![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Backup?
|
A backup is an additional copy of production data, created and retained for the sole purpose
of recovering lost or corrupted data. |
|
|
Backups are performed to serve what 3 processes?
|
Disaster Recovery
Operational Recovery Archive (Some organizations are required by law to archive a set number of years of data) |
|
|
What is Backup Granularity?
|
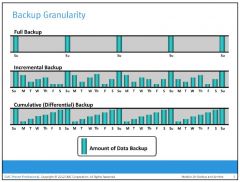
Backup granularity depends on business needs and the required RTO/RPO. Based on the granularity, backups can be categorized as full, incremental, and cumulative (or differential).
|
|
|
What is a Full Backup?
|
Full backup is a backup of the complete data on the production volumes. A full backup copy is created by copying the data in the production volumes to a backup storage device. It provides a faster recovery but requires more storage space and also takes more time to back up.
|
|
|
What is a Incremental Backup?
|
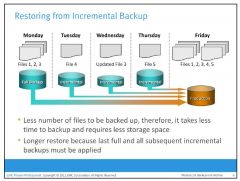
Incremental backup copies the data that has changed since the last full or incremental backup, whichever has occurred more recently. This is much faster than a full backup (because the volume of data backed up is restricted to the changed data only) but takes longer to restore.
|
|
|
What is a Cumulative Backup?
|
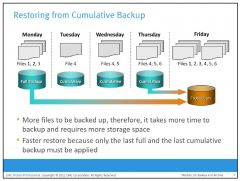
Cumulative backup copies the data that has changed since the last full backup. This method takes longer than an incremental backup but is faster to restore.
|
|
|
What is a synthetic (or constructed) backup?
|
This method is used when the production volume resources cannot be exclusively reserved for a backup process for extended periods to perform a full backup. It is usually created from the most recent full backup and all the incremental backups performed after that full backup. This backup is called synthetic because the backup is not created directly from production data. A synthetic full backup enables a full backup copy to be created offline without disrupting the I/O operation on the production volume. This also frees up network resources from the backup process, making them available for other production uses.
|
|
|
What makes up the Backup Architecture?
|
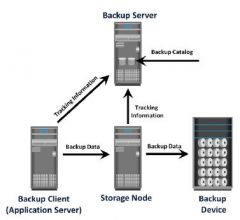
Backup Client
Backup Server Storage Node |
|
|
Who maintains the Backup catalog?
|
Backup Server
|
|
|
Who manages the backup operations?
|
The Backup Server
|
|
|
Who manages the backup device?
|
Storage Node
|
|
|
Who gathers the data that is to be backed up an sends it to the storage node?
|
Backup Client
|
|
|
Who is responsible for writing data to backup device?
|
Storage Node
|
|
|
What is the Backup Operation Sequence?
|

