![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
230 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Toxicology |
Is the study of the interaction between chemicals and biological system to determine quantitatively the potential for chemicals to produce toxicity |
|
|
|
The dose makes the poison |
The right does differentiate poison from a remedy Phillips paracelsus |
|
|
|
Type of toxicity |
Acute single dose Short term less 5% of whole life of animal Sub chronic 20% of life span Chronic whole life toxicity Transient irritants and allergen Permanent carcinogenic mutagenic teratogenic |
|
|
|
Factors determining environmental toxicity |
Toxic agent Exposure Host |
|
|
|
Independent toxicity |
Exert their own toxicity without influencing or interference from one another Silica dust and carbon monoxide Lead and sulphur acid |
|
|
|
Additive interaction |
Compounds with similar toxicity produce a response that is equal to the sum of the effects produced by each of the individual compounds acting alone Xylene and toluene |
|
|
|
Antagonistic interaction |
The toxicity of one chemical is reduced by the exposure to another BAL and EDTA |
|
|
|
Synergistic interaction |
Two materials act together to produce toxicity greater than that produced by either material if administered separately Carbon tetrachlorate and alcohol |
|
|
|
Potentiating interaction |
Where one substance does not have a toxic effect on a certain organ but when combined with exposure to another chemical it makes the latter much more toxic Isopronalol and carbon tetrachloride |
|
|
|
Interaction between chemicals |
Independent Additive Antagonistic Potential Synergistic |
|
|
|
Body burden |
The amount of substance that persist in the body |
|
|
|
Dose response |
The degree of exposure and the magnitude of the effect |
|
|
|
Threshold response |
No observed effect level- the highest dose in an experiment that did not produce and effect Lowest observed effect level the lowest point in an experiment that produced an effect |
|
|
|
Threshold response |
No observed effect level- the highest dose in an experiment that did not produce and effect Lowest observed effect level the lowest point in an experiment that produced an effect |
|
|
|
Hypersensitivity |
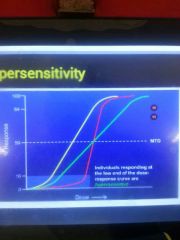
|
|
|
|
Resistant individual |
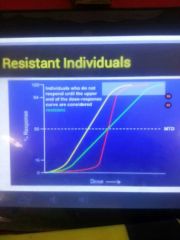
|
|
|
|
LD50 |
The dose of chemical needed to produce death to 50 percent of the test population when administered orally or dermally |
|
|
|
LC |
The dose of chemical needed to produce death to 50 percent of the test population when administered by inhalation |
|
|
|
Risk management |
The process of weighing policy alternatives and selecting the most appropriate regulatory action integrating the results of risk assessment with engineering data and with social economic and political concerns to reach a decision |
|
|
|
Classification of airborne contaminants |
Physical classification Physiological Other |
|
|
|
Physical classification of airborne contaminants |
Gases Vapours Dust Fumes Mist Fog- smaller than mist Smoke complex mixture of particles |
|
|
|
Troposphere |
10km Temperature decreases with height Tropopause- top of troposphere and bottom of stratosphere temperature isothermal |
|
|
|
Stratosphere |
30km Temperature increases with height at about 0 degree Stable weather Statopause- boundary between stratosphere and mesophere |
|
|
|
Composition of the atmosphere |
Nitrogen- 78% Oxygen-0.3% CO2- 20.9 |
|
|
|
Contemporary air pollution issues |
Ozone depletion Climate change Indoor environmental quality Acid rain |
|
|
|
Climate change/global warming |
Increase in the temperature on earth due to the increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere |
