![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fingers
|
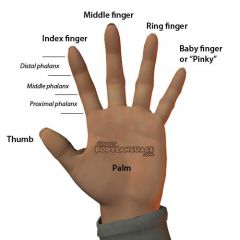
|
|
|
carpometacarpal (CMC) joints
|
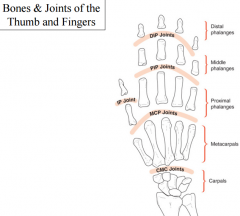
nonaxial joints which allow linear movements
(5th CMC joint is most mobile; 2nd CMC joint is least mobile) |
|
|
metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints
"knuckles" |
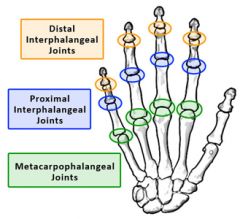
biaxial, condyloid joints that allow flexion & extension and abduction & adduction (the middle finger is the point of reference, it only abducts)
|
|
|
proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints
distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints |
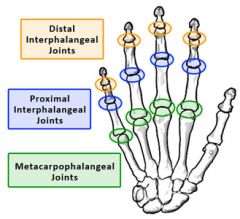
uniaxial, hinge joints that allow flexion & extension
|
|
|
thumb (pollicis) CMC joint
|
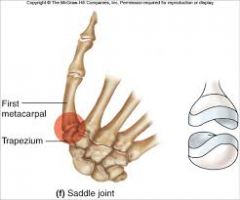
formed by the articulation of the trapezium & the 1st metacarpal (saddle-shaped)
|
|
|
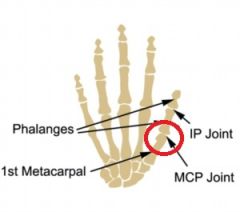
thumb (pollicis) MCP joint
|
|
|
|
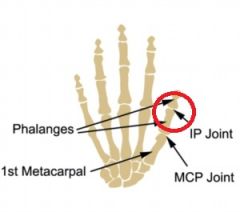
thumb (pollicis) IP joint
|
|
|
|
osteokinematics: fingers
|
|
|
|
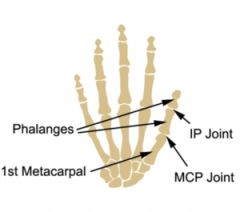
osteokinematics: the thumb
|
|
|
|
osteokinematics: CMC joint of the thumb
|
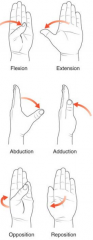
|
|
|
close-packed: finger MCP
|
full flexion
|
|
|
close-packed: finger IP
|
full extension
|
|
|
open-packed: finger MCP
|
slight flexion
|
|
|
open-packed: finger IP
|
slight flexion
|
|
|
capsular pattern: finger MCP & IP joints
|
equal limitation of flexion & extension
|
|
|
capsular pattern: thumb CMC joint
|
limitation of abduction
|
|
|
capsular pattern: thumb MCP joint
|
limitation of flexion & then extension
|
|
|
capsular pattern: thumb IP joint
|
equal limitation of flexion & extension
|
|
|
arthrokinematics: fingers
|
the CONCAVE surfaces of the finger proximal, middle, & distal phlanges glide/slide in the SAME direction as the diaphysis of the bones
|
|
|
arthrokinematics: thumb
|
the CONCAVE surfaces of the thumb proximal & distal phalanx glides/slides in the SAME direction as the diaphysis of the bone
|
|
|
arthrokinematics: CMC joint of the thumb during flexion & extension
|
the CONCAVE surface of the 1st metacarpal glides/slides in the SAME direction as the diaphysis of the bone
|
|
|
arthrokinematics: CMC joints of the thumb during abduction & adduction
|
the CONVEX surface of the 1st metacarpal glides/slides in the OPPOSITE direction as the diaphysis of the bone
|
|
|
base of the metacarpals & phalanges
|
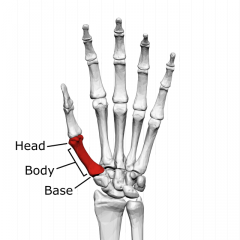
proximal end
|
|
|
head of the metacarpals & phalanges
|
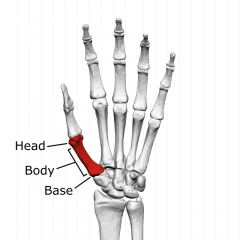
distal end
|
|
|
flexor retinaculum ligament
|
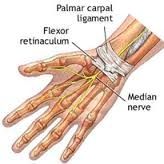
superficial to palmar radiocarpal ligament
|
|
|
palmar carpal ligament
|
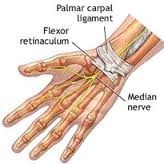
holds the flexor tendons close to the wrist
|
|
|
extensor retinaculum ligament
|
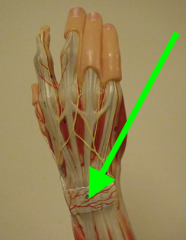
holds the extensor tendons close to the wrist
|
|
|
extensor expansion ligament (extensor hood)
|
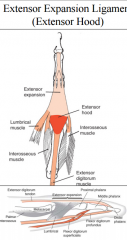
|
|
|
arches
|
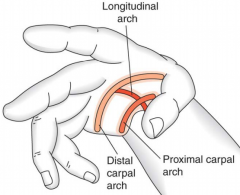
|
|
|
anatomical snuffbox
|
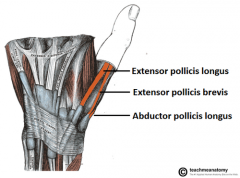
APL & EPB forms the anterior border, & the EPL forms the posterior border
|
|
|
thenar eminence
|
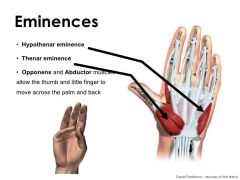
the mass on the lateral/palmar side of the palm
|
|
|
hypothenar eminence
|
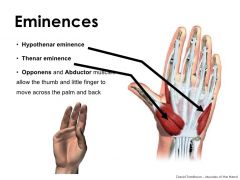
the mass on the medial/ulnar side of the palm
|
|
|
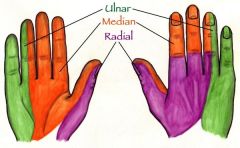
radial nerve
|
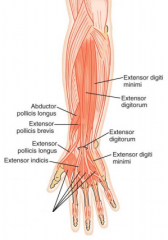
innervates muscles on the posterior surface of the hand
(ED, EI, EDM, EPL, EPB, APL) |
|
|
median nerve
|
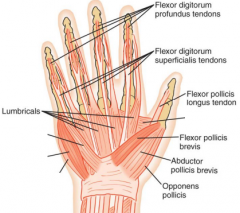
innervates muscles on the anterior, radial side of the hand
(FDS, FDP, FPL, FPB, APB, OP, 1st & 2nd lumbricales) |
|
|
ulnar nerve
|
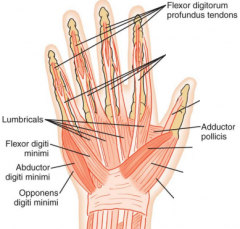
innervates muscles on the anterior, ulnar side of the hand
(FDP, AP, FDM, ADM, ODM, interossei, 3rd & 4th lumbricales) |
|
|
hand function
|
sensation is extremely important to hand function
|
|
|
functional position of the hand
|
optimal position of the wrist & hand for the hand to be most effective in terms of strength & preision
|
|
|
power grip: cylindrical
|
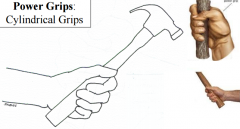
occurs when all the fingers are flexed around the object, which usually lies at a right angle to the forearm
|
|
|
power grip: spherical
|

