![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell theory |
The idea that cells are the basic units of life |
Biologists contributed data and ideas that led to the cell theory |
|
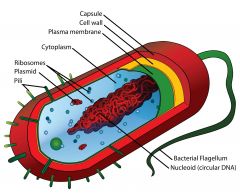
Prokaryotes |
The bacteria, simplest living cells |
They are everywhere. |
|
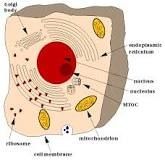
Eukaryotes |
It is larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
These more complicated cells can form multicellular organisms. |
|
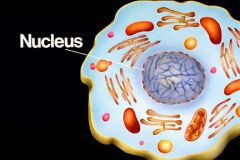
Nucleus |
Contains the DNA of eukaryotic cells. |
Most obvious difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. |
|
Chromosome |
any of several threadlike bodies, consisting of chromatin |
Chromosome have a several thread like bodies |
|
|
Nucleoid |
The chromosome is attached to the plasma membrane in an area of the cell known as the nuclear region. |
Nucleoid attached to the plasma membrane |
|
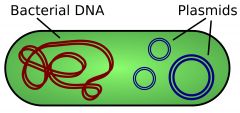
Plasmids |
It contains a few genes that help bacteria survive under specific conditions |
Plasmid contains a few genes |
|
|
Flagella |
Long, whiplike extensions made of protein that rotate like propellers |
Singular: fragellum |
|
|
Cell/ plasma membrane |
the semipermeable membrane enclosing the cytoplasm of a cell.
|
Enclosing the cytoplasm of a cell |
|
|
Cell wall |
Composed of stiff fibers of cellulose and other carbon compounds |
Cell wall - stiff fibers |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Small bodies composed of RNA and protein |
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
|
Cytosol, organelles, cytoskeleton, and various particles |
|
|
Cytosol |
Protein rich, semifluid material in the cell |
Surrounds and bathes the organelles |
|
|
Organelles |
a specialized part of a cell having some specific function; a cell organ.
|
A cell organ |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Formed by microtubules |
Occur in pairs during interphase |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Changes in this protein scaffolding also enables some cells to move or change shape |
Changes in this protein |
|
|
ER |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Form tubes and channels throughout the cytoplasm |
|
|
Golgi |
Sacs that modifies, sorts, and packages macromolecules |
Macromolecules |
|
|
Vesicles |
Appear to punch off of the Golgi membrane |
Can fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing their contents outside of the cell |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Special vesicles in animal cells and some other eukaryotes |
Contain enzymes that break down the cell 's old macromolecules for recycling |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Present in most plant cells are vesicles that enlarge as the cells mature |
Contain water, organic acids, digestive enzymes, salts etc |
|
|
Centrioles |
Tubular structures in the cells of animals and some fungi and algae. |
|
|
|
Cilia |
Short flagella |
Cells that have cilia are often covered with hundreds if these organisms |
|
|
Colony |
Some unicellular microorganisms live in groups called colonies |
Unicellular microorganisms group |
|
|
Multicellular |
|
Many cells complex cell |
|
|
Cell differentiation |
Cell differentiation
|
Differentiation of cell |
|
|
Tissue |
Each specialized mass or layer of cells is called a tissue |
Mass or layers |
|
|
Organ |
Different tissues may be organized into organ |
In our body organs |
|
|
Organ system |
Organs may be organized into organs |
Organ system. - organs , |
|
|
Organism |
All organ, organ system, tissues |
Organisms- organ system |