|
|
|
Stratosphere ozone depletion |
1)CFC released 2)CFC rise into ozone layer 3)UV release CL from CFC 4)CL converts Ozone to oxygen 5Deplete ozone 6)More UV 7)skin cancer |
|
|
|
Type of air pollution |
Primary- contaminants which enters directly in the atmosphere Seconday- contaminants that enters into the ozone due to chemical transformation |
|
|
|
Smog |
Combination of the word smoke and fog |
|
|
|
Two types of smog |
London type smog Los Angeles smog (photochemical smog) |
|
|
|
London type smog |
Burning coal leads to emissions of sulphur dioxide and dust Formed in the cold times |
|
|
|
Los Angeles smog photochemical |
Form on sunny days and is the result of emissions from traffic Nitrogen oxide |
|
|
|
Harmful effects of smog |
Burning of the Eyes Respiratory problems Shortness of breath |
|
|
|
6 common criteria for air pollutants |
Ozone nitrogen dioxide Sulphur dioxide Particulate matter Lead Carbon monoxide |
|
|
|
Ozone |
Ground level ozone is bad ozone From motor vehicles exhaust and industrial emissions |
|
|
|
Health problem caused by ozone |
Lung irritation and inflammation Wheezing coughing Difficulty breathing |
|
|
|
Control of tropospheric ozone |
Reduce NO emissions from power plants and industrial combustion sources Introducing low emission cars and trucks Use cleaner gasoline Improving vehicles inspection program |
|
|
|
Indirect release of particles |
Formed when gases from burning fuels react with sunlight and water vapor Results from fuel combusion in motor vehicles at power plants and other industrial process |
|
|
|
Heath effect of particulate |
Premature death Coughing Asthma Chronic bronchitis |
|
|
|
Carbon monoxide |
Colorless tasteless odorless Due to the incomplete combustion of carbon and its compounds Found where there is heavy traffic jam |
|
|
|
Health effects of CO |
Cardiovascular clogged arteries, congestive hearth failure CNS vision problem reduced ability to work and learn Smog formation |
|
|
|
Nitrogen oxides |
Reddish brown Colorless and odorless Formed when fuel is burned at High temperature Motor vehicles electrical utilities |
|
|
|
Health and environmental effects of NO |
Acid rain Smog Eutrophication Climate change |
|
|
|
Sulphur dioxide |
Dissolved readily in water Formed when you burn coal or extract gasoline from oil |
|
|
|
Health effects of sulphur dioxide |
Plant and water damage Acid rain respiratory effect |
|
|
|
Lead |
Leaded gasoline Metal processing Cause mental retardation |
|
|
|
Health effects of lead |
Organ damage bones kidney liver brain heart and lungs Affect brain and nerves seizures mental retardation Affects plants and animals slowdown vegetative growth |
|
|
|
Toxic air pollution |
Cancer Damage to immune system Neurological reproductive |
|
|
|
Indoor air quality |
Refers to the quality of a building environment in relation to the health and wellbeing of those who occupy space within it |
|
|
|
Mainstream smoke |
Exhale smoke after taking a puff on a lit cigarette |
|
|
|
Secondhand smoke |
Combination of Smoke from burning tobacco and smoke exhaled by a cigarette smoker |
|
|
|
Sidestream smoke |
Smoke that goes directly in the air from a burning cigar More toxic than mainstream smoke |
|
|
|
Weather |
Shirt p eriode of time Hour Day Season It is what you get |
|
|
|
Climate |
Longe p eriode of time What you expect |
|
|
|
Climate change |
The change in the state of the climate that can be identified |
|
|
|
Observation of climate change |
Increase sea level Melting of snow and ice Increase in global average air and ocean temperature |
|
|
|
Radiative forcing |
Change in earth energy balance between incoming solar radiation energy and outgoing thermal IR emission energy |
