![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
Synthesis |
A consolidation in terms of natural selection acting on genetic variation. |
Consolidation in terms |
|
Biosynthesis |
The formation of chemical compounds by a living organism |
Chemical compounds by a living organisms |
|
Decomposition |
Separating or resolving into constituent parts or elements |
Constituent parts or elements |
|
|
Cell respiration |
Decomposition pathway that Provides the energy cells need to function |
Decomposition pathway |
|
|
Aerobic |
Occurs in the presence of oxygen |
Needs oxygen |
|
Anaerobic |
Occuring without oxygen |
Do not need oxygen. Organisms that live without oxygen. |
|
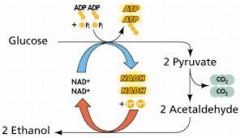
Fermentation |
Any of a group of living organisms |
The act or process of decomposing |
|
|
Glycolysis |
First stage of the aerobic respiration. Enzymes partially oxidize glucose and split into two 3- carbon molecules. |
First stage of the aerobic respiration. |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Second stage of the aerobic respiration. Additional ATP molecules form, conserving some of the energy released in this process. |
Second stage of the aerobic respiration. |
|
|
ETS |
Educational testing service |
Can't find in bio term |
|
|
NADH&FADH2 |
The chemically reduced from NAD |
Came from NAD |
|
|
Pyruvate& pyruvic acid |
An ester or salt of pyruvic acid |
Ester or salt |
|
|
Lactate&lactic acid |
An ester or salt of lactic acid |
Ester or salt |
|
|
Alcoholic ( fermentation) |
Caused by alcohol |
Alcohol |
|
|
Lactic acid ( fermentation ) |
A colorless or yellowish, syrupy water - soluble liquid |
Water - soluble liquid |
|
|
Mitochondrion |
An organelle in the cytoplasm of cells that functions in energy production. |
Organelle in the cytoplasm |
|
|
Matrix |
The intercellular substance of a tissue |
Ground substance |
|
|
Cristae |
A structure resembling a ridge or crest |
Formed by folding of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. |
|
|
Cytochromes |
Several carrier molecules in the mitochondria of plant and animal cells |
|
|
|
Faculative aerobes |
Can survive for long periods with or without oxygen. |
Bacteria, without oxygens |
|
|
Obligate anaerobes |
Generate ATP entirely from fermentation or anaerobic respiration |
Generate ATP |
|
|
Obligate aerobes |
They cannot survive for long without oxygen |
They need oxygen to survive longer. |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Components of water are inserted into the bond to break it. |
A type of breakdown. |

