![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cells were named by_______ in the year _____ |
Robert Hooke 1665 |
|
|
2 major parts of the cell are |
Nucleus & cytoplasm |
|
|
The nucleus when stained with H&E will show |
Dark blue to purple masses |
|
|
The nuclear membrane stains what color |
Crisp dark blue |
|
|
Nuclear pores can only be seen with what type of microscope? |
Electron microscopy |
|
|
The nucleolus can be seen with what type of microscope |
Electron microscopy & light micrograph |
|
|
The nucleolus produces what |
RNA |
|
|
Chromatin is seen under what microscope? |
Light microscopy |
|
|
Chromatin is known as what 2 types of chromatin? |
Heterochromatin (stable) Euchromatine (non stable) |
|
|
What is shown in the photo above? |
The nucleolus |
|
|
What is shown in the photo above?the |
A row of nuclei |
|
|
The cytoplasm can be seen with what type of microscope? |
Light & electron |
|
|
Plasma membrane can be seen with what type of microscope? |
Electron microscopy |
|
|
When staining with H&E, plasma membrane is ________ seen. |
Rarely |
|
|
The 2 types of staining mechanisms are ______ & ______. |
Physical & chemical |
|
|
A Physical stain example is |
The fat stain |
|
|
Adsorption is defined as: |
Attraction for minute particles from surrounding solution. Bound by ionic, covalent, or hydrogen bonds |
|
|
3 most common types of bonds in staining |
Ionic Covalent Hydrogen |
|
|
Salt linkage is also known as |
Ionic or electrostatic bonding |
|
|
Ionic bonding occurs when |
When the dye and substance being dyed have opposite chargers causing an attraction |
|
|
Hydrogen bonding occurs when |
Covalent bonded hydrogen is attracted to strong electronegative charge. |
|
|
Covalent bonding occurs when |
Atoms share electrons |
|
|
Nuclear staining is not_______. |
Fully understood |
|
|
Nuclear staining occurs through 2 different mechanisms. |
1) staining done with basic dyes 2) staining done with dyes with metal mordants |
|
|
Nuclear Staining done with basic dyes depend on _________ |
Presence of nucleus acids (DNA & RNA) |
|
|
Nuclear staining done with metal mordants occurs only if _______ |
The nucleic acids have been removed (eg. decalcified tissue) |
|
|
Cytoplasmic staining is what type of staining? |
Non nuclear |
|
|
Cytoplasmic staining occurs when |
Proteins/charged groups are on the side chains of amino acids |
|
|
The isoelectric point (IEP) is termed when: |
The positive and negative charges are equal & there is no migration |
|
|
Substances attracting basic dyes are said to be |
Basophilic |
|
|
Substances attracting acid dyes are said to be |
Acidophilic |
|
|
Factors that affect due binding include (5): |
- pH - temp -increase in concentration - salts - fixatives |
|
|
What is the oxidation product of hematoxylin? |
Hematein, a weak anionic dye |
|
|
Ripening is defined as |
Oxidizing a dye naturally or chemically |
|
|
Define chromophore |
A group that confers the property of color |
|
|
Natural dye examples are: |
Carmine Orcein Saffron Hematoxylin |
|
|
Progressive stains are used until... |
the desired intensity of color is achieved, then stopped |
|
|
Regressive staining is when |
The tissue is over stained then decolored |
|
|
Differentiated also means |
Decolored |
|
|
3 methods of differentiating are: |
1) weak acid solutions 2)excess mordant 3) using an oxidizer |
|
|
What is the most widely used nuclear stain? |
Hematoxylin |
|
|
Harris hematoxylin includes: |
Hematoxylin Absolute ethyl alcohol Ammonium aluminum sulfate Distilled water Mercuric oxide |
|
|
The oxidized dye for hematoxylin is |
Hematein |
|
|
Metachromatic is: |
When the tissue is stained a different color than the dye |
|
|
Polychromatic is: |
A single dye solution that dyes tissue components different colors |
|
|
Ionic bonds occur when |
Positive ions attract a negative molecule |
|
|
Covalent bonds occurs when |
Shared electrons between molecules |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds occur when |
Covalent interactions between hydrogen and molecules that have a strange electronegative charge |
|
|
Euchromatin: |
Loose DNA (doesn’t stain) |
|
|
Heterochromatin |
Clumped DNA (stains well) |
|
|
Common acid auxochromes: |
Sulfonic, carbonyl, hydroxyl |
|
|
Common basic auxochromes: |
Amino group (-NH2) |
|
|
methods for evaluating readiness: |
1) wine like smell w/ deep purple-red color 2) drop into tap water & see blueish black 3) drop on filter paper and see maroon spot with purple edge (Over/under oxidation produces red/brown color) |
|
|
Basic dyes attributes: |
Positive dye ion, cationic dyes, auxochromes is amino group, chloride salt |
|
|
Acid dye attributes: |
Negative charge dye ion, anionic dyes, auxochromes are sulfonic, carboxyl & hydroxyl groups |
|
|
What fixative binds to eosin less |
Formaldehyde |
|
|
What takes in hematoxylin less |
Potassium dichromate |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Pale eosin staining is shown
Check pH levels, pH may be >5 Cut thicker sections, too thin |
|
|
Common acid auxochromes: |
Sulfonic, carbonyl, hydroxyl |
|
|
Common basic auxochromes: |
Amino group (-NH2) |
|
|
methods for evaluating readiness: |
1) wine like smell w/ deep purple-red color 2) drop into tap water & see blueish black 3) drop on filter paper and see maroon spot with purple edge (Over/under oxidation produces red/brown color) |
|
|
Basic dyes attributes: |
Positive dye ion, cationic dyes, auxochromes is amino group, chloride salt |
|
|
Acid dye attributes: |
Negative charge dye ion, anionic dyes, auxochromes are sulfonic, carboxyl & hydroxyl groups |
|
|
What fixative binds to eosin less |
Formaldehyde |
|
|
What takes in hematoxylin less |
Potassium dichromate |
|
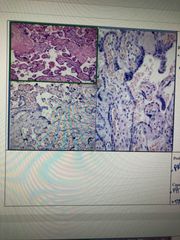
Front (Term) |
Pale eosin staining is shown
Check pH levels, pH may be >5 Cut thicker sections, too thin |

