![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
dorsal median sulcus |
The narrow midline cleft on spinal cord |
|
|
Ventral median fissure |
Broder midline cleft on ventral side of spine |
|
|
Gray matter |
makes up the dorsal and ventral horns causing the butterfly effect in the spine |
|
|
dorsal root ganglion |
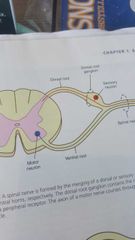
swelling on the dorsal root |
|
|
dynamic cavity |
Contains ear canal/hearing |
|
|
superficial face |
the part of the Face made up by the muscle and skin |
|
|
zagomatic arch |
separates the temporal and infratemporal fossa. |
|
|
Investing Fascia |
The outermost fascia encloses 2 superficial muscles of the neck |
|
|
musculofascial collar |
2 muscles found in the neck. involved in rotation of the head. |
|
|
muscular compartment |
contians muscle that elevate and depress the hyoid bone when swallowing and speaking. |
|
|
visceral compartment |
Contains the larynx, pharnx, esophagus, trachea, thyroid and parathyroid. |
|
|
neurovascular compartment |
surrounded by tubular sheath of fascia. Located lateral to visceral compartment. Contains major arteries, veins of neck as well as lymph vessels and nerves. |
|
|
prevertabral fascia |
encases cervical vertibrae and intrinsic muscles |
|
|
4th week of fetal development |
face begins to form stomdeum primitive mouth and primitive pharanyx merge. Six pairs of bronchial arches have formed 1st mandibularbarch- forms bones muscles nerves lower lip muscles of masticstion, anterior portion of aviolar process 2nd also know as hyoid arch- forms styloid process, stapes of ear, stylohyoid ligament, part of hyoid bone. 3rd forms body of hyoid bone and posterior tongue 4th-6 lower throat, thyroid cartilage, muscle and nerves of pharynx and larynx |
|
|
3rd week of development |
The three primary layers ectoderm mesoderm and endoderm form |
|
|
Middle layer on layer or mesoderm |
Forms the Denton cementon and pulp. Skeletor vascular and lymphatic system muscles are some internal organs |
|
|
Outer layer or ectoderm |
Forms tooth enamel and lining of nasal and oral cavity |
|
|
Inner layer Or endoderm |
Form the epithelial lining |
|
|
midface |
develops from first brachial arch and forms maxilary processes and mandible frontal process forms for head. occurs by 3 weeks Development takes place above stomodeum. |
|
|
palate |
Develops from brachial arch and frontal process. Derived from right and left palitine process and globular process Soft tussue fuses between 8-12 weeks gestation formed by 2 structures primary and secondary palate. Fusion makes a Y shaped pattern May e |
|
|
The tongue |
Formed from the brachial arches 1-4 anterior part derived from first brachial arch posterior part derived from arches to 2-4 formed by three anterior swellings that form the anterio portion; two lateral lingual swelling plays of all in the development of the thyroid gland: epithelial tissue is it he center of the toungue |
|
|
tuberculum impar |
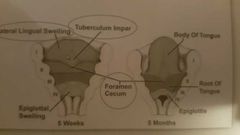
|
|
|
Foremen cecum |
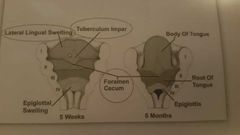
|
|
|
the dentition |
develops front first brachial arch and frontal process. begins at 6 weeks begins at anterior mandible does not begin calcifying until 4th month develops from thickened epithelium-primarily lamina dura develops from tooth germ-consists of 3 layer enamel organ, dental papilla, dental sac |
|
|
Bone and alveolar process |
derived from formal process and first brachial arch. outer dense bone(compact bone) inner sponge-like bone(trabecular bone/cancellous) 50% mineralized 50%non-mineralized. formed from connective tissue. developed in response to teeth. 1.7 grams of pressure to move teeth |
|
|
Bone and alveolar process |
Form from osteoblastic activity resort from osteoblastic activity decrease when teeth position is changed/tooth loss contain internal vascular canals contains internal cellular channels and space. |
|
|
Lamina dura |
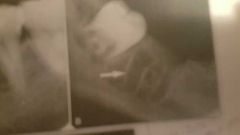
White substance between tooth and bone |
|
|
Histology of the periodontal ligament |
Thin layers of connective tissue surrounding root of tooth fibers are reflective of location fibers are made up of collagen fibroblasts contain specialized cells cementoblast cemento osteoblast and osteoclast May contain epithelial that can lead to tumor formation |
|
|
Periodontal ligament |
Support protect sensory nutritive formative and resorptive |
|
|
oral mucous membrane |
Lines the oral cavity. Derived from germ layer ectoderm Consists of outer epithelial layer(stratified squamous epithelium) and underlying connective tissue layer(lamina propria) some areas are keritinized |
|
|
Lining mucosa |
Softer texture moist stretchable red in color unattach has submucosa blood and nerves. Covers inside of cheeks, vestibule, lips, soft palate and ventral surface of tongue |
|
|
Masticatory mucosa |
Rubbery surface, resilient, light pink, keratinized, firmly attached to Bone. Includes attached gingiva hard palate and dorsum of tongue |
|
|
Specialized mucosa |
Dorsal surface of tongue Papillae |
|
|
Salivary glands |
Develop from epithelium that lines the early oral cavity contain Serous cells- amylase that breaks down starches mucous cells - Mucin that lubricates |

