![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
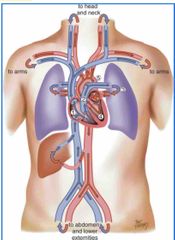
Blood flow of heart |
Liver — RA — inferior vena cava — superior vena cava — RA — Tricuspid — RV — Pulmonic valve — pulmonary artery — lungs — pulmonary veins — LA — mitral valve — LV — aortic valve — Aorta From liver to RA through inferior vena cava to Superior vena cava drains blood from the head and upper extremities to RA where venous blood then travels through the tricuspid valve to RV From RV venous blood flows through pulmonic valve to pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery delivers unoxygenated blood to the lungs Lungs oxygenate blood Pulmonary veins return fresh blood to LA From LA arterial blood travels through mitral valve to LV LV ejects blood through aortic valve into aorta. Aorta delivers oxygenated blood to body.
|
|
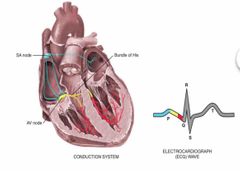
PQRST waves |
P wave - Depolarization of the atria PR interval (beginning of P to the beginning of QRS complex) - the time necessary for atrial depolarization plus time for the impulse to travel through the AV nose to the ventricles) QRS complex - depolarization of the ventricles T wave - repolarization for the ventricles |
|
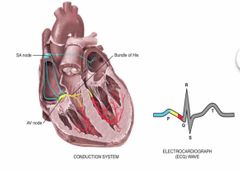
Electric flow of the heart |
SA node — Atria —AV node — Atria — Ventricle — Brindle of His — right and left bundle branches — ventricles SA node near superior vena cava initiate electrical impulse Across atria to AV node (low in the atrial septum) Atria to ventricle Brindle of His Right and left bundle branches And then through the ventricles |
|
|
Right sided heart failure (HEPA) |
Hepatomegaly Edema Ascites (swelling of abdomen) Distended neck vein |
|
|
Left sided heart failure (CHOP) |
Cough Hemoptysis Orthonpnea Pulmonary congestion |
|
|
Right heart failure |
My shoes are tight , I pee at night Edema in legs, nocturnal dyspnea |
|
|
Left heart failure auscultation |
Crackles Rails |
|
|
What is pericarditis |
Inflammation of the pericardium, can result in friction rub. |
|
|
When is friction of pericarditis common |
During the first week after a myocardial infarction and may last only a few hours |
|
|
Ribs |
2-5; heart, ribs 5-10, liver |
|
|
Pleural space namings |
Pericardium- is the whole anterior chest above the lungs; tough, fibrous, double walled sac that surrounds and protects the heart and is anchored to diaphragm. Myocardium - muscular wall of the heart Endocardium - thin layer of endothelial tissue that lines inner surface of the heart chambers and valves
|
|
|
What is a significant sign of right side heart failure |
Jugular vein distention |
|
|
Where is S1 loudest? |
At the apex which is in the left 5th intercostal space mid clavicle |
|
|
Where is the S2 loudest? |
At left 2nd intercostal space |
|
|
What is S3 indicative of? |
Murmur which indicates heart failure |
|
|
What is S4 indicative of? |
Murmur resulting in hypertrophy |
|
|
What are the nicknames for atrial kick? |
Pre systole or atrial systole, |
|
|
Function of atrial kick |
It works towards the end of diastole where the atria would contract and push the last amount of blood (about 25% stroke volume) into the ventricles. |
|
|
What does the atrial kick cause? |
A small rise in left ventricular pressure |
|
|
During systole, what contributes to the first heart sound S1? |
The closure of the AV valves which signal the beginning of systole |
|
|
What happens to the blood during systole |
The blood of pumped from the ventricles and fills the pulmonary and systemic arteries. |
|
|
When are the AV valves open? |
During diastole where the ventricles are relaxed |
|
|
Location of All-people- eat - taco - meat |
Aortic - right second intercostal space Pulmonic - left 2nd intercostal space is, S2 is heard louder at the base Reba - left 3rd intercostal space S1 and S2 are heard the same Tricuspid left 4th intercostal space Mitral(apical impulse) - left 4th or 5th intercostal space S1 is heard louder at the apex |
|
|
When do fetal heart functions begin? |
At week 3 |
|
|
What is the Foramen ovale? |
An opening in the atrial septum where 2/3 of the oxygenated blood from the placenta is placed into the left side of the heart where it is pumped to the aorta. |
|
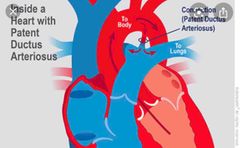
Ductus Arteriosus |
This is where the rest of the oxygenated blood gets pumped through the pulmonary artery by the right side of the heart after being detoured. |
|
|
What does inflation and aeration of the lungs at birth produce |
Circulatory changes |
|
|
High pressure in the right gives sign of |
jugular vein distention, edema, and abdomen abnormalities |
|
|
How do we assess heart sounds and valves? |
All people eat taco meat First heart sound = lub Second heart sound = dub Extra heart sounds or murmurs are heard at a3 and S4 S3 = heart failure (3 syllables) S4= hypertrophy (4 syllables)
|
|
|
Forman ovale closes within —— because? |
Within the first hour after birth because of the new negative pressure that is formed |
|
|
When does the ductus arteriosus close |
