![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Cardiac Cycle
|
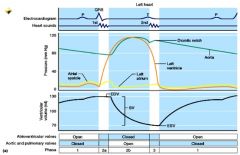
What is this Picture
|
|
|
When does the first heart sound occur?
|
Occurs in early Systole
|
|
|
Which pressure exceeds the other during the first heart sound?
|
Ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure
|
|
|
Which valves close during the first heart sound?
|
Mitral & Tricuspid Valves close during S1.
|
|
|
What causes the first heart sound (S1)?
|
The rapid bulging of the valve leaflets after they close produces the noise.
|
|
|
Where is the first heart sound loudest?
|
It is loudest at the apex.
|
|
|
Where is the first heart sound diminished?
|
It is diminished at the base
|
|
|
Describe the normal first heart sound?
|
"LUB"
|
|
|
When does the second heart occur?
|
Early in Diastole
|
|
|
What happens to ventricular pressure during the second heart sound (S2)?
|
Ventricular Pressure falls below Aortic & Pulmonary Artery Pressures.
|
|
|
What causes the second heart sound (S2)?
|
Aortic & Pulmonic Valves Shut, & Rapidly bulge, producing the S2.
|
|
|
Where is the Second Heart Sound Loudest?
|
It is Loudest at the base.
|
|
|
Where is the second heart sound diminished?
|
It is diminished at the Apex.
|
|
|
Describe the sound of the Second Heart Sound (S2)?
|
It's the "DUB"
|
|
|
What happens to pulmonary pressures during inspiration?
|
Pulmonary Pressures drop.
|
|
|
What causes the Pulmonic Valve to stay open longer?
|
The pressure dropping in the lungs.
|
|
|
What does splitting that goes away with expiration indicate?
|
A normal condition.
|
|
|
What does fixed splitting indicate?
|
Fixed splitting indicates disease
|
|
|
Why does splitting of S2 occur?
|
The second heart sound is really two valve sounds together A2 + P2.
|
|
|
What age group can the third heart sound be normal?
|
people < 30 yrs & (athletes?)
|
|
|
What produces the third heart sound?
|
Chordae Tendineae during rapid filling
|
|
|
What is the third heart sound described as?
|
Ventricular Gallop
|
|
|
When does the Third Heart Sound occur?
|
immediately after S2.
|
|
|
Where & what position is the third heart sound heard best(S3)?
|
Best heard at apex, with patient on their left side.
|
|
|
Which part of of the stethoscope should be used to ausculate the third heart sound?
|
Bell of Stethoscope with light pressure (low pitch)
|
|
|
What part of Ken-tuck-EE is the third heart sound?
|
EE.
|
|
|
This heart sound is rarely normal except in highly conditioned athletes.
|
The fourth heart sound (S4)
|
|
|
The contact of the atria against a stiff ventricle is called?
|
Atrial Gallop (S4)
|
|
|
When does the fourth heart sound occur?
|
Immediately before S1.
|
|
|
Where & in which position is the fourth heart sound best heard?
|
It is best heard at the apex, with the patient on their left side.
|
|
|
Which part of the stethoscope should be used to auscultate the fourth heart sound?
|
Bell with light pressure.
|
|
|
What part of TENN-e-ssee is the fourth heart sound?
|
TENN
|
|
|
What causes the sound of Heart Murmers?
|
Turbulent blood flow through a vascular structure.
|
|
|
How long can murmurs last?
|
longer than the four heart sounds.
|
|
|
When can murmurs occur?
|
During systole or diastole.
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of patients with innocent heart murmers
|
Young and/or
Pregnant |
|
|
What are the characteristics of innocent heart murmurs?
|
Tends to be early systolic
Rarely Holosystolic. |
|
|
When does a systolic murmur occur?
|
Between S1 & S2
|
|
|
When does a diastolic murmur occur?
|
between S2 & S1
|
|
|
What "shapes" are used to describe heart murmurs?
|
-crescendo
-decrescendo -crescendo-decrescendo -plateau |
|
|
Grade 1 murmur
|
Barely Audible
|
|
|
Grade 2 murmur
|
Little Louder
|
|
|
Grade 3 murmur
|
Clear audible - No Thrill
|
|
|
Grade 4 Murmur
|
Thrill Palpable
|
|
|
Grade 5 Murmur
|
Audible with Stethoscope partly off the Chest & Thrill
|
|
|
Grade 6 Murmur
|
Audible without Stethoscope
|
|
|
What are the pitches of heart murmurs?
|
-High
-Medium -Low |
|
|
Heart Murmur Qualities?
|
-Blowing
-Harsh -Musical -Rumble |
|
|
What are the systolic murmurs?
|
-Aortic & Pulmonic Stenosis
-Mitral & Tricuspid Regurgitation |
|
|
What are the Diastolic Murmurs?
|
-Mitral & Tricuspid Stenosis
-Aortic & Pulmonic Regurgitation |

