![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
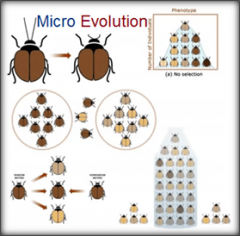
Microevolution |
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations |
1. An example of microevolution is the evolution of a species. 2. Microevolution is the opposite of macroevolution. |
|
Natural Selection |
the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. The theory of its action was first fully expounded by Charles Darwin and is now believed to be the main process that brings about evolution. |
1. An example of natural selection is a bad mutation being eliminated. 2. Natural selection was discovered by Charles Darwin. |
|
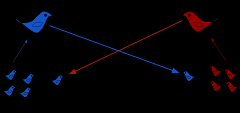
Gene Flow |
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration) is the transfer of alleles orgenes from one population to another. Migration into or out of a population may be responsible for a marked change in allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). |
1. An example of gene flow is a population of flowers on one side of a river transports pollen to the flowers on the other side of the river, producing offspring. 2. Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area |
|
|
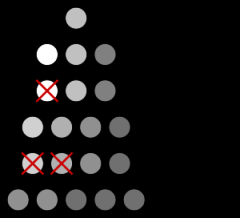
Genetic Drift |
variation in the relative frequency of different genotypes in a small population, owing to the chance disappearance of particular genes as individuals die or do not reproduce. |
1. An example of gene drift is a random succession of births results in all other hair colors going extinct within a village full of redheaded people. 2. Genetic drift refers to the change in a type of genes in a population because of the random nature of reproduction |
|
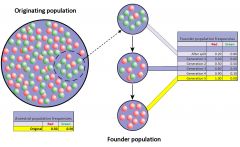
Founder Effect |
the reduced genetic diversity that results when a population is descended from a small number of colonizing ancestors. |
1. An example of founder effect is 2. In extreme cases, the founder effect is thought to lead to the speciation and subsequent evolution of new species. |
|
|
Inbreeding |
breed from closely related people or animals, especially over many generations. |
1. An example of inbreeding is a sister and brother having children. 2. Inbreeding can result in terrible mutations. |
|
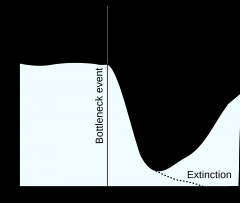
Population Bottleneck |
A population bottleneck is an event that drastically reduces the size of a population. The bottleneck may be caused by various events, such as an environmental disaster, the hunting of a species to the point of extinction, or habitat destruction that results in the deaths of organisms |
1. An example of population bottleneck is the elephant seal. 2. A classic example of a population bottleneck is that of the northern elephant seal, whose population fell to about 30 in the 1890s |
|
|
Inbreeding Depression |
Inbreeding depression is the reduced biological fitness in a given population as a result of inbreeding - ie., breeding of related individuals. Population biological fitness refers to its ability to survive and reproduce itself. |
1. An example of inbreeding depressions is outcrossing nematode Caenorhabditis remanei which has been demonstrated to suffer severely from inbreeding depression, unlike its hermaphroditic relative C. elegans, which experiences outbreeding depression. 2. Inbreeding depression is often the result of a population bottleneck. |
|
|
Quantitavtive Traits |
any trait such as height, weight, or color that varies continuously over a range; a multifactorial trait |
1. An example of 2. |
|
|
Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) |
a gene that affects quantitative traits |
|
|
|
Artificial Selection |
The breeding of plants and animals to produce desirable traits. Organisms with the desired traits, such as size or taste, are artificially mated or cross-pollinated with organisms with similar desired traits. |
|