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide |
Most important green house gas Responsible for increase in radiative forcing |
|
|
|
Methane |
Second most important greenhouse gas |
|
|
|
Nitrous oxide |
Emitted by both natural and man made sources Destroy stratosphere ozone which protects use from harmful UV rays of the sun |
|
|
|
Contributor to carbon footprint |
Cereals Meat and vegatable |
|
|
|
The greenhouse effect |
Due to greenhouse gases trapping the suns heat and keeping ot close to the earth |
|
|
|
Fatal occupational injury rates country |
Latin America and the Caribbean |
|
|
|
Primary occupational disease |
Hearing loss Acute pesticide and metal poisoning Skin disease Respiratory disease |
|
|
|
Definition of OH |
Promoting and mentainace Prevention Protection of workings Placing and maintenance Adaptation of work to man |
|
|
|
Hippocrates |
Discovered lead poisoning in miners |
|
|
|
Pliny the elder |
Describe a bladder derived mask used to control dust and lead fumes |
|
|
|
Bernardino ramazini |
Recognize as the father of occupational medicine Of what trade are you |
|
|
|
Alice Hamilton |
Introduce the practice of industrial hygiene in the USA |
|
|
|
Physical classification |
Based on the form of the substance |
|
|
|
Physiological classification |
Based on the adverse effect of the substance |
|
|
|
Threshold limit value average |
The time weight average concentration for a normal 8 hour workday |
|
|
|
TLV short term |
The concentration to which workers are exposed for a short periods of time 15 minutes |
|
|
|
TLV ceiling |
The concentration to which the worker is not exceeding |
|
|
|
Ionizing radiation |
Electromagnetic radiation capable of producing ions by interacting with matter |
|
|
|
Types of ionizing radiation |
Alpha particles Gamma particles Beta particles Neutrons X radiation |
|
|
|
Alpha radiation |
Originate from the nucleus of a radioactive atom Travel short distance Stop by dead skin paper film of water |
|
|
|
Beta particles |
Electrically charged particle ejected from the nuclei of radioactive atoms Negative electrical charge of 1 Can Penetrate the human skin |
|
|
|
Neutrons |
Have no electrical charge Have long or short ranges in air depending on their kinetic energy |
|
|
|
Neutrons |
Have no electrical charge Have long or short ranges in air depending on their kinetic energy |
|
|
|
Gamma radiation |
Similar to x radiation excrpt it originate from the nucleus of a radioactive atom Can Penetrate deep tissues |
|
|
|
X radiation |
Produce from free electrons or orbital electrons Machine produce Extent of penetration depend on wavelength |
|
|
|
X radiation |
Produce from free electrons or orbital electrons Machine produce Extent of penetration depend on wavelength |
|
|
|
Half value layer |
The thickness of a specific substance that when introduced into the path of a given beam of radiation reduces the value of the radiation quality by one half |
|
|
|
Low sensitivity |
Mature blood cells Muscle cells Ganglion cells Mature connective tissue |
|
|
|
High sensitivity |
Gastric mucosa Mucus membran Esophageal epithelium Urinary bladder epithelium |
|
|
|
Monitoring radiation exposure |
Ionizing chamber Geiger Muller counter Personal monitors: film badges Thermoluminescence detectors Pocket diameters |
|
|
|
Non ionizing radiation |
UV radiation Radio wave microwave Infrared Visible lights Laser radiation |
|
|
|
Bio safety levels |
They were developed for use in protection against living microorganisms that have the potential to cause disease in healthy adults |
|
|
|
Controls/exposure barriers |
Engineering control Administrative controls Good work practicing and good house keeping Personal protective equipment |
|
|
|
