![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In the temporal region, the frontal branch of the facial nerve is located within which of the following layers? A ) Subcutaneous tissue B ) Superficial temporal fascia C ) Superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia D ) Superficial temporal fat pad E ) Deep layer of the deep temporal fascia
|
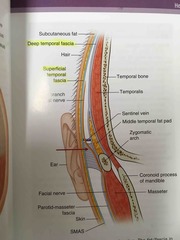
As depicted in the image shown, the temporal or frontal branch of the facial nerve is found within the superficial temporal or temporoparietal fascia. In the temporal region, the facial nerve can be injured with a coronal approach. The layers from superficial to deep in this region include: (1) skin, (2) subcutaneous tissue, (3) superficial temporal fascia also known as the temporoparietal fascia, (4) superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia, (5) superficial temporal fat pad, (6) deep layer of the deep temporal fascia, (7) temporalis muscle.
When the coronal flap is raised, as soon as the yellow superficial temporal fat pad is seen beneath the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia, the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia must be incised and included with the coronal flap to protect the frontal branch, which is in the superficial temporal fascia (temporoparietal fascia), one layer superficial to this. |
|
|
Name three main components made of endoderm. |
Respiratory and GI lining. Abdominal organs.wh |
|
|
When pharyngeal grooves failure to obliterate, cysts can form. Where are they most often found? |
▀Failure to obliterate results in pharyngeal cleft cysts (sealed within neck), sinuses (end in blind sac), or fistulas (connect with pharynx). •These anomalies are often detected in the second decade of life and are palpable at the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM). •Anomalies from groove II are the most common, running under the middle/lower SCM, over the glossopharyngeal nerve, and between the external and internal carotid arteries toward the tonsillar fossa. |
|
|
Which gland contributes the most to saliva production? |
The submandibular glands contribute the most to basal salivary production, approximately 60%. The parotid gland contributes approximately 20% to basal salivary production. Sublingual glands and minor salivary glands each contribute 10%. |
|
|
Which teeth are the last to erupt? Maxillary or mandibular? How old? |
Aside from the third molars, the maxillary canines are typically the last teeth to erupt of the available options (around 11 to 12 years of age). |
|
|
A 50-year-old man who underwent superficial parotidectomy for a benign tumor 9 months ago comes to the office because of a 6-month history of gustatory sweating. Which of the following nerves carries the parasympathetic postganglionic nerve fibers to the parotid gland in a healthy patient? A) Auriculotemporal B) External carotid plexus C) Facial (VII) D) Great auricular E) Marginal mandibular |
A auriculotemporal |
|
|
17 year-old boy with profuse bleeding from a stab wound to the neck above the angle of the mandible anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. After airway stabilization is established, vascular repair of a laceration of the jugular vein is performed. Which neck zone? |
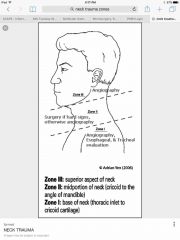
Zone 3 |
|
|
A 60-year-old man undergoes microvascular anastomosis. The proximal facial artery off the external carotid artery is to be dissected and used as a recipient vessel. During the procedure, a large, overlying, nerve-like structure is inadvertently transected. Which nerve? |
Hypoglossal The facial artery generally starts as part of the lingual-facial trunk, then travels below the hypoglossal nerve before it enters into the submandibular gland and along the lateral border of the mandible. Failure to recognize this structure could cause injury and subsequent loss of motor function of the ipsilateral tongue. Ipsilateral hypoglossal (XII) nerve injury causes the tongue to move toward the side of damage, resulting in dysarthria, and problems moving solid food to the oropharynx. |
|
|
Treatment for a sinonasal myxoma in an infant? |
Resection with clear margins. |
|
|
The classic presentation of X is cyanosis that improves with crying |
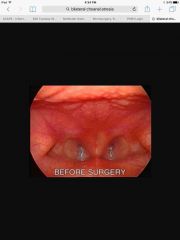
bilateral choanal atresia |
|
|
Which of the following cranial nerves provides parasympathetic innervention of the parotid gland? A) V B) VII C) VIII D) IX E) X
|
D) IX Innervation of the parotid gland comes from parasympathetic fibers that travel with the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX). It also receives taste sensation (afferent) from the posterior one-third of the tongue. |
|
|
Which of the following muscles is associated with the hyoid or second branchial arch? A) Lateral pterygoid B) Levator veli palatini C) Posterior digastric D) Stylopharyngeus E) Thyroarytenoid
|
The correct response is Option C. Posterior digastric |
|
|
A 6-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a laceration of the hard palate. Repair of the laceration with local anesthesia for greater palatine nerve block is planned. As the anterior portion is sutured in place, the patient feels pain. Which additional nerve block is most appropriate? |
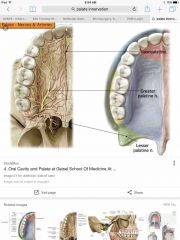
Nasopalatine also called sphenopalatine |
|
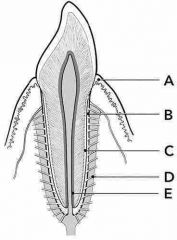
Which of the following structures (A-E) is responsible for anchoring the tooth in its socket? |

D periodontal ligament |
|
|
During the period of mixed dentition, which is the first permanent tooth |
