![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell Membrane
(plasma membrane) |
★ encases the cell
★ separates intracellular from extracellular ★ has different stages of permeability |
|
|
|
cell membrane made of?
|
★ phospholipids and protein
|
|
|
|
if a membrane is selectively permeable about the substances that cross it?
|
★ Semipermeable
|
|
|
|
function of:
cell membrane |
★ contains cellular contents: regulates what enters and leaves the cell
|
|
|
|
function of:
cytoplasm |
★ surrounds and supports organelles: medium through which nutrients and waste moves
|
|
|
|
function of:
nucleus |
★ contains genetic information; control center of the cell
|
|
|
|
function of:
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
★ contains the ribosomes where protein is synthesized
|
|
|
|
function of:
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
★ Transports material through the cytoplasm
|
|
|
|
function of:
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
★ Site of steroid synthesis
|
|
|
|
function of:
Mitochondria |
★ convert energy in nutrients to ATP (power plants of cell)
|
|
|
|
function of:
Golgi apparatus |
★ packages protein in membrane; puts the finishing touches on protein
|
|
|
|
function of:
Ribosomes |
★ sites of protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
function of:
Lysosomes |
★ “housekeeping” within the cell; phagocytoses through powerful enzymes
|
|
|
|
function of:
Cytoskeleton |
★ provides for intracellular shape and support
|
|
|
|
function of:
centrioles |
★ help separate the chromosomes during mitosis
|
|
|
|
function of:
cilia |
★ create movement over the cell surface
|
|
|
|
function of:
flagella |
★ create movement of cell (e.g. allow the sperm to swim)
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Diffusion |
★ Movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Facilitated diffusion |
★ a helper molecule within the membrane assists the movement of substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Osmosis |
★ movement of water (solvent) from an area with more water to an area with less
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Filtration |
★ movement of water and dissolved substance from and area of high pressure to an area of low pressure; the water and dissolved substances are pushed
|
|
|
|
Describe:
active transport pumps |
★ movement of a substance uphill (from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration). Requires an input of energy (ATP)
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Endocytosis |
★ taking in or ingestion of substances by the cell membrane
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Phagocytosis |
★ engulfing of solid particles by the cell membrane (cellular eating)
★ a form of endocytosis |
|
|
|
Describe:
Pinocytosis |
★ engulfing of liquid droplets (cellular drinking)
a form of endocytosis |
|
|
|
Describe:
Exocytosis |
★ secretion of cellular products (e.g., protein, debris) out of the cell
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Filtration |
★ movement of water and dissolved substance from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure; the water and dissolved substances are pushed
|
|
|
|
Describe:
active transport pumps |
★ movement of a substance uphill (from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration). Requires an input of energy (ATP)
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Endocytosis |
★ taking in or ingestion of substances by the cell membrane
|
|
|
|
Describe:
Phagocytosis |
★ engulfing of solid particles by the cell membrane (cellular eating)
★ a form of endocytosis |
|
|
|
Describe:
Pinocytosis |
★ engulfing of liquid droplets (cellular drinking)
a form of endocytosis |
|
|
|
Describe:
Exocytosis |
★ secretion of cellular products (e.g., protein, debris) out of the cell
|
|
|
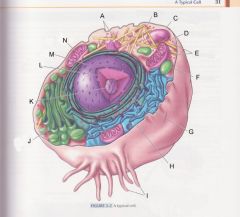
What is A?
|
Centrioles
|
pg 31
|
|
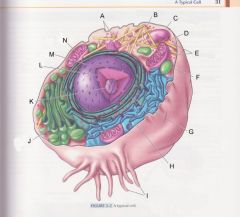
What is C?
|
cell membrane
(plasma membrane) |
pg 31
|
|
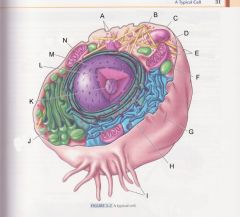
What is E?
|
cytoplasm
|
pg 31
|
|
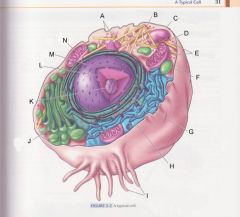
What is F?
|
Lysosome
|
pg 31
|
|
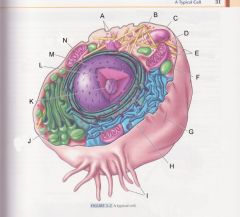
What is G?