Administrative controls |
Worker education and training Worker rotation Equipment maintenance |
|
|
|
Routine and specific infection control precautions |
Standard precautions Contact percaustion- gloves apron and gown Droplet percaustion- medical mask Airborne percaustion- respirator N95 |
|
|
|
Primordial prevention |
Banning smoking Outlawing alcohol |
|
|
|
Primary prevention |
Vaccination Cessation of smoking Adding fluoride to water |
|
|
|
Secondary prevention |
Screening Blood sugar test |
|
|
|
Teritary prevention |
Rehabilitation |
|
|
|
Environmental exposure history |
I- investigate potential exposure P- present work R- residence E- environmental concerns P- past work A- activities R- referrals and resources E- educate |
|
|
|
Del quervain's tendinitis |
Inflammation of the tendon swollen Meat packing manufacturing |
|
|
|
Respiratory condition |
Asthma Bronchitis Interstitial fibrosis Hypersensitivity pneumonia Upper airway irritation |
|
|
|
Neurological conditions |
Chronic encephalitis Peripheral polyneuropathy Hearing loss |
|
|
|
Radon |
Natural occurring radioactive substance |
|
|
|
Characteristics of good air |
Temperature 23-26 degree Celsius Humidity 30-65 Ventilation 20 cubic ft/person |
|
|
|
Ventilation rate |
Smoking lounge 60 |
|
|
|
Parasitism |
One organism benefit and harm to the other |
|
|
|
What is a protozoan |
Single celled animal |
|
|
|
Complication of malaria |
Anaemia Cerebral malaria Blackwater fever Tropical splenomegaly syndrome |
|
|
|
Malaria treatment |
Chloroquine P.vivax resistance to PNG and Indonesia |
|
|
|
Toxoplasmosis |
Obligate intracellular circadian Mouse sheep cattle goats Opportunistic in AIDs |
|
|
|
Sources of infection toxoplasmosis |
Ingestion of oocytes Ingestion of tissue cysts (uncooked meat) Transplacental Laboratory cultures Blood transfusion Organ transplantation |
|
|
|
Congenital toxoplasmosis |
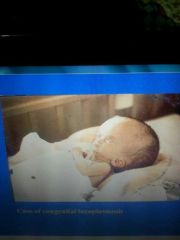
Sever Complete recovery in few cases Encephalomyelitis- cerebral calcification |
|
|
|
Diagnosis of toxoplasmisis |
IgG crosses placenta Detect igG and IgM in serum Sabin-feldman dye test |
|
|
|
Treatment of toxoplasmosis |
Pyremethamine Sulpfanomides |
|
|
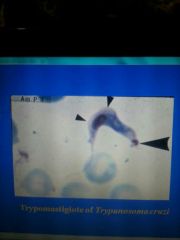
Trypomastigotes c s or u shape |

Chages disease Kissing bug Invade host cells Differentiate into intracellular amastigotes Amastigoites X differentiate into trypomastugoite |
|
|
|
Treatment of chagas disease |
Nifurtimox Benzinidazole- alternative |
|
|
|
Disaster |
Natural or manmade caused events which have a negative impact on people |
|
|
|
Hazard |
Is the potential of a natural or man-made even to have a negative impact on ones life |
|
|
|
Vulnerability |
The potential for a structure or content to fail once exposed to an damaging natural phenomena |
|
|
|
Structural element |
The portion of a building that supports it Eg. Columns, beams, floor or roof sheeting |
|
|
|
Seven steps to earthquake safety |
1)Secure 2)Make a plan 3)Make a kit 4)Is your place safe 5)Drop cover up and hold on 6)Check ot out 7)Communicate and replace |
|
|
|
What does a hurricane need |
1)Warm ocean water to provide energy to the hurricane 2)Wind come together and forced upwards 3) wind flow outward above the storm allowing the air below to rise 4)humid air rises making the cloud if the hurricane 5)Wind steer it as it grow |
|
|
|
Stages of disaster management |
Prevention Mitigation Preparedness Alert Response/rehabilitation Reconstruction |
|
|
|
Mitigation |
Reduce vulnerability of the system |
|
|
|
Infection and Dead bodies after a disaster |
Dead bodies are not epidemic after natural disasters Sickness do not survive beyond 48hrs |
|
|
|
Disposal of bodies |
