![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Photoautotroph
|
An organism that gets its energy from light through the process of photosynthesis.
|
Photo - Light, Auto - Self, Troph - Feeding.
The photoautotroph needed to conduct photosynthesis for energy and carbon compounds. |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
The process which converts light energy into chemical energy and carbon compounds.
|
A plant taking in light with a leaf.
The algae used photosynthesis to convert sunlight into usable energy. |
|
|
Thylakoids
|
Membranes in the grana of chloroplasts which contain pigments and enzymes involved in photosynthesis.
|
Pancakes in a stack! - Thylakoids in a granum!
The thylakoids contain pigments and enzymes which conduct photosynthesis. |
|
|
Grana
|
Stacks of thylakoids within a chloroplast within the cell of a photoautotroph.
|
A stack of membranes.
The grana were all full of thylakoids, which conducted photosynthesis. |
|
|
Stroma
|
The area in a chloroplast outside of the grana, which contains DNA, RNA, and the Calvin Cycle.
|
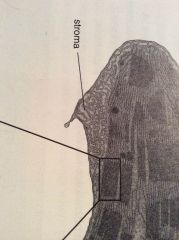
Outside the grana.
The stroma was full of enzymes that catalyzed the formation of sugar. |
|
|
Chloroplast
|
The green cell organelle specialized in photosynthesis and the Calvin cycle.
|
Green organelle in a cell.
The chloroplast contains different regions serving different purposes involved in photosynthesis and the Calvin cycle. |
|
|
Chlorophyll
|
The pigment in chloroplasts that reflects green light, but uses other light for photosynthesis.
|
The green in a chloroplast.
The chlorophyll absorbed light into the thylakoids. |
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
NADPH
|
The molecule that provides protons and electrons needed for the Calvin cycle.
|
The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine domicile pride phosphate, or NADP+, is NADPH.
|
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
NADPH
|
The molecule that provides protons and electrons needed for the Calvin cycle.
|
The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine domicile pride phosphate, or NADP+, is NADPH.
|
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
NADPH
|
The molecule that provides protons and electrons needed for the Calvin cycle.
|
The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine domicile pride phosphate, or NADP+, is NADPH.
|
|
|
PGAL
|
A three carbon sugar-phosphate, also known as phosphoglyceraldehyde.
|
PGA requires one molecule of ATP and one of NADPH to make PGAL during the Calvin cycle's second step.
|
|
|
Light reactions
|
Reactions in photosynthesis responsible for absorbing light, splitting water, and converting energy.
|
Absorption of light in PS1 and PS2.
The light reactions brought sunlight into the cell and changed its energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Calvin Cycle
|
Reactions turning carbon dioxide into 3-carbon sugars.
|
Carbon dioxide fixation.
CO2 is made into sugars by the Calvin cycle, and can be used for cell functions. |
|
|
NADPH
|
The molecule that provides protons and electrons needed for the Calvin cycle.
|
The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine domicile pride phosphate, or NADP+, is NADPH.
|
|
|
PGAL
|
A three carbon sugar-phosphate, also known as phosphoglyceraldehyde.
|
PGA requires one molecule of ATP and one of NADPH to make PGAL during the Calvin cycle's second step.
|
|
|
Photoinhibition
|
A decline in photosynthesis.
|
The result of the reaction of substances created by the reaction of water and oxygen with pigments and proteins can cause photoinhibition.
|

