![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
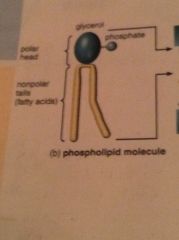
Phospholipids
|
Lipids consisting of a glycerol, two fatty acids, and a polar phosphate head.
|
PHOSPHO - phosphorous
LIPID - oil PHOSPHOLIPID - phosphorous + oil The membrane consisted of many phospholipids, each one with a non polar tail pointing into the membrane's center. |
|

Phospholipid Bilayer
|
The bilayer in cell membranes, which is semipermeable and consists of many phospholipids.
|
The membrane of a human's cells.
The phospholipid bilayer was selectively permeable, allowing only specific molecules to pass through. |
|
|
Polarity
|
The tendency of a molecule to have opposite ends with opposites charges.
|

H2O, with the oxygen atom positive and the hydrogen atoms negative.
|
|
|
Transport proteins
|
Special proteins, embedded in the membrane, which help charged molecules and small polar molecules into the cell.
|
Hemoglobin is the transport protein of oxygen.
|
|
|
Selective permeability
|
The specific regulation of membranes on the exchange of materials.
|
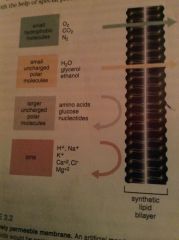
Ex. A membrane will allow water through, but not ions.
The selective permeability would not allow glucose through the membrane without a transport protein. |
|
|
Glycoproteins/glycolipids
|
Proteins/lipids that have a sugar attached to them. They are the receivers of chemical messages between cells.
|
Ganglioside in the gray matter of the brain.
The glycoproteins received messages from the other cell. |