|
|
|
What is the Recovery Operation sequence?
|

|
|
|
What are the two methods deployed for Backup?
|
Hot (Online)
Cold (Offline) |
|
|
Describe what a hot backup is.
|
This is when the Application is up and running, with users accessing their data during the backup.
|
|
|
Describe what a cold backup is.
|
This is when it requires the application to be shutdown during the backup process.
(This method is easier then Hot backup) |
|
|
What is a bare-metal recovery?
|
OS, hardware, and application configuration are appropriately backed up for a full system recovery.
Server Configuration backup (SCB) can also recover a server onto dissimilar hardware. |
|
|
What is a Server Configuration Backup?
|
Creates and backs up server configuration profiles, based on user-defined schedules.
(instructor said not as important) |
|
|
What are some Key Backup/Restore considerations?
|
What are the restore requirements - RPO & RTO?
Which data needs to backed up? How frequently should data be backed up? How long will it take to back up? How many copies to create? How long to retain backup copies? Location, size, and number of files? |
|
|
What is a Direct-Attached Backup
|
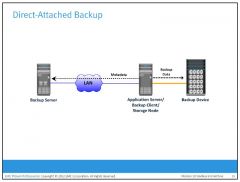
In a direct-attached backup, the storage node is configured on a backup client, and the backup device is attached directly to the client. Only the metadata is sent to the backup server through the LAN. This configuration frees the LAN from backup traffic.
|
|
|
What does the name of the backup topology tell you?
|
How the backup will travel.
(Ex. Direct-Attached, LAN-Based, SAN-based) |
|
|
What is the meta data in the backup also known as?
|
catalog
|
|
|
What is a LAN-based Backup?
|
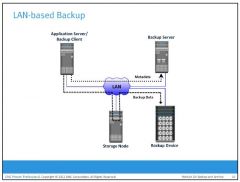
the clients, backup server, storage node, and backup device are connected to the LAN. The data to be backed up is transferred from the backup client (source) to the backup device (destination) over the LAN, which might affect network performance.
|
|
|
Where does pre-backup metadata come from?
|
Client
|
|
|
Where does post-metadata come from?
|
Storage node
|
|
|
What is a SAN-based (LAN-Free) Backup?
|
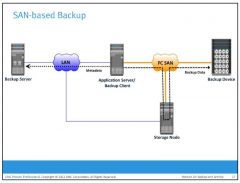
The SAN-based backup topology is the most appropriate solution when a backup device needs to be shared among clients. In this case, the backup device and clients are attached to the SAN. A client sends the data to be backed up to the backup device over the SAN. Therefore, the backup data traffic is restricted to the SAN, and only the backup metadata is transported over the LAN.
|
|
|
Mixed Backup Topology
|
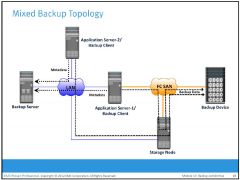
uses both the LAN-based and SAN-based topologies. This topology might be implemented for several reasons, including cost, server location, reduction in
administrative overhead, and performance considerations. |
|
|
What are the four backup implementations in a NAS environment?
|
Server-based backup
Serverless backup NDMP 2-way backup NDMP 3-way backup |
|
|
What is Server-based backup?
|
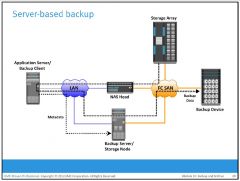
an application server-based backup, the NAS head retrieves data from a storage array over the network and transfers it to the backup client running on the application server. The backup client sends this data to the storage node, which in turn writes the data to the backup device. This results in overloading the network with the backup data and using application server resources to move the backup data.
|
|
|
What is a Serverless backup?
|
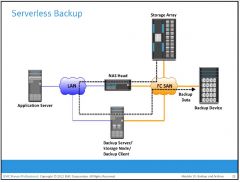
network share is mounted directly on the storage node. This avoids overloading the network during the backup process and eliminates the need to use resources on the application server. In this scenario, the storage node, which is also a backup client, reads the data from the NAS head and writes it to the backup device without involving the application server.
|
|
|
What defines a storage drive?
|
It is the only thing that can write to the array
|
|
|
What is NDMP 2-way Backup?
|
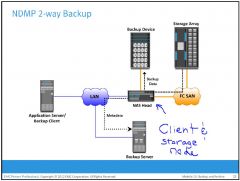
NDMP is an industry-standard TCP/IP-based protocol specifically designed for a backup in a NAS environment.
Network traffic is minimized by isolating data movement from the NAS head to the locally attached backup device. Only metadata is transported on the network. The backup device is dedicated to the NAS device, and hence, this method does not support centralized management of all backup devices. |
|
|
What is NDMP 3-way Backup?
|
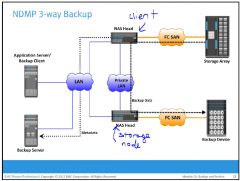
to avoid the backup data traveling on the production LAN, a separate private backup network must be established between all NAS heads and the NAS head connected to the backup device. Metadata and NDMP control data are still transferred across the public network.
|
|
|
Describe Backing up to tape.
|
Traditionally low cost solution.
Tape drives are used to read/write data from/to tape. Sequential/Linear access. Multiple streaming to improve media performance. (Can write from multiple streams to a single tape) Has limitations such as slow access, wear and tear, shipping/handling challenges, shoe shinning effect) |
|
|
What are benefits of Backing up to Disk?
|
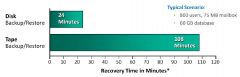
Enhanced overall backup and recovery performance. (random Access)
Much more reliable than tape. Can be accessed by multiple hosts simultaneously. |
|
|
What is Backing up to Virtual Tape?
|
When disks are emulated and presented as tapes to back up software.
This method does not require and additional modules or changes in the legacy backup software. Provides better performance than physical tape. This provides online and random disk access and faster backup and recovery. |
|
|
What is a virtual tape library?
|
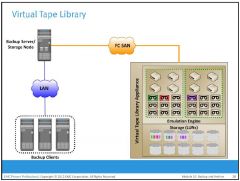
A virtual tape library (VTL) has the same components as that of a physical tape library, except
that the majority of the components are presented as virtual resources. |
|
|
What are some difference between the backup targets of Tape, Disk, and Virtual Tape?
|
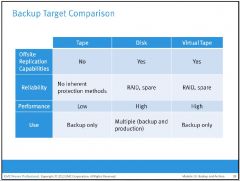
|
|
|
What is data and Deduplication?
|
A process of identifying and elimination redundant data
|
|
|
What are the two Deduplication methods?
|
File Level
Subfile Level |
|
|
What are the two Deduplication implements?
|
Source-based (Avamar)
Target-based (Data Domain) |
|
|
Explain File-Level Deduplication (single instance storage).
|
Detects and removes redundant copies of identical files.
After the file is stored, all other references to the same file refer to the original copy. |
|
|
Explain Subfile Deduplication.
|
Detects redundant data within and across the files
It does this with two methods: Fixed-length block & Variable-length segment. |
|
|
What data Deduplication implementation is source based and data is deduplicated on the backup client?
|
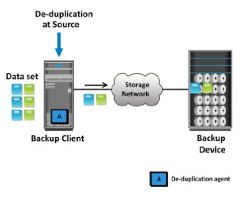
Avamar
|
|
|
What are benefits of source based Deduplication?
What is a negative effect? |
Backup client sends only new, unique segments across the network.
Reduces the storage capacity and network bandwidth requirements. Increases overhead on the backup client |
|
|
What are benefits of target based Deduplication?
What is a negative effect? |
Offloads the backup client from the Deduplication process by deduplicating the data at the target (backup device).
A negative is that all backup data must traverse the network to the backup device. |
|
|
What are some key benefits of Data Duplication?
|
Reduces infrastructure costs.
Enables longer retention periods. Reduces backup window. Reduces backup bandwidth requirement (source-based) |
|
|
What are the traditional Backup Approaches in a Virtualized Environment?
|

