![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
DNA |
Type of nucleic acid that stores genetic information
|

2. DNA is doubled during the cell cycle |
|
|
RNA |
Nucleic acid that transcribes genetic information into a sequence of amino acids |
2. There are three different types of RNA |
|
|
Gene Expression |
The process of using encoded genetic information |
1. UUC being expressed as serine 2. Gene expression is done through nucleic acids |
|
|
mRNA |
The type of RNA that copies genetic instructions |
2. mRNA is involved in transcription |
|
|
tRNA |
The type of RNA that creates the amino acid sequence |
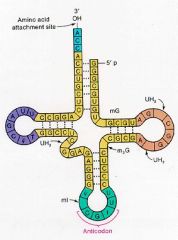
2. tRNA has an anticodon at one end and an amino acid at the other |
|
|
Genetic Code |
The combinations of nucleic acids that translate into specific amino acids |
2. ACG = Threonine 3. The genetic code is like the alphabet |
|
|
Codon |
Three nucleotides that stand for a specific amino acid on mRNA |
3. CCA 4. Codons are analogous to words |
|
|
Anticodon |
Three nucleotides that stand for a specific amino acid on tRNA |
4. GGU 5. Every codon has an opposite anticodon |
|
|
Transcription |
The stage of gene expression where the genetic code is copied and RNA is made |
1. The stage involving splicing 3. There are three stages of transcription |
|
|
RNA Polymerase |
An enzyme that unwinds DNA and synthesizes RNA |
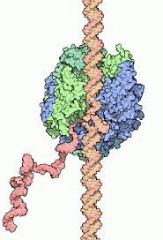
2. RNA Polymerase is similar to DNA polymerase in that they both unwind DNA and build a matching chain using nucleotides |
|
|
Intron |
Useless segments of RNA that are removed in transcription |
1. An RNA segment that starts with GU and ends with AG 2. Introns can cause serious problems if not spliced |
|
|
Extron |
Segments of RNA that code for proteins |
1. Segment that codes for alanine 2. After splicing only extrons remain in the RNA transcript |
|
|
RNA Processing |
The modification of RNA transcripts, so they can be used |
1. Adding a poly-A tail 2. During RNA processing the three types of RNA take shape |
|
|
Splicing |
The removal of introns and connecting of extrons in RNA processing |
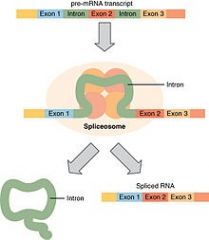
2. Splicing is a very exact process |
|
|
tRNA Charging |
When tRNA is matched to its correct amino acid |
1. A tRNA with an anticodon of CAG and valine amino acid 2. Each amino acid has its own enzyme for tRNA charging |
|
|
Translation |
The stage if gene expression where the amino acid sequence is ordered |
1. The stage that takes place on ribosomes 2. Translation uses all three types of RNA |
|
|
Tertiary Structure |
Shape of a protein determined by its primary structure, and that determines its function |
2. The tertiary structure of enzymes provide their active site |
|
|
Translational Error |
Errors that occur during the translation stage of gene expression |
1. A Frame Shift Mutation 2. Translational errors mean polypeptide chains may be incomplete |
|
|
Translational Frame Shift |
An error in which initiation is messed up and RNA codes for the wrong amino acids |
1. An AAU enzyme being read as AUG 2. Frame shift mutations mean a threonine protein may be coded for instead of aspartate |
|
|
Frame Shift Mutation |
A mutation where the frames being read can't translate to nucleotides |
1. A frame of 2 nucleotides 2. Frame shift mutations involve deleting nucleotides |

