![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
243 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Environmental health |
Determined by pbysical biological social chemical and psychological factors in the environment |
|
|
|
Six tests of a chemical's toxicity |
Acute toxicity Chronic toxicity Mutogenic Ecotoxicity Environmental fate Development and reproductive toxicity |
|
|
|
Environmental degradation |
Natures resources are being consumed more than how nature can regenerate them Humans destroy the ecosystem for development |
|
|
|
Outdoor air pollution |
Ozone Lead Carbon monoxide Sulfur dioxide Nitrogen dioxide |
|
|
|
Indoor air pollution |
Benzene from tobacco Formaldehyde in carpets and building materials |
|
|
|
Biological hazards |
Infectious/parasites > 50% Vectors 25% |
|
|
|
Ecosystem |
The interaction of biotic and abiotic factors |
|
|
|
Food chain |
Illustration of energy flow in a ecosystem |
|
|
|
Sustainable development |
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generation to meet their own needs |
|
|
|
Health promoting school |
School constantly strengthening it capacity as a health setting for leaving learning and working |
|
|
|
Sanitary and excreted disposal facility |
35-40 girls- 1 WC/toilet with partition 30-40 boy- I WC with 1 urinal 30 STudents - one had washing basin Drinking fountain 75 students |
|
|
|
Outdoor play area |
No sharp objects Enclosed protective surface |
|
|
|
Qualified staff |
Certified in first aid Background check Demonstrate respect for each child |
|
|
|
Health in prison |
Breeding ground for communicable diseases Worsen prisoners mental health Prisoner return to there community 1WC- 8inmate 1 shower- 15 inmates |
|
|
|
Major health concern in prison |
Drugs Mental Sexual Overcrowding Violence Communicable disease |
|
|
|
Hospital |
Provide acute care Diagnosis and treatment |
|
|
|
Nursing home |
Provide long term care Rehabilitation |
|
|
|
Nosocomal infection |
Infection contracted at the hospital |
|
|
|
Endogenous infection |
Self contaminated auto infection |
|
|
|
Cross contaminated |
Cross infection |
|
|
|
Food borne illness |
Caused by bacteria Disturbance in the GI system Eating food contaminated with harmful bacterial or their toxins |
|
|
|
Water activity |
An index of the available moisture in food for microbial growth |
|
|
|
Food temperature |
40-140 F 4.4- 60 C Danger zone |
|
|
|
Biotechnology |
Using living organisms or components of living organisms to make products |
|
|
|
Genetically modified foods |
Resistance to disease pests cold Reduce maturation time |
|
|
|
Nutraceuticals |
A group of natural substances |
|
|
|
Food infection |
Caused by live bacteria Salmonella and shigella |
|
|
|
Food intoxication |
Caused by bacteria waste produced called toxins Staphylococcus aureus clostridium botulinum |
|
|
|
Bacteria that causes FBI |
Salmonella Shigella Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
|
Virus that causes FBI |
Norwalk Adeno Rota Hepatitis A |
|
|
|
Disease with the largest environmental factors |
Diarrhea Lower respiratory infection Other injuries Malaria |
|
|
|
Exposure pathway |
The route a substance take from its source to its end point and how people can come onto contact with it. |
|
|
|
Exposure pathway five parts |
A source of contamination An environmental media transport mechanism A point exposure A route of exposure A receptor population When all five are present its called complex exposure pathway |
|
|
|
Housing development and hazardous waste in jamaica |
Old harbour- asbestos waste site Kingston red pond (st.catherine ) lead waste |
|
|
|