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
pg 31
|
|
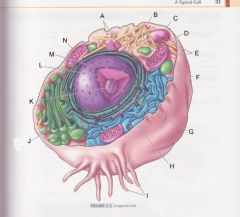
What is H?
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
pg 31
|
|
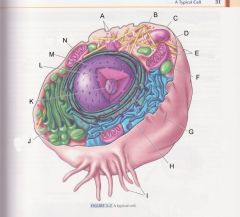
What is I?
|
cilia
|
pg 31
|
|
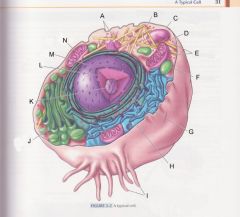
What is J?
|
Golgi apparatus
|
pg 31
|
|
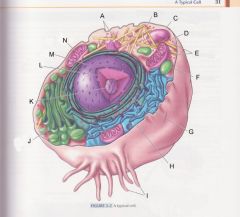
What is K?
|
Nucleolus
|
pg 31
|
|
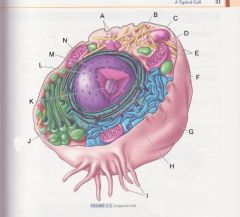
What is L?
|
Nuclear membrane
|
pg 31
|
|
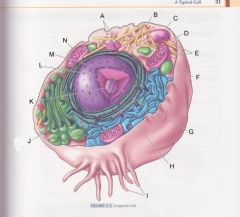
What is M?
|
Nucleus
|
pg 31
|
|
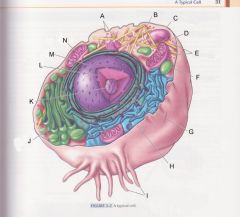
What is N?
|
Mitochondrion
|
pg 31
|
|
|
What is an istonic solution?
|
has the same concentration as intracellular fluid. Consider a red blood cell (RBC) placed in an isotnic solution. Because the solution is isotonic, no net movement of water occurs; the cell neither gains nor loses water.
|
|
|
|
What is tonicity?
|
the ability of a solution to affect the volume and pressure within a cell
|
|
|
|
Hypotonic solution?
|
If an red blood cell (RBC) is placed in pure water (a solution containing no solute), water moves into the cell by osmosis (from where there is more water to where there is less)
|
|
|
|
What is a possible complication of a hypotonic solution?
|
can cause red blood cells (RBC) to burst
|
|
|
|
Hypertonic solution?
|
If a red blood cell (RBC) is placed within a very concentrated salt solution, water diffuses out of the red blood cell (RBC) into the bathing solution, causing the RBC to shrink, or crenate. The salt solution is referred to as a hypertonic solution.
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
O |
Oxygen
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
C |
Carbon
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
H |
Hydrogen
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
N |
Nitrogen
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
K |
Potassium
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
Na |
Sodium
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
Cl |
Chlorine
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
Fe |
Iron
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
Ca |
Calcium
|
|
|
|
Symbol:
S |
Sulfur
|
|
|
|
What does Superior mean?
|
a part is above another part or is closer to the head
ex. the nose is superior to the mouth |
opposite of Inferior
|
|
|
What does Inferior mean?
|
a part is located below another part or is closer to the feet.
ex. the nose is inferior to the eyes |
opposite of Superior
|
|
|
What does Anterior mean?
|
toward the front surface (the belly surface)
ex. the heart is anterior to the spinal cord |
opposite of Posterior or dorsal
another word for anterior is ventral |
|
|
What does Posterior mean?
