![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
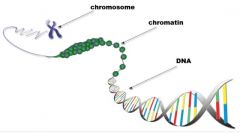
Chromatin |
The material the composes everything except bacteria. Protein RNA DNA |
Hair chromatins are in humans |
|

Mutation |
The changing of the structure of a gene, results in a different form that may be passed down to next generation |
Wolverine many people have mutstions |
|
|
Mutagen |
An agent that cause genetic mutation |
Radiation radiation is a mutagen |
|
|
Excision repair |
A cellular mechanism that repairs damaged DNA |
BER excision repair occurs in humans |
|
|
Sister chromatids |
Either of the two copies that is formed by the copying of a chromosome |
Duplicated chromosome humans have sister chromatids |
|
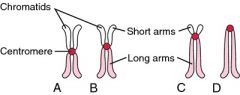
Centromere |
The point on a chromosome by which it's attached to a spindle fiber in cell division |
Chromosome centromeres are on chromosomes |
|
|
Aneuploid |
Having certain genes or chromosome regions present in extra or fewer copies than usual |
Genes aneuploids are unusual numbers |
|
|
Prophase |
The first stage of cell division, the chromosome becomes visible as paired chromatids |
Cells prophase is the first step |
|
|
Metaphase |
The second stage of cell division, chromosome becomes attached to spindle fibers |
Cells metaphase is the second step |
|
|
Anaphase |
The stage of meiotic or mitotic cell division chromosomes move away from one another |
Cells anaphase involves cells |
|
|
Telophase |
The last phase of cell division chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cells, two nuclei formed |
Cells telophase is the last stage |
|
|
(Mitotic) spindle (fibers) |
The macromolecular machine that separates chromosomes into two daughter cells in mitosis |
Chromosome Spindle involved mitosis |
|
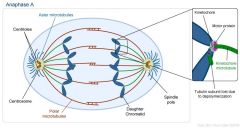
Spindle poles |
Microtubule organizing center in yeast cells similar to the centrosome |
Cells spindle poles are organizers |
|
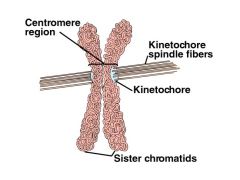
Kinetochore |
The point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber in cell division |
Cells kinetochore is on a chromosome |
|
|
Cyclins |
All proteins associated with the cycle of cell division, thought to initiate processes of mitosis |
Proteins cyclins involved cell division. |
|
|
Kinases |
An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specific molecule |
Protein kinases involve ATP |
|
Cell-cycle arrest |
The stopping of the cell cycle, termination |
Cells cell-cycle arrest isn't good |
|
|
Cancer |
The disease caused by the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in apart of the body |
Cells cancer is very bad |
|
|
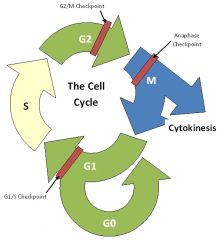
Cell cycle |
An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell |
Yeast
Produces two new identical organisms
|
|
|
Mitosis |
The process of distributing a copy of each chromosome to each new cell during eukaryotic cell division |
Daughter cells
Sorting and distributing the chromosomes |
|
|
Interphase |
The period between divisions |
During interphase, the individual chromosomes aren't visible in the nucleus
Growth and DNA synthesis |
|
|
G1/G0 |
The first phase of the cell cycle |
Prereplication
When cells stop dividing in G1, they enter G0 |
|
|
S |
DNA synthesis |
Replicator
Phase of the cell cycle |
|
|
G2 |
Synthesizes specific types of RNA and proteins |
Premitosis
Prepares cell for mitosis |
|
|
M |
A series of events that ensures each daughter cell receives one copy of each chromosome |
Mitosis
Chromosomes are condensed and visible through a microscope |
|
|
Restriction point |
Once this point is passed the cell must go through the whole cell cycle |
Point of no return
Occurs in G1, G0 |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the whole cell |
Cytoplasm divided
After cytokinesis each cell enters G1 |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the whole cell |
Cytoplasm divided
After cytokinesis each cell enters G1 |
|
|
Daughter cell |
New created cell off of another cell |
Parent having a child (daughter)
Mitosis provides each daughter cell with a replicant set of chromosomes as the parent cell |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the whole cell |
Cytoplasm divided
After cytokinesis each cell enters G1 |
|
|
Daughter cell |
New created cell off of another cell |
Parent having a child (daughter)
Mitosis provides each daughter cell with a replicant set of chromosomes as the parent cell |
|
|
Nucleotide base pairing |
The structure of DNA |
A+T, G+C
This depends in how many hydrogen bonds each nitrogen base can form with it's counterpart |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
Holds together the strands of DNA in their double helix |
A+T, G+C
The two strands have opposite orientations |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
Holds together the strands of DNA in their double helix |
A+T, G+C
The two strands have opposite orientations |
|
|
Antiparallel |
The arrangement of DNA structure |
A divided highway
They are parallel but run in opposite directions |
|
|
DNA polymerase |
The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the new DNA strands |
The equivilant of copying from an older model
Uses one of the original strands as a template |
|
|
Semiconservative |
Replaces the old DNA double helix with two new ones |
Half conservative
One strand of old DNA and one strand of new DNA |
|
|
Chromosome |
A tightly condensed structure wrapped by proteins |
Extra chromosomes cause downsyndrome
Shape is visible only at mitosis |
|
|
Histone |
Family of basic proteins doing DNA work in the nucleus |
Forms nucleosomes
Nuclear DNA is highly condensed and wrapped around histones |

