![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
183 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When inspecting the external nose you are observing
|
-shape
-size -skin -color -presence of deformity or inflammation *If swelling or deformities exist, palpate nose -Note any tenderness, masses or underlying deviation |
|
|
Patency
|
-should be present for each nostril w/o excessive faring
*Assess by occluding 1 nare @ at time while client is breathing with mouth Closed |
|
|
Normal mucosa of nares
|
-pink and moist w/o lesions
|
|
|
Illuminate the Anterior Nares and assess for?
|
-color
-lesions -discharge -swelling -evidence of bleeding |
|
|
Pale mucosa with clear discharge indicates?
|
Allergy
|
|
|
Mucoid discharge indicates?
|
Rhinitis
|
|
|
Yellowish or greenish discharge from nose is a result of?
|
Sinus Infection
|
|
|
Habitual use of intranasal cocaine and opioids causes?
|
-puffiness
-increased vascularity of nasal mucosa -perforation of septum |
|
|
Assess client with NG tube for?
|
-skin breakdown
-redness -skin sloughing |
|
|
EXCORIATION?
|
-skin breakdown
|
|
|
CN I?
|
Olfactory (smell)
|
|
|
POLYPS
|
-tumor-like growths
*Note any polyps or purulent drainage |
|
|
Assess the Integrity of the NOSE by using?
|
-Inspection
-Palpation-sinuses -Percussion-sinuses |
|
|
Most effective way to assess for tenderness of sinuses?
|
-Palpate frontal & Maxillary facial areas (do not apply pressure to the eyes)
|
|
|
Technique for assessing the frontal sinuses?
|
-Palpate by Pressing upward with thumbs from just belowthe eyebrows on either side bridge of nose
|
|
|
Technique for assessing Maxillary Sinuses?
|
-Palpate by pressing upward at the skin crevices that run from the sides of nose to corner of mouth
|
|
|
*Client Teaching strategies for Nose & Sinus Assessment?
|
-caution againt otc nasal sprays (leads to "rebound" effect, causing excessive nasal congestion)
-Instruct parents in care of a child with nosebleeds -Older adults to install smoke detectors/check dated labels on food for spoilage |
|
|
Cherry colored lips indicates?
|
-carbon monoxide poisoning
|
|
|
Lips normally appear?
|
-darker pigmented skin than face
-symmetrical -smooth -soft with no Lesion -non tender |
|
|
Pallor of the Lips is caused by?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
Any lesions on Lips are related to?
|
-infection
-irritation -skin cancer |
|
|
Inspect Lips for
|
-color
-hydration -contour -lesions |
|
|
Assessment of the mouth and pharynx detects signs of ...?
|
-overall health
-oral hygiene needs |
|
|
When viewing the molar, the nurse should note?
|
-color of teeth
-caries -tarter -extraction sites |
|
|
What is the early indication for dental caries?
|
-brown or black discolorations
|
|
|
When Inspecting the Oral Mucosa you are looking for?
|
-color
-hydration -texture -lesions (ulcers, abrasions,cysts) |
|
|
Normally the Oral Mucosa appears?
|
-pink
-soft -moist -smooth |
|
|
Cherry colored lips indicates?
|
-carbon monoxide poisoning
|
|
|
Lips normally appear?
|
-darker pigmented skin than face
-symmetrical -smooth -soft with no Lesion -non tender |
|
|
Pallor of the Lips is caused by?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
Any lesions on Lips are related to?
|
-infection
-irritation -skin cancer |
|
|
Inspect Lips for
|
-color
-hydration -contour -lesions |
|
|
LEUKOPLAKIA
|
-thick white patches
-precancerous lesion seen in heavy smokers & alcoholics |
|
|
Gums should appear?
|
-coral pink
-tight against the teeth w/ no bleeding on gloves when palpated |
|
|
Gingivae
|
-gums
|
|
|
Inspection of Gums include?
|
-color
-edema -retraction- -bleeding -lesions |
|
|
Spongy gums that bleed indicates?
|
-periodontal disease
-Vit C deficiency |
|
|
Inspections of the Tongue include?