occurs when the fingers are more spread apart
|
|
|
power grip: hook
|
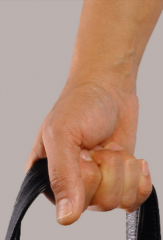
occurs when the 2nd-5th digits are flexed around an object in a hook-like manner
|
|
|
precision grips
|
provide more find movement & accuracy
|
|
|
tip
|

the most distal end of the finger
|
|
|
pad (pulp)
|
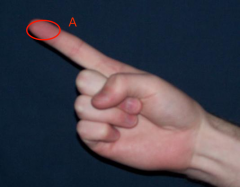
the anterior, distal end of the finger
|
|
|
precision grip: pad-to-pad
|
occurs when the pads of the fingers & thumb are brought together
|
|
|
precision grip: pinch
|

involves the thumb & one finger
|
|
|
precision grip: three-jaw chuck
|

involves the thumb & two fingers
(most common precision grip) |
|
|
precision grip: tip-to-tip (pincer)
|
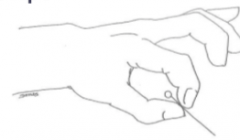
occurs when the tip of the thumb presses against the tip of another
|
|
|
precision grip: pad-to-side (lateral prehension)
|
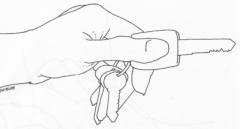
occurs when the pad of the thumb presses against the radial side of the index finger
|
|
|
precision grip: side-to-side
|

requires adduction of two fingers
|
|
|
precision grip: lumbrical (plate)
|
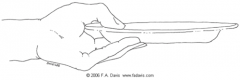
occurs when the thumb opposes the fingers when holding an object in the horizontal position
|