It closes later than 10 - 15 hours after birth |
|
|
When the ductus arteriosus closes, who has the greater workload? |
The left ventricle has the greater workload of pumping into the circulatory system. |
|
|
How do babies with cardiac problems show signs during feedings of cardiac problems |
Not breathing well = nasal flare Sleeping a lot Not eating because they are obligatory nose breathers. |
|
|
How to assess carotids? |
Inspect: inspect them for stroke and smooth contour Note characteristic of smooth rapid upstroke Summit rounded and smooth, Downstroke more gradual and smooth has a dicrotic notch caused by closure of aortic valve. |
|
|
Main purpose of valves |
To prevent back flow |
|
|
Characteristics of valves |
Unidirectional Open and close passively Anchored by collagenous fibers (chordate and trendiness) to papillary muscles embedded in ventricle floor |
|
|
When the valves open and close |
AV valve open for ventricles to fill during diastole At valve close during systole to prevent regurgitation SL valve open during systole to allow blood in |
|
|
High pressure in the left side gives person symptoms of |
pulmonary congestion or congestive heart failure |
|
|
What do we auscultate for when assessing carotids |
The presence of a bruit (blowing swishing sounds indicating blood flow turbulence) |
|
|
When does the BP decrease to lowest point in pregnancy |
During the second trimester and then slowly rises in the third trimester |
|
|
Position and effect on BP I’m pregnant woman |
Left lateral recumbent position - BP is lowest Supine - BP is a bit higher Sitting - BP is highest |
|
|
What do hormones do to the vessels? |
Cause vasodilation and results in drop of blood pressure Vasoconstriction |
|
|
B |
G |
|
|
When assessing the carotids, where should you put your stethoscope (bell part) |
Angle of the jaw The mid revival area The base of the neck |
|
|
What can lead to an artificial bruit |
Compressing the artery |
|
|
True or false: Some aortic valve murmurs (aortic stenosis) radiate to the neck and must be distinguished from a local bruit. |
True |
|
|
Differences in structure of heart and position in body for pregnant women, infants, heart failure, |
Pregnant woman - heart is higher because of baby pushing Infant - Heart is more horizontal than diagonal Heart failure - instead of being in the 5th intercostal space midclavicular, heart would move further back to side of body, ventricle would be growing lateral and down
|
|
|
What are risk factors for hypertension? (DOGF) |
Diabetes obesity genetics family history |
|
|
What are modifiable risk factors for heart disease |
Sedentary life style Diet Smoking Exercise Alcohol use |
|
|
Non modifiable risk factors for heart disease |
Age Race Sex |
|
|
How to asses arteries and veins |
Arteries - Patient should be sitting up Veins - Patient should lie supine with head slightly elevated (standing on patient right side) Check pulse Capillary refill vs veins Assess varicosity Edema |
|
|
Expected changes in pregnant vitals |
Blood volume increase by 30-40% BP decrease due to peripheral dilation Increase in resting pulse rate of 10 to 20bmp |
|
|
What do we auscultate for when assessing carotids |
The presence of a bruit (blowing swishing sounds indicating blood flow turbulence) |
|
|
When does the BP decrease to lowest point in pregnancy |
During the second trimester and then slowly rises in the third trimester |
|
|
Position and effect on BP I’m pregnant woman |
Left lateral recumbent position - BP is lowest Supine - BP is a bit higher Sitting - BP is highest |
|
|
What do hormones do to the vessels? |
Cause vasodilation and results in drop of blood pressure Vasoconstriction |
|
|
When assessing the carotids, where should you put your stethoscope (bell part) |
Angle of the jaw The mid revival area The base of the neck |
|
|
What can lead to an artificial bruit |
Compressing the artery |
|
|
True or false: Some aortic valve murmurs (aortic stenosis) radiate to the neck and must be distinguished from a local bruit. |
True |
|
|
Differences in structure of heart and position in body for pregnant women, infants, heart failure, |
Pregnant woman - heart is higher because of baby pushing Infant - Heart is more horizontal than diagonal Heart failure - instead of being in the 5th intercostal space midclavicular, heart would move further back to side of body, ventricle would be growing lateral and down
|
|
|
What are risk factors for hypertension? (DOGF) |
Diabetes obesity genetics family history |
|
|
What are modifiable risk factors for heart disease |
Sedentary life style Diet Smoking Exercise Alcohol use |
|
|
Non modifiable risk factors for heart disease |
Age Race Sex |
|
|
How to asses arteries and veins |
Arteries - Patient should be sitting up Veins - Patient should lie supine with head slightly elevated (standing on patient right side) Check pulse Capillary refill vs veins Assess varicosity Edema |
|
|
Expected changes in pregnant vitals |
Blood volume increase by 30-40% BP decrease due to peripheral dilation Increase in resting pulse rate of 10 to 20bmp |