|
-color
-size -position -texture -coatings or lesions |
|
|
How do you test the function of the hypoglossal nerve (CN-XII)?
|
-relax mouth
-stick the tongue out halfway |
|
|
Normal appearance of tongue?
|
-medium or dull red
-moist slightly rough on top surface -smooth along the lateral margins |
|
|
Area of tongue that is highly vascular?
|
-under surface of the tongue
-floor of mouth |
|
|
VARICOSITES
|
-swollen, tortuous veins
-common in older adult/rarely cause problems |
|
|
EXOSTOSIS
|
-bony growth
*commonly seen b/w soft and hard palates |
|
|
dysphagia
|
-difficult swallowing
|
|
|
Children, adults and older adults should have regular dental exam every?
|
-6 months
|
|
|
Common complaints and findings with Oral Cancer include?
|
-nonhealing lip or mouth sore
-swelling or mass -leukoplakia -erthroplakia=slightly raised red patch or lesion,bleeds easily -unusual bleeding -unusual sensation -chronic sore throat -foreign body sensation in throat (tingling) -voice change -dysphagia |
|
|
Abnormality of Lymph Nodes reveal the presense of?
|
-infection
-malignancy |
|
|
Muscles of the neck that divide each side of the neck into 2 trianagles?
|
-SCM
-Trapezius |
|
|
Assessment of the MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM includes:
|
-alignment
-symmetry & muscle mass -Muscle tone -ROM -any involuntarymvmt -signs of inflammation (redness,swelling, warmth, tenderness, loss of function |
|
|
Age-Related changes in Musculoskeletal system:
|
-height loss is due to thinner intervertebral discs, osteoporosis or kyphosis
-skeletal muscles decreases in size -ROM decreases -Posture changes are a result of a wider stance -flexion of hips, knees & elbow is typical |
|
|
2 techniques used to assess musculoskeletal system?
|
-inspection
-palpation |
|
|
Flexion
|
decrease angle
|
|
|
extension
|
extend angle
|
|
|
Hyperextension
|
extreme extension (neck, back)
|
|
|
supination
|
ventral surface facing up
|
|
|
Pronation
|
ventral surface facing down
|
|
|
Abduction
|
move extremity away from midline
|
|
|
Adduction
|
move extremity toward midline
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion
|
mvmt toward dorsum (top of the wrist or foot)
|
|
|
Plantar Flexion
|
mvmt toward the plantar surface (bottom of foot)
|
|
|
Eversion
|
turn body part Away from midline
|
|
|
Inversion
|
turn body part Toward midline
|
|
|
Which CN do you assess during the head & neck exam?
|
-CN V (trigeminal)= assess face for strength & sensation
-CN VII (facial)= assess face for mvmt -CN XI (spinal accessory) assess shoulders for strength |
|
|
3 Techniques used to examine a client's neck and head
|
-inspection
-palpation -auscultation |
|
|
What questions should the nurse ask the client during Head and Neck exam?
|
-Headaches? (how often & location)
-pain in neck -able to move head & shoulders w/ ease? -Any unusual facial mvmt -Lymph nodes swollen? |
|
|
What are you assessing for when u Inspect & Palpate the skull?
|
-size
-depression -deformities -masses -tenderness -overall contour & symmetry |
|
|
Normocephalic
|
normal skull size
|
|
|
Inspection & Palpation of the FACE includes:
|
-symmetry of facial features
-symmetry of expressions -involuntary mvmts (abnormal) -proportinate features (no thickening as in acromegaly) |
|
|
Acromegaly
|
-excessive amoutn of growth hormone and the body tissues gradually enlarge.
|
|
|
CN V ?
*Motor= *Sensory= |
-Trigeminal
*test the STRENGHT of the muscle contraction by asking client to clench teeth while palpating the masseter and temporal muscles, then the temporomandibular joint *Test LIGHT TOUCH by having client close her eyes, gently touching her face w/ a cotton swab & asking her to tell you when the touch is felt |
|
|
CN VII?