Institution |
A complete property with building facilities and service having a social educational and religious purpose |
|
|
|
Recommended group size to staff ratio in DCC |
Infants -12 Toddlers 15 Two years 18 Three four five 20 School age 30 |
|
|
|
Pest |
Any organism that annoys human being compete for space and food and spread disease to humans and their animals |
|
|
|
Mechanical transmission of vectors |
Parasites neither changes or multiply the arthropod is a vehicle which transport the parasite Cockroaches and flies |
|
|
|
Prevention of nosocomial infection |
Isolation proper sanitation Equipment steralize |
|
|
|
Biological transmission |
Parasite multiple and or change |
|
|
|
Types of biological transmission |
Propagative Cyclo- developmental Cyclo-propagated |
|
|
|
Propagative |
The parasite multiply in the vector but does not change its form Eg. Yellow fever virus |
|
|
|
Cyclo-developmental |
Parasite change its form but do not multiply Eg. Filarial parasite in a vector mosquito |
|
|
|
Cyclo-propagative |
The parasite changes its form and multiply Eg. Malaria parasite |
|
|
|
Primary host |
A animal in which a parasite undergoes maturity or carry out its sexual cycle |
|
|
|
Secondary host |
An animal in which the parasite is in its larva stage or carries on asexual development |
|
|
|
Intrinsic incubation periods |
The time interval between the entrance of the parasite in the man and the appearance of the signs and symptoms of the disease |
|
|
|
Extrinsic incubation period |
Time interval for the parasite to infect someone else |
|
|
|
German and American cockroaches |
Survive 2-3 months without food 1 month without water Cockroach in the Caribbean Produce odorous secretion which can affect the flavor of food |
|
|
|
American cockroach |
800 offsprings per year Live 14-15 months Males live shorter Egg | Nyphm | Nymph | Adults |
|
|
|
German cockroach |
3500 per year Prefer kitchen and bathroom |
|
|
|
Fly life cycle |
Egg -> larva (maggot) -> pupa -> adult |
|
|
|
Fly |
Females lay 500 batches Larva 3-9mm emerge out of egg 8-20 hours in warn weather Adult live 15-25days Suck substances containing sweets and decayed substanced |
|
|
|
Mosquito |
Aedes aegypti yellow and dengue fever Anopheles albimanus malaria |
|
|
|
Anopheles |
Only female have a blood meal can transmitte malaria |
|
|
|
Lice |
Eggs called nits Egg(nits)- nymph> adults Cycle complain 21-27 days Live 35-40 days Adult lice killed in 5 minutes and egg in 10 minutes in water 125F water Feed on blood |
|
|
|
Bed bugs |

Live 6-12 months Egg-> larva-> adult Cimex lectularius |
|
|
|
Fleas |

Feed on blood Detect changes in CO hence jump when animal breath Continue to feed long after their hunger is satisfied Affects humans and animals Carry bubonic plague Egg-> larva -> cocoon-> adults |
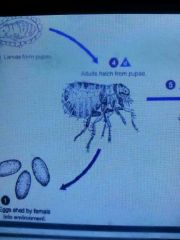
|
|
|
Rattus norvegicus |
Brown sewer Norway rat Tail shorter than head and body tail darker Color e on top Nose and muzzle blunt |
|
|
|
Rattus rattus |
Black roof rat Tail longer than body and head Same color tall nose and muzzle pointed |
|
|
|
Mus musculus |
House mouse Tail Longer than head and body combined |
|
|
|
Disease transmitted by rodents |
Virus rabies Bacteria leptospirosis |
|
|
|
Component of IPM |
Inspection/monitoring Identification Establishment implementation of two or more control measures Measurements and evaluation |
|
|
|
Symptoms of celiac disease |
T cell mediated Malabsorption |
|
|
|
Outbreak |
An unexpected unexplained increase of disease |
|
|
|
Endemic epidemic and pandemic |
Geographical area Community or small group Worldwide |
|
|