|
toward the back surface
ex. the heart is posterior to the breast bone |
opposite of Anterior or ventral
another word for dorsal |
|
|
What does ventral mean
|
toward the front surface (the belly surface)
ex. the heart is anterior to the spinal cord |
opposite of dorsal or posterior
another word for ventral is anterior |
|
|
What does dorsal mean?
|
toward the back surface
ex. the heart is posterior to the breast bone |
opposite of ventral or anterior
another word for dorsal is posterior |
|
|
What does Medial mean?
|
toward the midline of the body
ex. the nose is medial to the ears (because it is closer to the middle of the body. |
opposite of lateral
|
|
|
What does Lateral mean?
|
away from the midline of the body
ex. ears are lateral to the nose (because the nose is closer to the midline than the ears are |
opposite of medial
|
|
|
What does Proximal mean?
|
the structure is nearer the point of attachment
ex. elbow is proximal to the wrist , the wrist is proximal to the fingers |
opposite of distal
|
|
|
What does Distal mean?
|
a part is farther away from the point of attachment than is another part.
ex: wrist is distal to the elbow, fingers are distal to the wrist |
|
|
|
What is anatomical position?
|
the body is standing erect, with the face forward, the arms at the sides, and the toes and palms of the hands directed forward
|
pg 7
|
|
|
What does Superficial mean?
|
a part is located on or nearer the surface of the body
ex: the skin is superficial to the muscles |
opposite of deep
|
|
|
What does Deep mean?
|
part is farther away from the point of attachment than is another part.
ex: the bones are deep to the skin |
opposite of superficial
|
|
|
What does Central mean?
|
part is located in the center
ex: the heart is located centrally |
opposite of peripheral
|
|
|
What does Peripheral mean?
|
located away from the center
ex: the blood vessels are located peripherally (away from the center and extending toward the limbs |
opposite of central
|
|
|
What is homeostasis?
|
staying the same
refers to the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment in response to a changing external environment. |
pg 4
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body lengthwise into right and left portions?
|
Sagittal plane
|
pg 8
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions?
|
Frontal plane
|
pg 8
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body horizontally, creating an upper (superior) and a lower (inferior) body?
|
Transverse plane
|
pg 8
|
|
|
What is considered to be a universal solvent?
|
water
|
|
|
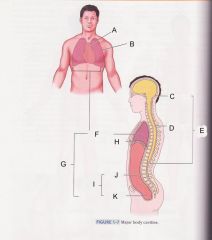
What is cavity B?
|
pleural cavity
|
|
|
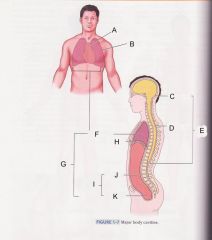
Which is cavity A?
|
Mediastinum
|
|
|
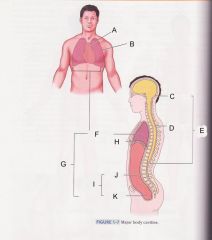
Which cavity is C?
|
cranial cavity
|
|
|
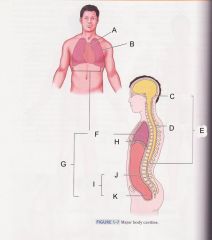
Which cavity is D?
|
spinal cavity
|
|
|
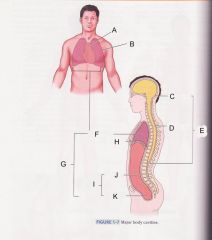
Which cavity is E?
|
Dorsal cavity
|
|
|
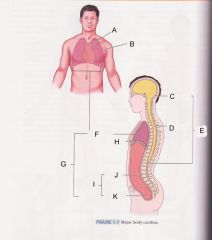
Which cavity is F?
|
Thoracic cavity
|
|
|
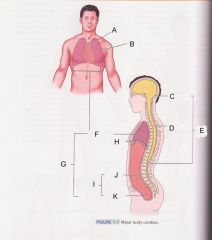
Which cavity is G?
|
ventral cavity
|
|
|
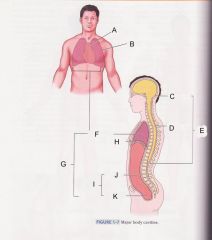
Which cavity is J?