*Motor? |
-Facial
*Test FACIAL MVMT by having client smile, frown puff out cheeks, raise eyebrows, close eyes tightly & show teeth |
|
|
Normal appearance of muscles in the NECK?
|
-should be equal in ht & w/ normal muscle mass
|
|
|
(ROM) The client should be able to move head smoothly and w/o distess in what 3 directions?
|
-chin to chin (flexion)
-ear to shoulder bilaterally (lateral flexion) -Chin up (Hypertension) |
|
|
How do you assess for CN XI in the neck?
|
-Hands on clients shoulders & ask the client to shrug the shoulders against resistance
|
|
|
LYMPH NODES (glands)
|
-small clusters of cells, surrounded by a capsule. Ducts go in and out of them. The cells in lymph nodes are lymphocytes, which produce antibodies (protein particles that bind foreign substances including infectious particles) and macrophages which digest the debris. They act as the "cleaner" cells of the body.
- part of the lymphatic system, a component of the body's immune system -vital role in your body's ability to fight off viruses, bacteria and other causes of illnesses. -Most often, lymph nodes swell and become inflamed as a result of an infection |
|
|
Lupus erythematosus
|
auto immune disease
|
|
|
**Lymph Nodes Location**
1. Occuipital 2. Preauricular 3. Postauricular 4. Submandibular 5. Tonsillar (retropharyngeal) 6. Submental 7. Anterior Cervical 8. posterior Cervical |
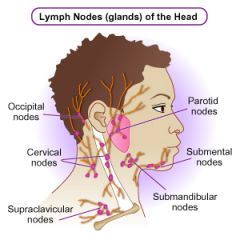
1. base of the skull
2. in front of the ear 3. over the mastoid 4. along the base of the mandible 5. angle of the mandible 6. midline under the chin 7. SCM muscle 8. posterior to SCM muscle |
|
|
*Client Teaching for Neck Assessment includes:*
|
-stress importance of compliance w/ meds in clients w/ Thyroid disease
-instruct about lymph nodes & how infection commonly causes node tenderness -call MD if client notices an enlarged lump of mass in the neck -risk factors for HIV infection and other STD's |
|
|
When assessing lymph nodes they are normally?
|
-Nonpalpable and nontender
|
|
|
Abnormal assessment would indicate?
|
-local infection
-systemic disease -neoplasm |
|
|
Tenderness of the lymph nodes is an indication for?
|
-inflammation
|
|
|
Problem involvinga lymph node of the head & neck mean an abnormality in the?
|
-mouth
-throat -abdomen -breast thorax arms |
|
|
Examine the Thyroid GLand by
|
1. inspecting lower half of neck (looking for any enlargement)
2. have client sip H20 & watch the thyroid tissue move up 3 hyperextend neck |
|
|
While palpating the thyroid gland the nurse is looking for?
|
-masses
-size -smoothness |
|
|
Location of thyroid gland
|
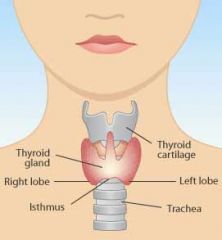
|
|
|
Goiter
|
visibly enlarged thyroid gland
|
|
|
2 body systems that interacts with the musculoskeletal system?
|
1. neurological-coordinates the functionof the musculoskeletal systems
2. depends on the muscles of the chest to protect the lungs and help with breathing (diaphram) |
|
|
Question to ask the client during assessment include:
|
-pain in joints or muscles
-stiffness, weakness or twitching -experienced any recent falls -able to care for youself -activity limited by any physical factors -describe physical activity -exercise? -bone/muscle surgery? -hx of arthritis, osteoporosis, fractures -any changes in ADL's -artifical limbs? -assistive device? |
|
|
Major symptoms to watch for during musculoskeletal system assessment include:
|
-pain (head/neck=place hand on side of face, ask client to push against your hand)
-weakness (check grip by having client squeeze your fingers) -stiffness -balance/coordination problems |
|
|
Muscular d/o are the result of
|
neurological disease
|
|
|
ataxia
|
Ataxia is not a specific disease or a diagnosis, it is just a word used to describe certain, similar, types of symptom. Ataxia will mainly involve clumsiness and loss of coordination. Ataxia may affect the fingers and hands, the arms or legs, the body, speech or eye movements - it is a description of physical problems. Ataxia symptoms may included staggered gait (unsteady walking), problems with balance, poor limb control (co-ordination), slurred speech, choking problems, irregular eye movements and loss of reflexes.
