![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom |
The smallest possible unit of measurement while still being n element |
There are more than a trillion atoms in this little space. |
|
|
Molecule |
An element built up of one or more atoms |
The molecule was very small. hydrogen and oxygen |
|
|
Element |
Many different ones make up the earth and everything in it. |
Copper there are many different elements on earth. |
|
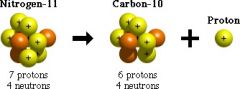
Proton |
Positively charged |
Protons have a positive charge. in every element |
|
|
Electron |
Negative charge |
The electrons have a negative charge. |
|
|
Neutron |
Neutral |
The neutrons have no charge |
|
|
Ion |
Loss of electrons |
The element lost an electron so it's now an ion. |
|
|
Isotope |
More than two forms of an element |
That is an isotope |
|
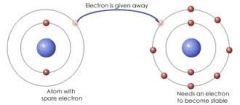
Ionic bond |
A bond of a metal and a nonmetal |
A ionic bond would be a metal element and a nonmetal element put together. |
|
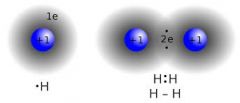
Covalent bond |
A bond between two nonmetals |
Carbon dioxide is a covalent bond. |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |
A covalent bond where atoms are shared unequally |
Polar covalent bonds aren't as common as most bonds. |
|
|
Law of conservation of matter |
Mass of matter must remain the same. |
The law of conservation of matter is very important. |
|
|
Activation energy |
Minimum energy used to make a chemical reaction. |
Some chemicals have a high activation energy. |
|
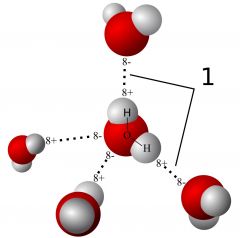
Hydrogen bond |
A bond containing hydrogen |
Water is an example of the result of a hydrogen bond |
|
|
Ph scale |
Measures how acidic neutral or basic a substance is |
Chemists need ph scales. |
|
|
Acid |
A substance that can dissolve even metal. |
The acid was deadly. |
|
|
Base |
A substance used to help start chemical reactions. |
Base was used in every experiment. |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Molecules contain carbon |
Some of those groups are organic compounds. |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Large molecules |
Those are the biggest macromolecules I've seen. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Sugars in food that give you energy. |
The bread and pasta was full of carbohydrates. |
|
|
Lipids |
Fats |
There was too many lipids in the food. |
|
|
Proteins |
Energy in food needed to build muscle |
You could tell she had a lot of protein |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Includes DNA and rna |
The lab was full of nucleic acids. |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
A basic unit of carbohydrates |
There were 1000 monosaccharides |
|
|
Fatty acids and glycerol |
Made to make explosions |
The chemist had to use fatty acids and glycerol. |
|
|
Amino acids |
Organic compounds |
There were many amino acids in the room. |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Organic molecules |
Nucleotides are very important. |
|
|
Disaccharide |
Sugars with two monosaccharides |
There were too many disaccharides |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
Long segments of monosaccharides |
He didn't need polysaccharide |
|
|
Polypeptide |
Segments of amino acids |
The polypeptide wasn't enough |
|
|
Peptide bond |
Covalent chemical bond |
The chemist studied peptide bonds |
|

DNA |
Genetic instructions |
He studied dna |
|
|
Gene |
Personality trait |
His parents gave him good genes |