|
Sand fly |
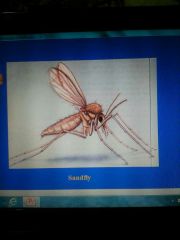
Small Related to mosquito Fly rapidly Transmitted leishmaniasis |
|
|
|
Kissing bug |
Large Nocturnal habitual Painless bit Bit and release infected faeces when a person scratches it release th infection in it Bit soft area Cause chagas disease |
|
|
|
Chagas disease |
Caused by tryponsomia crues Kissing bug Chronic organ failure and risk of death due to decrease heart function over the years |
|
|
|
Tick |
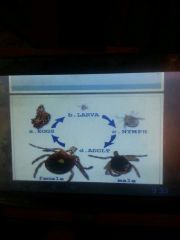
On animals Lyme disease Egg-> larva;> nymph-> adult Detect changes in CO level |
|
|
|
Lyme disease |
Borrelia bugdorferi EM Arthritis Bells palsy Caused by ticks |
|
|
|
Dracunculiasis |

Crippling disease Painful blisters after one year of infection on legs relieved by placing feet in water and larva run out 10-14 months |
|
|
|
Leishmaniasis |
Caused by sand fly Cutaneous Diffuse cutaneous Mucocutanous Visceral |
|
|
|
Black flies |

Egg-> larva-> pups -> adult River blindness Oncho Nodules Bite in the day Ivermectin
|
|
|
|
Shitosomiasis |
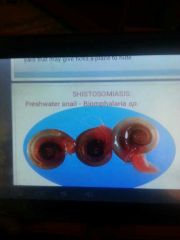
Worm egg has the infection Haematuria Bladder cancer Proziquantel |
|
|
|
Lighting in operating table |
Major - 1000 Minor - 200 |
|
|
|
Route of transmission for nosocomial infection |
Direct Indirect Airborne Vector |
|
|
|
Staff to resident ratio in nursing home |
1:15 day 1:25 night |
|
|
|
Vector |
Agent that transmit infection |
|
|
|
Transovarial transmission |
The passing of the infection from females to eggs |
|
|
|
Transstadial transmission |
The passing of infection from larva/nymph to adult |
|
|
|
Hydrologic cycle |
Evapo-transiration Condensation Precipitation infiltration Run off All continuous except precipitation |
|
|
|
Infiltration |
Water soaking through soil Confide to the root |
|
|
|
Percolation |
Deep vertical movement of water in the soil goes beyond the root |
|
|
|
Run off |
Surface soils become saturated |
|
|
|
Rainfall intensity |
The amount of rainfall occurring during a specific time |
|
|
|
Evaporation |
Heat from the sun evaporates water The water vapor move in the cloud and stay there by moving air masses |
|
|
|
Sources of water used for domestic use |
Rain water Surface water ground water Sea and ocean water |
|
|
|
Watershed |
An area where surface runoff is carried away by a single drainage system |
|
|
|
Surface water from |
Ground water Precipitation Mote heavily chlorinated can gain more THM |
|
|
|
Aquifer |
The soil that holds ground water |
|
|
|
Ground water |
Water in its zone of saturation Best source for domestic water |
|
|
|
Water table |
The upper surface of the zone of saturation |
|
|
|
Water usage country |
Asia has 60% |
|
|
|
Water stress |
When water drop below 1700 cubic meter per person |
|
|
|
Water scarcity |
Water below 1000 cubic meter per person |
|
|
|
Country not in the MDG water drinking target |
Sub Saharan Africa |
|
|
|
Water quality characteristics |
Physical Chemical Biological Radiological |
|
|
|
Portable water |
Water free from toxic chemical, pathogen odorless, palatable colorless and palatable |
|
|
|
Safe water |
Water that is free from pathogens and toxic chemicalshave have a cloud taste bad and may have a smell |
|
|
|
Water borne disease |
When u drink the water Eg cholera typhoid |
|
|
|
Water washed disease |
Due to inadequate amount of water Eg salmonella shigella |
|
|
|
Water related disease |
Communion contact with water Guinea worm schistomomiasis |
|
|
|
Water based insect vector disease |
Insects that breath in water Malaria dengue yellow fever |
|
|
|
Sanitation related disease |