(cerebellum d/o) |
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
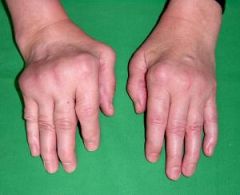
associated with morning stiffness
|
|
|
How do you inspect a client's gait and posture
|
1.gait=observe when client is walking in room
-walk a straight line *normal gait=walk w/ arms swinging freely at the sides and head leading the body 2. posture=observe client from the side in a standing position *normal standing posture=upright w/ parallel alignment of hips and shoulders/holding the head erect |
|
|
Lordosis
|
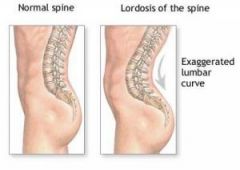
exaggerated curvature of the lumbar sping (common during toddler years and pregnancy)
|
|
|
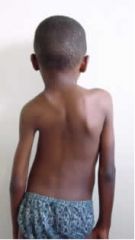
Kyphosis
|
exaggerated curvature of the Thoracic spine (hunchback)
|
|
|
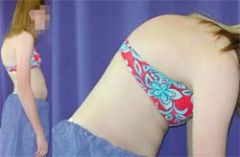
SCOLIOSIS
|
-lateral spinal curvature
|
|
|
SCOLIOSIS
|
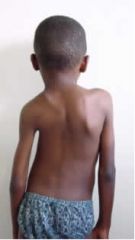
-lateral spinal curvature
|
|
|
Goniometer
|

measures the degree of motion in a joint (use for clients who have a suspected reduction in joint mvmt
|
|
|
Passive ROM
|
assess by moving the client's joints through full ROM.
-Do Not move a joint past a point of pain or resistance |
|
|
Active ROM
|
client repeats the mvmts demonstrate by the nurse
|
|
|
Muscle Tone & Strength
1.HYPERTROPHY |

-enlargement of the muscle due to strengthening
- |
|
|
Hypotonicity
|
-little tone
-feels flabby -stroke patient |
|
|
HYPERTONICITY
|
-increased muscle tone
- |
|
|
ATROPHY
|
decrease in muscle size due to miss use
|
|
|
Recommended Ca+ dose for
1. adult 2. post-menapause |
1. 1000mg/day
2. 1500mg/day |
|
|
Normal curvatures of the spine
|
1. concave cervical
2. convex thoraic spine 3. concave lumbar spine |
|
|
When do you assess for muscle Tone?
|
-during ROM
*Tone is determined by the presence of slight resistance of the muscles during relaxation |
|
|
Expected finding when assessing Muscle Strength?
|
-strength equal or slightly stronger on the dominant side
|
|
|
NEUROLOGICAL Assessement
*Integrate into other parts of the head to toe assessment *Extent- based on the client LOC & general health status |
*
|
|
|
Questions nurse should ask during Neuro Assessment/
|
-any dizziness?
-Headaches? -seizures -hx of head trauma or LOC -any change in speech, ability to think clearly, loss or change in memory -weakness? -numbness -tremor or tingling (where?) |
|
|
Neuro Exam includes:
|
-mental status to test cerebral function
-Cranial nerves -motor function to test cerebral function -sensory function -reflexes - |
|
|
Levels of Consciousness (5)
1. ALERT |
1. responsive & able to fully respond by opening eyes & attending to a normal tone of voice & speech
|
|
|
2. LETHARGY
|
2. open eyes and respond, BUT is DROWSY and falls ASLEEP readlily
|
|
|
3. OBTUNDATION
|
3. client needs to be lightly shaken to respond, BUT may be CONFUSED and SLOW to RESPOND
|
|
|
4. STUPOR
|
4. requires painful stimuli (pinching a tendon or rubbing the sternum) to achieve a brief response
-may not be able to respond verbally |
|
|
5. COMA
|
-NO response to repeated painful stimuli
|
|
|
What are the 2 Abnormal posturing in the comatose client?