Back up agent on VM.
(Requires installing backup agent on each VM, can only backup virtual disk data, does not capture VM swap file, and is a challenge in a VM restore) Backup agent on hypervisor. (Requires installing backup agent only on hypervisor and backs up all the VM files) |
|
|
What are two backup options?
|
Image-based backup approach
Traditional backup approach |
|
|
What is the Backup optimization?
|
Deduplication
|
|
|
Archive Solution Architecture consists of what 3 components?
|
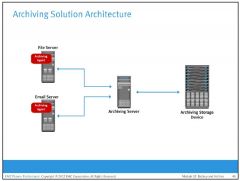
archiving agent
archiving server archiving storage device |
|
|
What is a Image-based backup?
|
Creates a copy of the guest OS, its data, VM state, and configurations.
The backup is saved as a single file (image). Mounts image on a proxy server. Offloads backup processing from the hypervisor. Enables quick restoration VM. |
|
|
How much percent does fixed content growing annually?
|
90%
|
|
|
What is a Data Archive?
|
A repository where fixed content is stored.
A place where organizations retain their data for extended period of times. |
|
|
What can a Archive be implemented as?
|
Online
Nearline Offline |
|
|
What is Fixed Content?
|
As data ages, it is less likely to be changed and eventually becomes “fixed” but continues to be accessed by applications and users. This data is called fixed content.
|
|
|
What are some Challenges of Traditional Archiving Solutions?
|
Both tape and optical are susceptible to wear and tear.
Has no intelligence to identify duplicate data. inadequate for long-term preservation (years-decades). Unable to provide online and fast access to fixed content. |
|
|
What does CAS stand for?
|
Content Addressed Storage
|
|
|
What is CAS?
|
Disk-based storage that has emerged as an alternative to traditional archiving solutions.
A means to access archive data online. Enables organizations to meet SLAs Provides features that are required for storing archive data (Content authenticity/integrity, location independence, single-instance storage, retention enforcement, data protection) |
|
|
What is an application that benefits mostly by an archival solution?
|
Email
|
|
|
What is EMC Networker
|
a backup and recovery software that centralizes, automates, and accelerates data backup and recovery operations across the enterprise.
|
|
|
What are some key features of EMC Networker?
|
Supports Windows, UNIX, Linux, and also virtual environments.
Supports different backup targets - tapes, disks, and virtual tapes. Supports Multiplexing of data. Provides both source and target based Deduplication. Cloud-backup operation enables backing up data to cloud. |
|
|
What is EMC Avamar?
|
Disk-based backup and recovery solution that provides source-based data Deduplication.
The three major components include Avamar server, Avamar backup clients, and Avamar administration. Avamar Server includes software only, Avamar Data Store, Avamar Virtual Edition. |
|
|
What is EMC Data Domain
|
Target-based Deduplication solution.
|
|

|
C
|
|

|
A
|
|

|
C
|
|

|
C
|
|

|
D
|