Failure to dispose of stool result in direct contact Hookworm |
|
|
|
Improved drinking water |
Water from pipes |
|
|
|
Other improve drinking water |
Water from wells Porter springs and rivers |
|
|
|
Unprotected water |
Bottled water Unprotected water |
|
|
|
Water disinfection methodes |
Cholrination UV light - kill microorganisms Ozone Microiltration Boiling |
|
|
|
Bromine |
Dark reddish brown Irritates eyes nose and throat Painful burns slow healing Leave a residue unstable Clean swimming pool |
|
|
|
Iodine |
No residue Bluish black Use for medical purpose |
|
|
|
Ozone |
Bluish Toxic gas Requires a lot of energy |
|
|
|
Water treatment process |

Screening- removal of large rocks and debris Microstraining- remove small Ricks and debris Aeration- remove gas and odours Coagulation- convert non settle particles into syllable particle Flocculation same as coagulation Sedimentation - remove settable particles Softening- remove hardness Filtration - remove fine particle Absorption- remove organics and colour Fluoridation - strength tooth enamel Stabilization - prevent scaling and erosion Disinfection - remove disease causing organisms Clean water |
|
|
|
Five factors for successful chlorination |
Substance in water Concentration Contact time pH Temperature |
|
|
|
Reverse osmosis |
Movement of solvent from a region og high concentration to a region of low concentration under pressure |
|
|
|
Treatment for bottled water |
Chlorination filtration Ozone UV light Reverse osmosis |
|
|
|
Excreta |
Waste matter eliminated from the body |
|
|
|
Waste water |
Used water from house or community |
|
|
|
Black water |
Waste water from water closet and other thing |
|
|
|
Grey water |
All the other domestic waste water |
|
|
|
Type of on site disposal |
Non water carriage or conservancy Water carriage Sewage works/ small treatment plants |
|
|
|
Ventilated improved pit |
Where odour nd fly is controlled No lid over squat hole Inside dark as possible Double compartment leave airspace so the faeces can breakdown and you can reuse for life |
|
|
|
Composting toilet |
Where kitchen waste and toilet waste come together to form compost Costly Use where human excreta is used as fertilizer |
|
|
|
Non water carriage disposal |
Simple pit VIP Composting toilet Parachuting Bucket latrine Bore hole latrine |
|
|
|
Water carriage system |
Chemical toilet Pour flush toilet Septic tanks |
|
|
|
Pour flush toil |
Not used in cold areas as water will freeze Odour and flies are controlled Contrails a water trap to prevent odour of commuting back up in the bathroom |
|
|
|
Septic tank |
Water tight tank design to settle out and break down sewage solids to prevent clogging Tile field always with it |
|
|
|
Palatable water |
Unpleasant water |
|
|
|
Chlorination |
Increase Chlorine decrease the residual Keep increasing leads to the breaking point The more chlorine the more protection |
|
|
|
Chlorination products |
Trihalomethanes more in saturated water Chloroform carcinogenic |
|
|
|
Pathogens |
Ability to cause infection |
|
|
|
Inoculum |
Number of organisms present |
|
|
|
Opportunistic organisms |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
|
Hospital acquired infection |
UTI Septicemia RTI |
|
|
|
Conservancy |
Sanitation system where fecal matter is retained in a closet apparatus |
|
|
|
Cryptosporidiodis |
Chlorine resistant Get rid of by filtration Water borne Located in swimming pool |
|
|
|
Exotic disease |
Disease imported in a country eg rabies in UK |
|
|
|
Sporadic disease |
Scattered about the world |
|
|
|
Biochemical oxygen demand BOD |
It is a measure of the degree of water pollution 5 days at 20 degree Celsius |