|
1. DeCORTicate RIGIDITY= flexion and internal rotation of upper extremity joints and legs
2. DeCEREbrate rigidity= neck and elbow extension, wrists and fingers flexed |
|
|
Equip for NEURO assessment
|

-snellen & rosenbaum eye charts
-aromatic substances (CN I =olfactory) -tongue blades -penlight- PERRLA -salt and sugar -tuning fork -reflex hammer -cotton balls -2 test tubes with 1 hot and 1 cold water - |
|
|
*Assessment Category*
1.Determine client use of analgesics, alcohol, sedatives, hypnotics, antipsychotics, antidepressants or recreational drugs. What is the Rationale? |
-these meds alter LOC or cause behavioral changes.
-Abuse can cause tremors, ataxia, and changes in peripheral neve function |
|
|
2. Determine if client has recent history of seizure/convulsions
What is the Rationale? |
-Seizure activity often originates for CNS alteration
|
|
|
3. Screen client for sx of HA, tremors, dizziness, vertigo, numbness or tingling of body part, visual changes, weakness,pain or changes in speech.
What is the Rationale? |
-These sx frequently originate from alterations in CNS or PNS function.
-id of specific patterns aids in dx of pathological condition |
|
|
4. Discuss w/ client's family any recent changes in client's behavior (mood swings, memory losss, changes in energy level)
What is the Rationale? |
-Behaviral changes sometimes result from intracranial pathological states
|
|
|
5. Assess client for hx of change in vision, hearing, smell, taste or touch.
What is the rationale? |
-sensory nerves originate from brain stem. These symptoms help to localize nature of the problem
|
|
|
6. If an older client displays suddne acute confusion (delirium), review hx for drug toxicity (anticholinergics, diuretics, digoxin, cimetidine, sedatives, antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics) serious infections, metabolic disturbances, heart failure and severe anemia
What is the rationale |
-one of the most common mental d/o in older persons.
-condition is always potentially reversible |
|
|
7. Review past hx for head or spinal cord injury, meningitis, congenital anomalies, neuro disease
What is the rationale? |
7. factors cause neuro sx or behavioral changes to develop
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Neuro system?
|
-initiation
-coordination of mvmt -reception and perception of sensory stimuli -organization of thought process -control of speech -storage of memory |
|
|
The client will need a complete neuro assessment with c/o Headache or recent loss of function in an extremity.
T/F |
True
|
|
|
Test used to measure orientation and cognitive function?
|
The Mini-Mental state Examination (MMSE)
-score of 21 or less reveal cognitive impairment. *Question -orientation to time -registration =say 3 words/have client repeat back to you -naming= "what is this" (point to a pencil) -Reading= "please read this and do what it says" CLOSE YOUR EYES |
|
|
What are the functions of the cerebral cortex?
|
-controls and integrates intellectual functioning
-controls and integrates emotional functioning |
|
|
A disturbance in cerebral function reflects an alteration in?
|
-emotional or emotional status
|
|
|
What are some example of factors that change Cerebral Function?
|
-primary brain d/o
-medication -metabolic changes |
|
|
An acute mental d/o characterized by confusion, disorientation and restlessness
|
Delirium (common mental d/o in older adults
-often misdiagnosed for dementia -it is NOT due to a preexisting or evoling dementia. -develops over a short period of time, usually hors to days and tends to flucutate during the course of the day. -a direct physiological consequence of a general medical condition -can occur in younger clients |
|
|
Why is Delirium so often overlooked in older adults?
|
-failure to adequately assess mental status
|
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms for Delirium?
