![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Population Genetics
|
the field of biology that studies microevolution |
Mendel's laws of inheritance Population Genetics uses many techniques to microevolution |
|
|
Gene Pool |
all of the genes of a local population of organisms |
Homozygous purple flowers There are certain percentages of each allele in gene pools |
|
|
Population |
the number of organisms in a group |
40 People The population of humans on Earth is about 7 billion |
|
|
Evolution |
progression and change of a species over time |
Human evolution |
|
|
Polymorphic |
two or more alleles present in a gene pool |
eye color The color of apples is polymorphic because there are multiple alleles. |
|
|
Gene Variation |
difference in the types of genes |
amino acid sequence Gene variation causes a variation in alleles. |
|
|
Mutation |
the source of variation |
base pair of human genome Mutation is the first source of variation. |
|
|
Genetic Recombination |
recombination of alleles during meiosis |
cross-over Genetic Recombination is the second source of variation. |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg model/ equation |
a mathematical model of gene pools |
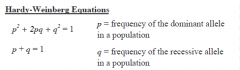
Hardy-Weinberg model/ equation was proposed 1908 |
|
|
p |
purple flower frequency |

|
|
|
q |
white flower frequency |

|
|
|
p2 |
second generation homozygous purple |
|
|
|
2pq |
second generation heterozygous purple |
|
|
|
q2 |
second generation homozygous white |
|
|
|
Microevolution |
change within species |
posture Microevolution occurs over dozens or hundred of generations |
|
|
Natural Selection |
organisms adapting to their environment for better survival |
peppered moths Natural selection changes frequency in the gene pool |
|
|
Gene Flow |
the effects of migration in gene pools |
After many generations of gene flow separated populations become similar in gene pools. |
|
|
Genetic Drift |
a random change in allele frequencies |
gene pool percentage Genetic drift effects small populations the most |
|
|
Founder effect |
genetic drift that influences new populations |
Canadian and Hawaiian Geese The founder effect cause the new population's gene pool to be higher. |
|
|
Inbreeding |
the gradual increase in homozygosity |
California Condor Inbreeding is common among smaller species. |
|
|
Population bottleneck |
when a population is drastically reduced for a few generations |
American bison Population bottleneck causes species to be partially inbred. |
|
|
Inbreeding depression |
inbred fertility and survival is reduced compared to populations that are not inbred |
zoo animals Endangered species are subject to inbreeding depression |
|
|
Quantitative traits |
multifactorial traits |
lifespan Quantitative traits are called this because of the way they are measured. |
|
|
Quantitative traits loci (QTls) |
genes that affect quantitative traits |
height genes They are variables in most populations. |
|
|
Artificial Selection |
controlled natural selection |
larger chickens Artificial selection is controlled by a breeder. |