|
|
|
Chemical oxygen demand |
It is measured in relation to industrial wastes |
|
|
|
Suspended solids |
Solid that are visible and in suspension in water |
|
|
|
Eutrophication |
Over enrichment of water with nutrients resulting in the excess growth of organisms and depletion of oxygen concentration |
|
|
|
Wastewater treatment |
Preliminary Primary secondary Tertiary |
|
|
|
Preliminary treatment |
Screening Grit chamber remove abrasive suspenders particle eg sand Comminutor shred materials not removed by screen |
|
|
|
Secondary treatment |
Sludge is produce remove pathogen Followed by chlorination Trickling filter remove pathogens but not legislates Stabilizating pond remove everything |
|
|
|
Tertiary treatment |
Removal of nutrients |
|
|
|
Measles |
Kopliks spots on buccal mucosa Respiratory distress Fever Rash ssRNA Lipid envelope |
|
|
|
Clinical features of measles |
IP- 10-14 Kopliks spot on buccal mucosa Splenomegaly appendicitis lymphodenopathty Conjunctivitis |
|
|
|
Rubella |
Toga virus Haemagglutinis ssRNA |
|
|
|
Clinical features of rubella |
IP 16-21 days Rash Mild conjunctivitis Low grade fever Sore throat |
|
|
|
Congenital defects because of rubella |
Eye defect retinopathy glaucoma cataract Heart disease patent ductous arteriol Mental retardation Sever hepatitis Bone lesion Heptosplwnmegaly |
|
|
|
Rubella shots |
15 months of age |
|
|
|
Varicella zoster virus |
Chicken pox- primary Shingles- recurrent VSV 3 DNA virus |
|
|
|
VSV clinical features |
IP 10-23 days Enanthem vesicles in mouth and palete |
|
|
|
VSV syndrome |
Scarring of skin Hypoplasia of limbs Muscle dystrophy Cataracts Vesicles in mouth |
|
|
|
HPV |
dsDNA Papilloma |
|
|
|
Ano-genital |
HPV 16 18 31 33 Associated with invasive cancer |
|
|
|
Parvovirus |
DNA Mild rash |
|
|
|
Small pox |
IP 10-14 days High fever Fatigue Delirium vomiting and diarrhoea Rash
|
|
|
|
Molluscum contagiosum |
IP 14-50 days |
|
|
|
Cohorting |
Placing a patient with the same pathogen in the same room. |
|
|
|
Special measures |
Placing patron with the same suspected diagnosis in the same area before the cause agent is lab Confirmed |
|
|
|
Engineering controls |
Methods of isolating or removing hazards from the workplace |
|
|
|
Oxidation beds |
Lotd of land Practice in jamaica cheaper |
|
|
|
Extended aeriation system |
Fit in small area Need air in the tank at all time Expensive Need a stand by generated electricity |
|
|
|
Solid waste |
Non liquid waste material other than solids in waste water |
|
|
|
Refuse |
All perishable and non perishable solid waste except human body waste |
|
|
|
Garbage |
Consist of animal and vegetable waste |
|
|
|
Swill |
Special type of garbage that is useable or have some type of value |
|
|
|
Rubbish |
Combustible and non combustan me waste |
|
|
|
Composting |
Biological degradation or breakdown of organic matter under aerobic or anaerobic condition |
|
|
|
Types of landfill |
Uncontrolled type A Controlled type B Isolated/secure type C |
|
|
|
Hyperendemic |
Disease is of high prevalence and affect all age group |
|
|
|
Holoendemic |
Disease is prevelance but affect younger children |
|
|
|
Herpesvirus structure |
Spherical Linear dsDNA Glycoprotein spikes amorphous layer of protein 162 campsomers |
|
|
|
Alpha herpes virus |
HHV 1 HHV 2 HHV 3- VZV |
|
|
|
Gamma herpes |
HHV 4 EBV HHV 8 Kapossi sarcoma |
|
|
|
Beta herpes |
HHV 5 CMV HHV 6 HHV 7 |
|
|
|
HSV |
IP 2-12 days HSV 1 close contact oral secretion perinatal oral HSV 2 genital secreation perinatal close contact genital neonate IgG |
|
|
|
Types of infection for 1 HSV |