Mandibular first molar In the maxilla, the order of eruption is as follows: first molar, central incisor, lateral incisor, first premolar, second premolar, canine, second molar, and third molar. In the mandible, the order is slightly different and is as follows: first molar, central incisor, lateral incisor, canine, first premolar, second premolar, and second molar. The permanent first molars erupt between ages 6 and 7 years, the central and lateral incisors erupt between ages 6 and 8 years, and the first premolars erupt between ages 8 and 9 years. The first tooth to erupt is the permanent mandibular first molar, which erupts first in a position posterior to the deciduous second molar. |
|
|
A 35-year-old woman is evaluated because of numbness of the upper helical rim of the left ear 30 days after she underwent neurosurgical decompression to treat facial pain. Which of the ear nerves was most likely injured? |

auriculotemporal |
|
|
Which nerves or vessels emerge from the following: A) Jugular B) Lacerum C) Ovale D) Rotundum E) Stylomastoid |
A) The glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), and spinal accessory (XI) nerves emerge from the jugular foramen B) foramen lacerum & internal carotid artery C) foramen ovale & mandibular (V3) nerve D) foramen rotundum & maxillary (V2) nerve, respectively E) facial nerve & stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
Branches of the external carotid? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Where does the auriculotemporal nerve come from? |
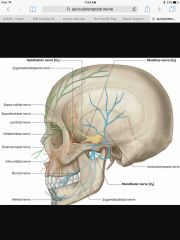
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trauma zones of the neck: two landmarks that separate zones? Which is most superior? |
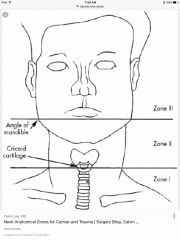
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Which syndrome has keratocystic odontogenic tumors? What else does it have? How do they odontogenic tumors look on pathology? |
The histologic features of keratocystic odontogenic tumors include keratinized epithelium without characteristic epidermal architecture, such as rete ridges. Gorlin syndrome. |
|
|
Palisading basaloid cells with large nuclei are characteristic of which jaw tumor? |
Palisading basaloid cells with large nuclei are characteristic of ameloblastoma. |
|
|
An otherwise healthy term 6-month-old male infant is evaluated for a mobile, firm, well-circumscribed mass at the right lateral brow in the area of the zygomaticofrontal suture. Which of the following procedures is the most appropriate next step in management? A) CT scan B) Fine-needle aspiration of the mass C) MRI D) Surgical excision of the mass E) Ultrasonography |
D surgical excision. Midline masses are worrisome because of risk of intracranial extension. |
|
|
A 20-year-old man comes to the office because he has had paraesthesia of the anterior lateral aspect of the tongue since undergoing removal of the mandibular third molars 3 weeks ago. The most likely cause is injury to which of the following nervous structures? A ) Chorda tympani B ) Facial C ) Glossopharyngeal D ) Hypoglossal E ) Lingual |
E ) Lingual General sensation of the anterior two thirds of the tongue is supplied by the lingual nerve, which is a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal. Taste in the anterior two thirds of the tongue is supplied by the chorda tympani from the facial nerve. The chorda tympani joins the lingual nerve and runs anteriorly in its sheath. The glossopharyngeal nerve supplies the mucosa of the posterior one third of the tongue. The hypoglossal nerve is the motor nerve to the tongue, and the facial nerve is the motor nerve to the face. |
|
|
A 58-year-old man comes to the office for consultation regarding treatment 3 weeks after receiving a diagnosis of squamous cell cancer of the soft palate. He says he has had pain in the left ear for the past 2 months. Examination of the ear shows no abnormalities. The most likely cause of the pain is involvement of which of the following nerves? A ) Auricular branch of the vagus (X) B ) Auriculotemporal C ) Great auricular D ) Superficial temporal E ) Vestibulocochlear (VIII) |
The auricular branch of the vagus nerve (Arnold nerve) carries sensory input from the ipsilateral concha and oropharynx. Chronic external ear pain may alert the astute physician of more serious intraoral pathology. |
|
|
A 4-year-old child has a congenital sinus tract opening at the anterior border of the lower third of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Which nerve is most likely to be injured during surgical excision of the fistulous tract? |
Hypoglossal The second branchial arch descends over the third, resulting in an external opening in the lower neck. The internal opening lies at the anterior aspect of the posterior pillar of the fauces, just behind the tonsil (which is the junction between the second and third branchial arches). Usually, the fistula will follow the carotid sheath upwards before crossing the hypoglossal (XII) nerve and passing between the internal and external carotid arteries to reach the tonsillar fossa. As a result, the hypoglossal nerve is at risk during surgery. |
|
|
Recommended treatment for thyroglossal duct cysts? |
Excision of lesion with any tract and a section of hyoid bone |
|
|
Which branchial cleft develops into the external auditory canal? |
The first branchial cleft develops into the external auditory canal |
|
|
Which of the following structures contributes to the formation of the tragus? A) First branchial arch B) First branchial cleft C) Second branchial arch D) Second branchial cleft |
The first branchial arch contributes to the formation of the tragus and anterior helix. |