|
-reduced clarity of awareness of the environment
-ability fo focus, sustain or shift attention is impaired -irrelevant stimuli easily distract the person -change in cognition (memory impairment, disorientation, language disturbacne -effects recent memory -language disturbance (inability to name objects) -perceptual disturbances=hallucination,unsteady gait, tremors, asterixis or myoclonus |
|
|
An objective measurement of consciousness on a numerical scale
|
GLasgow Coma Scale
-allows evaluation of a clients neurological status over time -the higher the score the better the clients neuro function -use caution when using the scale if a client has sensory losses (vision/hearing) |
|
|
A response that indicates the absence of muscle tone in the extremities and severe injury to the brain tissue
|
Flaccid
|
|
|
What is the normal response to a painful stimuli?
|
withdrawal of the body part
-elicit the pain response by applying firm pressure with the thumb over the root of the clients' fingernail |
|
|
GLASGOW COMA SCALE
*ACTION 1. Eyes Open What is the response and score? 2. Best Verbal Response: What is the response and score? 3. Best Motor Response |
-spontaneoulsy 4
-to speech 3 -to pain 2 -None 1 Oriented 5 confused 4 inappropriate words 3 incomprehensible sounds 2 None 1 Obeys commands 6 localized pain 5 flexion withdrawal 4 abnormal flexion 3 abnormal extension 2 flaccid 1 |
|
|
What is Intellectual Function?
|
includes memory (recent, immediate & past)
-knowledge -abstract thinking -association -judgement |
|
|
MEMORY (immediate, past, recent)
How do clients demonstrate IMMEDIATE MEMORY? |
by repeating a series of numbers (6 9 12), in the order they are presented or in reverse
|
|
|
What are some questions to ask the client that will test their PAST MEMORY?
|
-Mother's madien name
-DOB -special date in history -ask open-ended questions *stoke patient's DON'T loss past memory* |
|
|
What question do you ask client that will test their RECENT MEMORY?
|
-Who came to see you today?
-Ask questions that recall events occurring the same day (Vaildate infor w/ family member) *Stoke patient LOSE their recent memory* |
|
|
What are some questions to ask to assess client's KNOWLEDGE?
|
-ask how much does the client know about their illness or reason for seeking health care
*Helps to determine a clients ablity to learn or understand |
|
|
How do you assess ABSTRACT THINKING?
|
-ask the client the interpretation of a cliche such as "A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush"
*determines a higher level of thought |
|
|
Assessment of APPEARANCE includes:
|
-hygiene
-grooming -clothing choice *expected findings: well-kept, clean, and dressed appropriately for the environment or situation |
|
|
GLASGOW COMA SCALE
*ACTION 1. Eyes Open What is the response and score? 2. Best Verbal Response: What is the response and score? 3. Best Motor Response |
-spontaneoulsy 4
-to speech 3 -to pain 2 -None 1 Oriented 5 confused 4 inappropriate words 3 incomprehensible sounds 2 None 1 Obeys commands 6 localized pain 5 flexion withdrawal 4 abnormal flexion 3 abnormal extension 2 flaccid 1 |
|
|
Intellectual/Cognitive Function includes?
|
-memory (recent, immediate & past)
-knowledge -abstract thinking -association -judgement |
|
|
MEMORY (immediate, past, recent)
How do clients demonstrate IMMEDIATE MEMORY? |
by repeating a series of numbers (6 9 12), in the order they are presented or in reverse
|
|
|
What are some questions to ask the client that will test their PAST MEMORY?
|
-Mother's madien name
-DOB -special date in history -ask open-ended questions *stoke patient's DON'T loss past memory* |
|
|
What question do you ask client that will test their RECENT MEMORY?
|
-Who came to see you today?
-Ask questions that recall events occurring the same day (Vaildate infor w/ family member) *Stoke patient LOSE their recent memory* |
|
|
What questions would you ask a client to assess their KNOWLEDGE?
|
-"What do you Know about your about current hospitalization or illness?"