Primary first infection with either HSV 1 or 2 with no pre existing antibodies to either type Non primary first infection with HSV 1 or 2 with pre existing antibodies to either type |
|
|
|
Type of infection 2 HSV |
Endogenous infection of the same strain of virus at a different site Exogenous infection of different strain of virus |
|
|
|
EBV |
Gamma HHV 4 Transmission Oral secretion kissing disease Perinatal Direct contact Blood transfusion Organ transplantation IgM and IgG |
|
|
|
EBV symptoms |
Fatigue Fever Sore throat Swollen lymph glands Oral hairy leukoplakia HIV Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Chinese Burkitts lymphoma blacks |
|
|
|
CMV |
Beta HHV 5 Mononucleosis Sore throat headache Guillain barre syndrome Pneumoniae Myocardium Encephalitis Retinitis Icteric hepatitis IgM and IgG |
|
|
|
HSV stages of infection |
1- acute mucocutanous infection 2- spread to local sensory nerve ending 3- period of latency 4- reactivation of the virus and distal spread 5- recurrent cutaneous infection |
|
|
|
Important fleas |
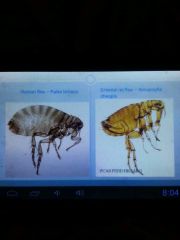
Human flea- pulex irritans Oriental rat flea- xenopsylla cheopis |
|
|
|
Mosquito |
Anopheles albimanus- malaria Aedes aegypi- yellow fever and dengue Aedes taenioehynchus- serious biting pest Culex quinquefasciatus- evenings night biting pest of west Nile fever Culex negripalpus- encephalitis |
|
|
|
Anapheles |
Malaria Single egg with floats Air tube absent Rest parallel to water surface More body touches surface Palps long Angled |
|
|
|
Aedes |
Yellow fever dengue Single eggs on dry surface Air tube present Rest at an angle below water surface Less body touches surface Palps short Horizontal |
|
|
|
Culex |
Floating egg raft Water tube present Rest at an angle below water surface Less of the body touches surface Palps short Horizontal |
|
|
|
Malaria |
Eradicated from jamaica in the early 60 Caused by plasmodium parasites Plasmofium falciparum is the most deadly Spread by anopheles Bite at night Egg-》 larva-》pupa-》adult The first three stages complete in 5-14days Last stage is when it acts as a malaria vector last 1-2days |
|
|
|
Malaria clinical features |
IP 10-15 days Fever Headache Chills Vomiting |
|
|
|
Relative risk |
The measure of the association of exposure and illness The ratio of the attack rate for ill persons who are exposed to the ratio of the attack rate for ill persons who were not exposed (A/a+b)/(c/c+d) |
|
|
|
Examples of arthropod |

|
|
|
|
Diseases caused hemorrhagic fever |
Dengue Yellow fever |
|
|
|
Antiviral encephalitides |
Eastern equine encephalitis Western equine encephalitis St.Louis encephalitis La Crosse encephalitis Ticks |
|
|
|
Toga virus |
EEE WEE VEE chik |
|
|
|
Bunyaviruses |
Sand fly Rift valley fever |
|
|
|
Flaviviruses |
Yellow fever Dengue WNV |
|
|
|
Chikungunya |
Toga virus Aedes mosquito RNA virus Alpha virus Daytime biter on ankle 2-12 days |
|
|
|
Symptom of chick V |
Fever chills Headache nausea vomiting abdominal pain Joint pain with or without swelling Rash No hemorrhagic or shock syndrom High fever flu like symptoms headache |
|
|
|
Pregnancy and ChickV |
Can pass to fetus 3-4 months of gestation IgG develops in 2 weeks after chick V No miscarriage |
|
|
|
Dengue virus |
Flavivirus RNA Aedes mosquito Human mosquitoes human cycle Virus replicate in salivary glands |
|
|
|
Four dengue clinical feature |
Undifferentiated fever Dengue fever Dengue hemorrhagic fever Dengue stroke syndrome |
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic manifestation of dengue |
Skin bleeding Gingival bleeding Nasal bleeding Everything woth bleeding Fever followed by hypothermia Red spots |
