![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is normal glucose metabolism? |

|
|
|
Information about Type 1 diabetes |

|
|
|
Information about Type 2 diabetes |

|
|
|
What are normal BGLs and why do we do them? |
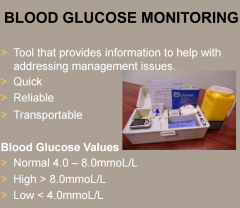
(4 to 10 for a normal level in most hospital patients). |
|
|
What is the equipment used for BGLs? |

|
|
|
What are some causes of hyperglycaemia? |
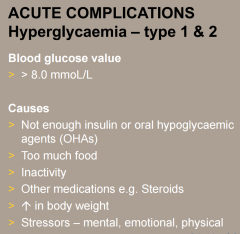
|
|
|
What are some of the symptoms of hyperglycaemia? |

|
|
|
How is hyperglycaemia managed? |

|
|
|
What happens during the formation of ketones?
|

|
|
|
What are some symptoms of ketoacidosis? |

|
|
|
What are some symptoms of hypoglycaemia? |

|
|
|
How are patients with hypoglycaemia managed? |

Between step 2, wait 15 minutes. If BGL above 4, go to step 2. |
|
|
What's included in a hypoglycaemia kit? |

|
|
|
Information about diabetic retionopathy |

|
|
|
What is glaucoma caused by? |
Occlusion of the outflow channels of the eye |
|
|
What is macular degeneration? |

|
|
|
What are cataracts? |

|
|
|
Pregnancy and diabetes |

|
|
|
Normal BGLs for a diabetic |

|

