![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Patterns of Inheritance |
The manner in which a gene is transmitted. |
1. An RR and Rr genotype being transmitted as a round seed phenotype. 2. For example, the pattern of inheritance may be as an autosomal dominant trait that is transmitted from father or mother to son or daughter. |
|
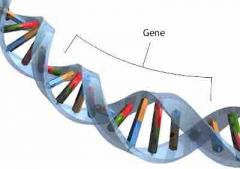
Gene |
The fundamental physical unit of heredity which transmits a set of specifications from one generation to the next. It's a segment of DNA that codes for a specific product. |
1. An example of a gene is a strand of DNA. 2. A gene is defined as a segment of DNA whose sequence of nucleotides codes for a specific functional product. |
|
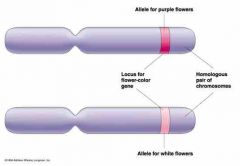
Allele |
An allele is one of two or more possible forms of a gene. |
1. An example of an allele is a gene. 2. Each allele of a particular gene has a different base sequence. |
|
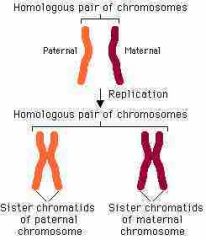
Homologous Chromosome |
A homologous chromosome is a set of one maternal chromosome and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. |
1. A paternal and maternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside during meiosis. 2. Homologous chromosomes are important in the processes of meiosis and mitosis. |
|
|
Dominant |
Referring to an allele that masks the presence of another allele of the same gene in a heterozygous organism |
1. An example of a dominant trait is brown hair. 2. The allele for a dominant trait is commonly represented by a capital letter. |
|
|
Recessive |
A trait whose expression is masked in a heterozygous organism. |
1. An example of a recessive trait is red hair. 2. The allele for a recessive trait is represented by a lowercase letter. |
|
|
Principle of Segregation |
The principle stating that homologous chromosomes, with the genes they carry, separate into different gametes during meiosis such that the two alleles for a given trait each appear in a different gamete |
1. Only one of the factors, either wrinkled or round, went into each gamete formed by the F1 plants. 2. Mendel called this separation of factors the principle of segregation. |
|
|
Genotype |
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations. |
1. An example of a genotype is the 22 numbered pairs of chromosomes, two sex chromosomes and the mitochondrial chromosome. 2. So far the complete genotype a of more than 100 species of bacteria, and dozens of eukaryotes have been sequenced. |
|
|
Phenotype |
The expression of a genotype in the appearance or function of an organism; an observed trait. |
1. An example of a phenotype is the genotype of each individual. 2. Because the round-seeded phenotype is dominant, both the homozygous RR Nd the heterozygous Rr genotype a produce plants with round seeds. |
|
|
Homozygous |
Having two identical alleles for a given trait |
1. An example of homozygous is RR. 2. Plants with the homozygous genotype rr will have the recessive phenotype, wrinkled seeds. |