|
|
|
Dengue shock syndrome |
Circulatory failure Rapid and weak pulse Narrow pulse pressure Hypotension Cold clammy skin and altered mental status |
|
|
|
Yellow fever |
Flavivirus Aedes aegypi West africa South africa Jungle yellow fever involve forest mosquito |
|
|
|
Symptoms of yellow fever |
Chills fever headache Myalgias GI complaints Bradycardia Jaundice Heamorrhage Frank YF develop hypotension Available vaccine |
|
|
|
West nile virus |
Flavivrus ssRNA Bird reservoir host Culex species 2-14 days |
|
|
|
Syndrome of west nile |
Fever Seizures Weakness Change in mental status Optic neurosis Encephalitis Can have meningitis without encephalitis |
|
|
|
Japanese encephalitis |
Culex mosquito Mosquito birds and pigs Encephalitis Vaccine available |
|
|
|
Acyclovir MOA |
1-It is phosphorylated by virus specific thymidine kinase to ACV-MP 2-cellular kinases subsequently phosphorylate ACV-DP then ACV-TO 3-ACV-TP competes with natural substrate dGTP for viral DNA polymerase 4- ACV-TP becomes incorporated into newly synthesized vDNA chain termination |
|
|
|
Lighting in classroom and auditorium |
50 10 |
|
|
|
Residual chlorine value |
0.2-0.5 mg/l |
|
|
|
Conservancy |
Sanitation system in which fecal matter is retained in a closet appertus rather than being water carried |
|
|
|
Simple pit latrin |
Cheap When water is not available Source for fly and odors |
|
|
|
Ventilated improved pit |
Odor and fly is controlled No lid on squat hole Inside dark Double compartment |
|
|
|
Compositing toilet |
Suitable where human excreta is useful for fertilization Costly Unhealthy |
|
|
|
Septic tank |
Water tight tank designed to settle out and break down sewage solids to prevent clogging |
|
|
|
Non water carrige conservancy |
Simple pits VIP Composting toilet Parachuting |
|
|
|
Water-carriage |
Septic tank Chemical toilet Pour flush tiolet |
|
|
|
Eutrophication |
The over enrichment of nutrients in the water which leads to rapid growth of the organism and decrease in oxygen concentration |
|
|
|
Grit chamber |
Remove abrasive suspended particles such as sand |
|
|
|
Comminutor |
Shred particls not removed by sand |
|
|
|
Pre liminary treatment for water |
Screening Grit chamber Comminutor |
|
|
|
Secondary treatment for water |
Oxidation/stabilization ponds Trickling filters Followed by chlorination |
|
|
|
Sludge in oxidation system |
Remove bacteria but not lepsospirosis |
|
|
|
Stabilization pond |
Prevent all virus bacteria and leptospirosis |
|
|
|
Tertiary treatment for water |
Remove nutrients |
|
|
|
Measle |
IP 10-14days Koplike spot Conjunctivitis cough and coryza Use giemsa stained smears |
|
|
|
Rubella |
16-21days IP ENCEPHALITIS Patent ductous arteriol |
|
|
|
Varicella zoster virus |
Cause chicken pox and shingles IP- 10-23DAY |
|
|
|
EBV |
Infective mononucleosis Sore throat Fever Lymphodenopaty Manifestation- nasopharyngeal carcinoma Oral haity leukocyte Burkitts lymphoma |
|
|
|
Aeration system |
Expensive Secondary water treatment Require lots of energy |
|
|
|
Direct detection EBV diagnosis |
PCR EM electron microscope IEM |
|
|
|
CMV symptoms |
Encephalitis Retinitis hepatitis M yocarditis Pneumonia Gillian Barre syndrome |
|
|
|
Treatment for EBV |
Acyclovir |
|
|
|
Treatment for CMV |
Fomivirisen Foscarnet |
|
|
|
Solid waste |
Non liquid waste material other than solid in water |
|
|
|
Swill |
Garbage with value and can be re used |
|
|
|
Garbage |
Perishable items such as vegetable and meat |
|
|
|
Rubbish |
Non perishable items plastic |
|
|
|
Leachate |
Any liquid when passing through matter extract soluble and suspended solids |
|