*these questions help to understand client's ability to learn or understand* |
|
|
Asking a client to interpret Cliche such as "a stitch in time saves nine" or "don't count your chickens before they hatch" , is assessing which intellectual function?
|
-ABSTRACT THINKING (this would demonstrate a higher level of thought process)
-client w/ altered mental status will probably interpret the phrase literally or merely rephrase the words |
|
|
When asking client to explain how various concepts are related, such as a creek and a river you are assessing which intellectual functioning?
|
ASSOCIATION-involves finding similarities or associations b/w concepts
*a dog is to a beagle as a cat is to a Siamese |
|
|
Requires a comparison and evaluation of facts and ideas to understand their relationships and to form appropriate conclusions. Which intellectual functioning is being assessing?
|
JUDGEMENT-ask client about the solution to a specific dilemma
"what would you do if you locked your keys in your car?" (the response should be logical) |
|
|
What are the 6 SENSORY FUNCTION TEST that are performed on all four extremities with the client's eyes closed?
|
1. Pain
2. Temperature 3. Light touch 4. Vibration 5. Position 6.2-Point Discrimination *perform all test w/ the clients eyes CLOSED! |
|
|
How do you assess for PAIN sensation?
|
-alternating sharp and dull objects on the skin & asking client to report what he feels.
*note areas of numbness or increased sensitivity* Equip: broken tongue blade Precautions: areas where skin is thick, such as heel or sole of foot are less sensitive to pain |
|
|
How do you assess for TEMPERATURE?
|
-touch skin w/ test tube, asking client to identify hot & cold sensation
-Equip: 1 test tube w/ hot H2O 1 test tube w/ cold H2O -Precautions: omit test if pain sensation is normal. |
|
|
LIGHT TOUCH sensory function test includes:
|
-applying different wisp of cotton to different points along skins surface.
-Ask client to voice when the feel a sensation -Precaution: apply to areas where skin is thin or more sensitive (neck, face, inner aspect of arms, top of feet and hands) |
|
|
Assess VIBRATION sensory function by asking client?
|
-to report when & where they feel the handle of the vibrating tuning fork on the skin
-apply stem of vibrating fork to distal interphalangeal joint of fingers and interphalangeal joint of great toe, elbow and wrist. -Precautions: be sure client feels vibration and not pressure |
|
|
How do you assess the POSITION sensory function?
|
-by repositioning the client's appendages and asking him to report whether it is positioned up or down. Ask client to state when finger is up or down, alternating w/ the toes (up/down)
-Precautions: avoid rubbing adjacent appendages as you move finger or toe. -don't move joint laterally;return to neutral positon before moving again. |
|
|
Explain TWO_POINT DISCRIMINATION sensory function test:
|
-use open paper clips or broken tongue blades to determine the distance at which the two points are felt as one
-compare bilaterally -minimal distance will vary depending on the body part being evaluated (2 to 8 cm) -apply to the same anatomical site (palm of hand, upper arms, fingertips) |
|
|
What are 2 other DISCRIMINATION test?
|
-stereognosis
-graphesthesia |
|
|
test that uses a familiar object (key, cotton ball) by placing it in the client's hand and asking client to identify object is?
|
Stereognosis
|
|
|
Graphesthesia
|
ask client to identify a number drawn on his palm with the blunt end of a pencil
|
|
|
What part of the brain controls coordination, balance and reflexes?
|
-cerebellum (motor function)
*Cerebellum coordinates muscular activity, maintains balance and equilibrium and controls posture* |
|
|
How do you assess for COORDINATION?
|
-by asking the client to extend arms and rapidly touch his finger to his nose, alternating hands and then doing the technique w/ eyes closed
-expected findings include:smooth, coordinated mvmt |
|
|
Assess balance by using what to 2 test?
|
1. romberg
2. Heel to toe walk |
|
|
ROMBERG test?
|
-ask client to stand w/ feet at a comfortable distance apart, arms at sides and eyes closed. (30 sec. w/ eyes open, 30 sec. w/ eyes closed)
*Expected findings: client should be able to stand w/ minimal swaying for at least 5 sec. *loss of balance=Positive Romberg *assess gross motor function |
|
|
HEEL to TOE WALK?
|
-ask the client to place the heel of one foot in front of the toes of the other foot as he walks in a straight line.