Burial is most practical as it preserves forensic evidence Cremation destroy evidence Large amount of fuel need |
|
|
|
Eosinophilic meningitis |
Angiostrongylus cantonensis |
|
|
|
Rapid testing eg OptIMAl |

Use to test for malaria Dispense 30 nanoliter of buffer into a sample well. Add 10nanoliter of whole blood and mix well for 60s Add OptIMAL test strip Wash the strip with buffer |
|
|
|
Test for anigostrongylus cantonensis |
Western blot |
|
|
|
Angiostrongylus cantonensis |

Rat lungworm Smail Most common cause for esophillic meningitis L3
|
|
|
|
Cutaneous larva Migans |
Ancylostoma braziliensis A.caninum Hookworm of dog Uncinaria sp. |
|
|
|
CLM |
Serpiginous tunnels Red itchy wounds Invasion by wander for weeks or months Treatment thiabendazole |
|
|
|
Visceral larva migrants |
Toxocara canis T.cati Asymptomatic Preschool children Treatment- diethylcarbamazine |
|
|
|
Wucheria Bancroft |
Lymphatic filariasis Vector anopheles and culex Attack lymph node |
|
|
|
Elphantiasis |
Enlargement of limb scrotum breasts vulva associated woth high levels of secondary bacterial infection Lymphatic filariasis |
|
|
|
Tapeworm |
Taenia solium Taesnia saginata |
|
|
|
Cysticercosis |
Ingested of eggs of taenia solium Skeletal muscle Epilepsy |
|
|
|
Diagnosis of tape worm |
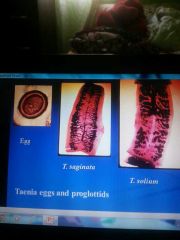
T.saginat- 15- 20 on each side T.solium- 7-13 |
|
|
|
Shistosomiasis |
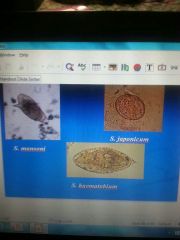
S.mansoni in the Caribbean |
|
|
|
Acute schistosmiasis |
Called katayama's fever |
|
|
|
Chronic schistosomiasis |
Portal hypertension with harmatemesis splenomegaly Pulmonary hypertension Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
Treatment for schistosomiasis |
Praziquantel |
|
|
|
Amoebiasis |

Entamoeba histolytica Cysts;- infective Trophozoit- non-infective |
|
|
|
Hepatic amoebisasis |
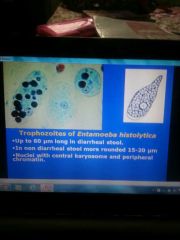
Trophozoites reaches liver via blood multiply under ulcer formation Liver tender but funcrion are normal Hepatomegaly upper abdominal pain |
|
|
|
Giardiasis |
Giardia duodenale/G.lamblia |
|
|
|
Gardiatis life cycle |
1)Trophs attach to the cells of duodenum Jennie and upper ilium 2)Feed on mucous secretions 3)Reproduction by binary fission 4)New cyst have 2 nuclei older one have 4 5)The cyst is in its infective stage 6)Fecal oral transmission common 7)Person to person transition possible |
|
|
|
Clinical giardiasis |
Few organisms penetrate the mucosa Deficient IgA hypogammaglobulinaemia Achlorhydria |
|
|
|
Giardia symptoms |
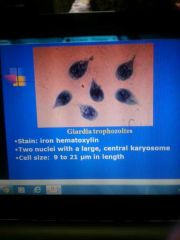
Malabsorption of fats Diarrhea Malaise Flatulence Foul smelling greasy stools Abdominal cramps, weight loss and anorexia |
|
|
|
Treatment of giardiasis |
Metronidazole |
|
|
|
Epidemiology of giardia |
The cysts are resistant to chlorine and other disinfectants Remain viable for weeks in cold water |
|
|
|
Balantidium coli |
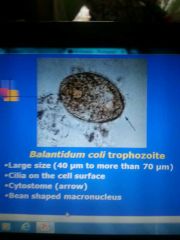
Only ciliate parasite of man Paracites of pig Perforation of appendix or large intestine death Treatment- carbasone or tetracycline diiodohydroxyquin |
|
|
|
Cryptosporidiosis |
Cryptosporidium parvum Opportunistic in AIDs major cause of waterborne outbreaks |
|
|
|
Symptoms of crypotosporidiosis |
Diarrhea Weight loss Abdominal pain Anorexia Nausea Vomiting |
|
|
|
Cyclospora cayetanensis |
Oocytes larger than cryptosporidium No auto infection |
|
|
|
Symptoms of cyclosporia |
Opportunistic in AIDs Self limited diarrheal cycle relapse |
|
|
|
Diagnosis of cyclospora |

Acid fast |
|
|
|
Treatment of cyclospora |
Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole |
|
|
|
Isospora belli |
Investe cells of the small intestine |
|
|
|
Life cycle of isospora |

Meronozoites Gamonts Gametes Zygote Oocytes 2Sporocysts 4Sporozoites |