|
abdominal cavity
|
|
|
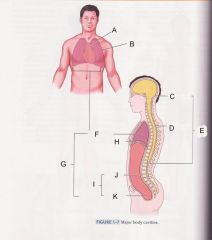
Which cavity is K?
|
pelvic cavity
|
|
|
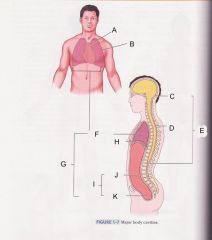
Which cavity is I?
|
Abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
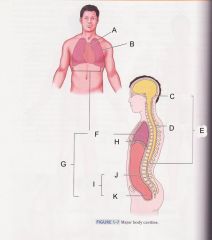
What muscle that separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity is H pointing at?
|
diaphram
|
|
|
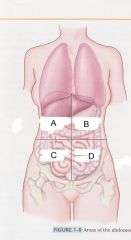
Which quadrant is A?
|
right upper quadrant
ruq |
|
|
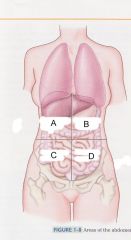
Which quadrant is B?
|
left upper quadrant
luq |
|
|
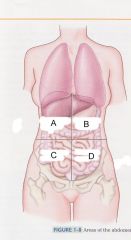
Which quadrant is C?
|
right lower quadrant
rlq |
|
|
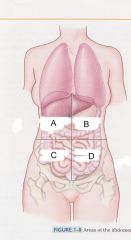
which quadrant is D?
|
left lower quadrant
llq |
|
|
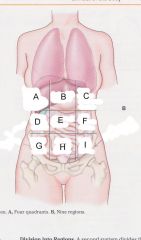
Which region is A?
|
Right hypochondriac region
|
|
|
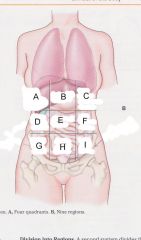
Which region is B?
|
epigastric region
|
|
|
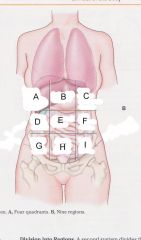
Which region is C?
|
Left hypochondriac region
|
|
|
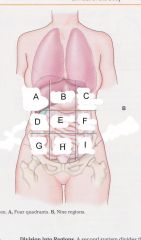
Which region is D?
|
Right lumbar region
|
|
|
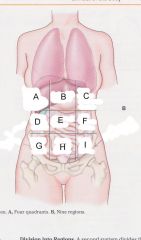
Which region is E?
|
umbilical region
|
|
|
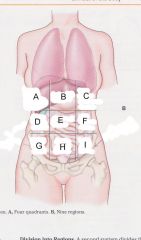
Which region is F?
|
left lumbar region
|
|
|
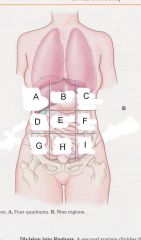
which region is G?
|
right iliac (unguinal) region
|
|
|
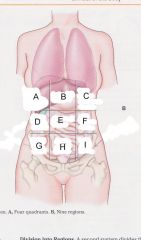
Which region is H?
|
hypogastric region
|
|
|
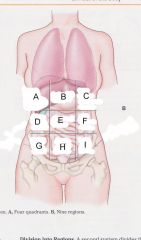
Which region is I?
|
left iliac (inguinal) region
|
|
|
|
Which cavity can be divided into four quadrants?
|
the abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
|
In which quadrant would pain for appendicitis be?
|
RLQ
or Right Lower Quadrant |
|
|
|
What is the first phast of mitosis?
|
Prophase
|
|
|
|
Whast is the second phase of mitosis?
|
Metaphase
|
|
|
|
What is the third phase of mitosis?
|
Anaphase
|
|
|
|
What is the fourth phase of mitosis?
|
Telophase
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 stages of mitoses?
|
Prophase
metaphase anaphase and telophase |
|