*Expected findings: the client is able to walk in a straight line w/o losing his balance |
|
|
What test is used to assess COORDINATION?
|
-RRAM (assesses fine motor function)
R-apid R-hymatical A-lternating M-ovement |
|
|
2 ways to assess coordination by using RRAM??
|
1. ask client to extend arms and rapidly touch finger to nose, alternating hands, then doing same technique w/ eyes closed.
-Expected findings: smooth, coordinated mvmts 2. upper extremity coordination: touching each finger w/ the thumb of the same hand in a rapid sequence |
|
|
Provides data about the integrity of sensory & motor pathways of th reflex arc & specific spinal cord segments?
|
-Elicting REFLEX (does not determine higher neural center functioning)
|
|
|
Each muscle contains a small sensory unit called_________.
|
Muscle spindle which controls muscle tone and detects changes in the length of muscle fibers.
*Reflex hammer=tapping a tendon w/ reflex hammer stretches the muscle & tendons, lengthening the spindle |
|
|
What are the 2 categories of REFLEXES?
|
1. Deep tendon reflexes (DTRs)=elicited by milding strengthing a muscle & tapping a tendon
2. Superficial/Cutaneous Reflex= elicted by stimulating the skin superfically (Babinski reflex) |
|
|
Babinski Reflex?
|
-superficial reflex
-assess w/ head injury -tests plantar reflex *Abnormal Finding= -Positive BABINSKI**= dorsiflexion of great toe w/ or w/o fanning of other toes |
|
|
Why is it normal for an infant to have a "Present Babinski"?
|
-Most newborn babies are not neurologically mature and therefore show a Babinski response. Upon stimulation of the sole, they extend the great toe . Many young infants do this, too, and it is perfectly normal. However, in time during infancy the Babinski response vanishes and, under normal circumstances, should never return.
A Babinski response in an older child or adult is abnormal. It is a sign of a problem in the central nervous system (CNS), most likely in a part called the pyramidal tract. Asymmetry of the Babinski response -- when it is present on one side but not the other -- is abnormal. It is a sign not merely of trouble but helps to lateralize that trouble (tell which side of the CNS is involved). |
|
|
If superficial reflexes were tested on a 12 month old, what would be the result of the Babinski test?
|
Babinski's reflex is one of the infantile reflexes. It is normal in children up to 2 years old, but it disappears as the child ages and the nervous system becomes more developed. It may disappear as early as 12 months.
The presence of a Babinski's reflex after age 2 is a sign of damage to the nerve paths connecting the spinal cord and the brain (the corticospinal tract). This tract runs down both sides of the spinal cord, therefore a Babinski's reflex can occur on one side or on both sides. An abnormal Babinski's reflex can be temporary or permanent. |
|
|
Grading of deep tendon reflex(dtf) is done on a scale of ______.
|
- 0 to 4
0= No response 1+ sluggish or diminished 2+ active or expected repsonse 3+ more brisk than expected, slightly hyperactive 4+ brisk and hyperactive w/ intermittent or transient clonus |
|
|
What reflex grade would a client w/ alcohol, cocaine or opioid intoxication have?
|
4+ hyperactive
|
|
|
-acute elevations in Mg levels
-hypoactive Deep tendon reflexes -decreased depth & rate of respiration, hypotension & flushing |
_Hypermagnesemia=electrolyte imbalance
*Related Causes: renal failure excess oral or parenteral intake of Mg |
|
|
-What is the abnormal flexion position? (medical term)
-assessment of Motor Response using Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), Flexion Upon Pain (Decorticate) = 3 pts |
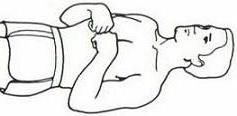
DECORTICATE
|
|
|
-Lacking firmness, resilience, or muscle tone
|
FLACCID
|
|
|
Using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCA), how often do you assess a client neruological status changes?
|
-every 15 minutes the 1st hour, then every 30 mins for 1 hour
|