|
|
|
Treatment for I.belli |
Sulfamethoxazole/trimerhoprim |
|
|
|
Microdporidia symptoms |
Neurological Eyes Enteric with diarrhea Dissemination |
|
|
|
Diagnosis of microsporidia |
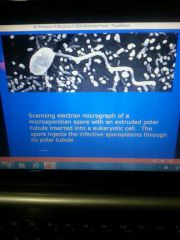
Detect spore using trichrome strains Stained with PAS Infection-spore |
|
|
|
Bioterrorism |
The deliberate release of viruses, bacteria or other germs used to cause illness or death in people animals or plants |
|
|
|
Agents of concern |
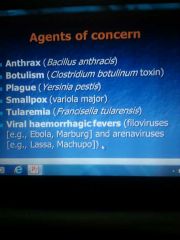
Bacillus anthracis (anthrax)- gram positive bacillus spores of the organism are airborne transmission form Yersinia pestis- gram negative bacillus cause pneumatic/bubonic disease airborne or contact transmission Francisella tularensis (tularemis) gram negative bacillus cause tularemia airborne or contact transmission
|
|
|
|
Disasters that announce themselves |
Fires Explosion |
|
|
|
Insidious disasters |
Quiet No outward sign that anything is wrong |
|
|
|
Dirty bomb |
A conventional explosive that scatters radioactive materials Radioactive potency varies depending on material used Designed to induce terror as much as personal injury |
|
|
|
Hookworm |

Males are smaller Eggs passed out in faeces First stage rhabditiform L3 penetrate skin
|
|
|
|
Hook worm cycle organ |
Venous system Lungs Trachea Pharynx Small intestine |
|
|
|
Acute hookworm disease |
Tissue necrosis within the mouth of the worm Blood loss |
|
|
|
Chronic hookworm disease |

Fe deficiency anaemia with pallor Edema of the feet and face Impaired cognitive development |
|
|
|
Strongyloidosis |
S.fulleborni in PNG and Africa |
|
|
|
Strongilody life cycle |
Similar to hookworm No parasitic males Auto infection occurs Infections long lived |
|
|
|
Treatment of S.stercoralis |
Thiabenzole- many side effect Ivermectin- no notable side effects |
|
|
|
Trichuriasis |
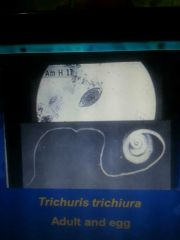
Trichuris trichiura Most prevalent |
|
|
|
Trichuris colitis |
Child presents with short statue or pica rather than chronic diarrhoea |
|
|
|
T.trichiura |

Eggs in the stool following concentration Egg bipolar Quantify |
|
|
|
Ascariasis |

Large round worm |
|
|
|
round worms symptoms |
Migrate out of anus Migrating worms may block ducts and intestine Contributing to malnutrition |
|
|
|
Loeffler's pneumonia |
Ascaris Large number of worms Allergic reaction Dyspnea Dry, productive cough Wheezing Fever Charcot-leyden crystals and larvae may be in spectrum |
|
|
|
Treatment for the use of ascaris |
Mebendazole Pyrrantel pamoate Albendazole |
|
|
|
Pinworm infection |
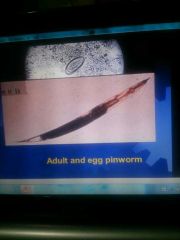
Enterobius vermicularis Infection by ingestion of eggs Eggs hatch in the small intestine |
|
|
|
Treatment of pinworm |
Pyrantel pamoate albenzole Mebendazole |
|
|
|
Characteristics of occupational disease |
Occupational disease is identical of that of non occupational disease e.g. asthma Occupational disease may occur after the termination of exposure |
|
|
|
Non observable effect level |
The highest dose in an experiment that did not produce an observable adverse effect |
|
|
|
Lowest observable effect level |
The lowest dose in an experiment that produce an observable adverse effect |
|
|
|
Very low sensitivity cells |
Spermatozoa Lens Pre mature blood vessles Ovarian follicular cells |
|
|
|
Radiative forcing |
Change in earths energy balance |
|
|
|
Herpes virus |
dsDNA 162 capsomeres IP- 2-12days |
|
|
|
Beta herpes virus |
HHV5/ CMV HHV6 HHV7 |
|
|
|
Gamma herpes virus |
HHV4/ EBV HHV8/ kaposi |
|
|
|
Exogenous infection |
Infection with the virus of a different strain |
|
|
|
Endogenous infection |
Infection of virus of the same strain |
|
|
|
HSV 1 location |
Labialis Encephalitis |
|
|
|
HSV 2 |
