![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
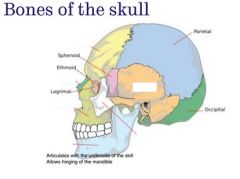
Name the following facial bones |
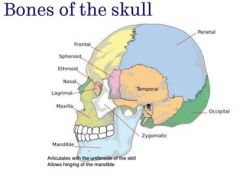
|
|
|
Describe the distribution of the facial nerve |
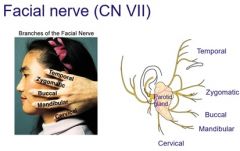
|
|
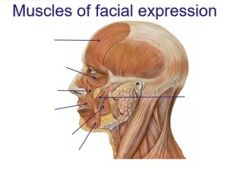
Name the following muscles of facial expression |
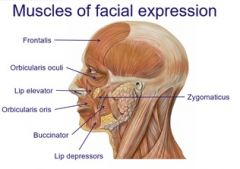
|
|
|
What are the superficial muscles of mastication? |
Masseter and Temporalis (they are involved in chewing, eating and speech but this is a secondary function) |
|
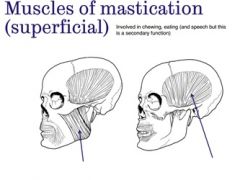
Label the superficial muscles of mastication |
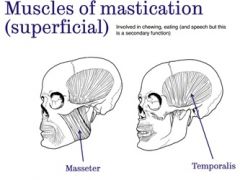
|
|
|
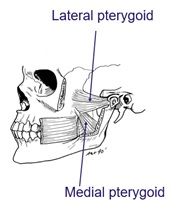
What are the deep muscles of mastication? |
Lateral pterygoid and medial pterygoid |
|
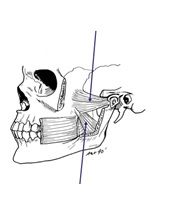
Label of the deep muscles of mastication |
|
|
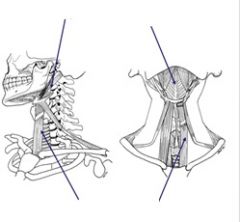
Label the following image |
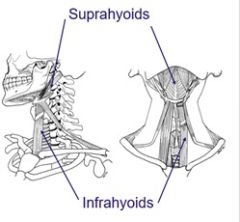
|
|
|
What are the 4 muscles of mastication? |
Masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the masseter? |
- Powerful elevator of the mandible - Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the temporalis? |
- Elevator and retractor of the mandible - Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the lateral pterygoid? |
- Protrudes mandible - Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the medial pterygoid? |
- Powerful elevator of the mandible - Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve |
|
|
What other muscles are involved in mastication? What is their function? |
- The suprahyoids and infrahyoids - They depress the mandible when the groups contract together. The hyoid bone is stabilised and the suprahyoid pulls down on the mandible. The lateral pterygoids protrude the madible. This results in forward and downward movement of the mandible |
|
|
What are the 6 muscles of facial expression? |
Orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, buccinator, lip elevators/depressors, zygomaticus and frontalis |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the orbicularis oris? |
- Closes the eyelids - Temporal (orbital, palpebral) and zygomatic (lacrimal) branches of the facial nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the orbicularis oculi? |
- Closes the mouth and puckers lips when it contracts - Buccal branch of the facial nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the buccinator? |
- Compresses cheeks against the teeth and is used in actions such as blowing - Buccal branch of the facial nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the frontalis? |
- Raises eyebrows and wrinkles forward - Temporal branch of facial nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of lip depressors/elevators? |
- Buccal branch of facial nerve |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of the zygomaticus? |
- Draws angle of mouth upward and laterally (smile) - Buccal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the facial nerve between the brainstem and middle ear? |
- All branches and functions are lost |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the facial nerve after the middle ear? |
- Taste and lacrimation are intact but facial expression is lost on that side |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the facial nerve on the face? |
- Individual muscle groups are lost depending on the branches damaged |
|
|
What is the overall likely consequence of damage to the facial nerve? |
- Weakness of muscles of facial expression. The face may "droop" on the damaged side due to the effects of gravity |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the mandibular branch of the facial nerve? |
- Lower lip paralysis - Difficulty opening mouth and distortion in smiling and grimace - Affects muscles of the lips and the production of bilabial or labiodental sounds |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the buccal branch of the facial nerve? |
- Difficulty blowing out cheeks - Affects production of bilabial or labiodental sounds |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the temporal branch of the facial nerve? |
- Unable to frown or wrinkle forehead |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the zygomatic branch of the facial nerve? |
- Affects ability to blink and lacrimation |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of damage to the trigeminal nerve? |
- If mandibular branch is damage - there will be difficulty with articulation as it is responsible for movement of the lower jaw |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of unilateral damage to the trigeminal nerve? |
- Weakness of paralysis in jaw/velar muscles on the same side as damage. - The jaw might deviate towards affected side when open |
|
|
What is the likely consequence of bilateral damage to the trigeminal nerve? |
- Most people cannot raise their jaw sufficiently to produce most consonant and vowel phonemes, especially those requiring bilablia, linguadental and linguapalatal contact - Rate of speech is often lowed due to reduced ability to elevate the jaw |
|
|
How can the function of the facial nerve be tested? |
- Asking patients to make exaggerated facial expressions |
|
|
How can the function of the trigeminal nerve be tested? |
Sensory innervation: sharp blunt test over all divisions Motor innervation: ask patient to protrude jaw - if damage it will deviate to the injured side |
|
|
How can the function of the following muscles be tested? a) frontalis b) orbicularis oculi c) orbicularis oris d) buccinator |
a) wrinkle forehead b) screw up eyes tightly c) purse lips d) puff out cheeks |

