Stenosis murmur.
-systolic -crescendo-decrescendo -ejection click -best heard LUSB |

|
|
|
Draw Pulmonic Insufficiency (regurgitation) murmur.
-diastolic -decrescendo -best heard LLSB |

|
|
|
Draw a Mitral Stenosis murmur.
-diastolic -decrescendo -best heard cardiac apex in left lateral decubitus -opening snap |

|
|
|
Draw a Mitral Insufficiency (regurgitation) murmur.
-holosystolic -best heard cardiac apex -systolic click if MVP |

|
|
|
Draw a Tricuspid Insufficiency (regurgitation) murmur.
-holosystolic -best heard LLSB -increase with inspiration |

|
|
|
Draw an ASD (atrial septal defect) murmur.
-systolic -crescendo-decrescendo -best heard RUSB -fixed split S2 |

|
|
|
Draw a VSD (ventricular spetal defect) murmur.
-holosystolic -best heard LLSB -palpable thrill |

|
|
|
Draw a PDA (patent ductus arteriosus) murmur.
-continuous |

|
|
|
Draw an S3 heart sound.
|

|
|
|
Draw an S4 heart sound.
|

|
|
|
Draw a HOCM (hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy) murmur.
-systolic -crescendo/decrescendo -best heard LLSB -Valsalva and squat/stand to increase intensity |
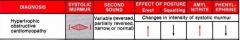
|
|
|
True/False: An S4 can be present during atrial fibrillation.
|
False
Atrial kick is required for S4 to occur. |
|
|
True/False: An S4 is always pathologic and indicates diastolic heart failure.
|
True
|
|
|
True/False: S3 can indicate severe diastolic heart failure.
|
False
S3 can be normal or indicate systolic heart failure. |
|
|
True/False: A wide split S2 can be from an ASD.
|
False
A fixed split S2 can be from an ASD. |
|
|
True/False: A paradoxical S2 split can be caused by AS, HOCM or RBBB.
|
False
A paradoxical S2 split can be caused by AS, HOCM, or LBBB |
|
|
True/False: A wide S2 split can be caused by severe MR, PS, or RBBB.
|
True
|
|
|
True/False: A holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border louder with inspiration is due to tricuspid regurgitation
|
True
|
|
|
True/False: The best position to hear the murmur of aortic regurgitation is to have the patient lean forward and listen after a forced, held expiration.
|
True
|
|
|
True/False: The Austin-Flint murmur is a systolic rumble at the cardiac apex in a patient with aortic regurgitation
|
False
The Austin-Flint murmur is a diastolic rumble at the cardiac apex in a patient with aortic regurgitation |
|
|
True/False: The murmur of mitral regurgitation decreases with handgrip and transient arterial occlusion since these maneuvers increase afterload.
|
False
The murmur of mitral regurgitation increases with handgrip and transient arterial occlusion since these maneuvers increase afterload. |