Genital Neonatal |
|
|
|
Acceptable indoor air quality |
Air in which there is no known contaminants |
|
|
|
Ventilation room for smoking and operating |
60 30 |
|
|
|
Characteristics of good indoor air |
Temperature- 23-26 degrees Humidity- 30-65 Ventilation- 20 cubic |
|
|
|
Generation |
The amount of material and products that enters the waste stream |
|
|
|
Materials recovery |
Removal of materials from the waste stream for recycling or composting |
|
|
|
Discarding |
Solid waste remaining after material recovery |
|
|
|
Waste management hierarchy |
Reduce Reuse Recycle Recovery (savagery) Responsible disposal |
|
|
|
Occupational health |
Promote Protect Placement Prevent Adaption of work to man |
|
|
|
Control effectiveness best |
Elimination Substitution Engineering Administrating Personal protective equipment |
|
|
|
Mitigation |
Activities that reduce the risk of a disaster |
|
|
|
Disaster manage |
Prevention Mitigation Preparation Alert Respond Rehabilitation Reconstruction |
7 |
|
|
Evacuation shadow phenomenon |
Three mile island |
|
|
|
Colour code in mass casualties |
Green and black- non acute Red and yellow- acute |
|
|
|
Toxiplasmosis life cycle |
1) Trophozoites in the cytoplasm of tge small intestine of the cat 2) trophozoites - meronts- merozoites- invade new cells - amounted 3) gamontes fuse- zygote - thick wall oocystes- passed out in faeces and contain sporozoites Ingestion of occytes with bradyzoites(tissue) 4) sporozoites enter macrophages and form teachyzoites (psuedocys) 5) teachyzoites spread via blood |
6 |
|
|
Pathogenesis of trypomastigotes |
Spread beyond lymph nodes Invade CNS- spreading of the menniges and cortex Romana's sign |
|
|
|
Sandfly |
|
|
|
|
Non opportunistic prorozoan |
Entamoeba histolytica Giardia |
|
|
|
Opportunistic protozoa |
Cyclosporidium spp Cyclospora Isospora belli |
|
|
|
Intestinal amoebiasis |
Mimic ulcerative colitis |
|
|
|
Amoebic dysentery |
Proteolytic enzymes that cause necrosis of tissue Associated with salmonella shigulla camplobacter anf E.coli |
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of amoebiasis |
1)Penetrate the muscularis mucosa into the submucosa 2) spread out in a flask shape ulcer 3) mucosa appear normal 4)erode blood vessel 5) lead to intraluminal bleeding |
|
|
|
Crypto life cycle |
Same as toxoplasmosis but stop at oocytes Single shell- auto infection Double shell- exist host |
|
|
|
Microsporidia |
Cause of AIDS infection via spore |
|
|
|
Type of hookworm |
Necator Americanus- new world Ancylostoma duodenale- old world |
|
|
|
Ancylostoma duodenle |
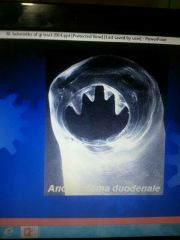
Can infect if L3 is swallowed Passed though mothers Milk |
|
|
|
Hookworm pathogenesis |
Adult worms feed on blood- iron deficiency anemia microcytic Bone morrow hyperplastic |
|
|
|
Strongyloidiosis symptoms |
Septecima Large L3 St eatorrhoea protein losing enteropathy with generalized edema Mimic peptic ulcer P neumonitis Bacterial meningitis |
|
|
|
Life cycle of trichuris |
Ingest eggs Eggs hatch in small intestine Migrate to the crisp od lieberkuhn Tunnels towards lumen Head embedded in epithelium causing anemia hypochromic |
|
|
|
Pinworm symptoms |
Mucoid discharge Migrate to vagina Become encapsulated |
|
|
|
Host of angiostrongylosis |
Shrimp/prawn Toad liver Monitor lizard |
|
|
|
Treatment for A.cantonensis |
Lumbar puncture Steriods |
|
|
|
Treatment for CLM |
Thiabendazole Albenzole Ivermectin |
|
|
|
Visceral larva migrans |
Toxocara canis Toxocara cati Present in dog stool |
|
|
|
Treatment of wuchereria bancrofti |
Diethylcarbamazine |
|
|
|
Amastigote |
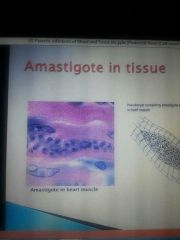
Found in tissue |
|
|
|
Trypanosoma brucei |
Sleeping sickness |
|
|
|
Crab louse |

|
|

