![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the subdivisions of the Cerebrum?
|
Prosencephalon
|
|
|
What are the subdivisions of the prosencephalon?
|
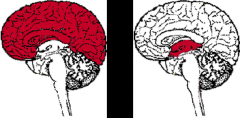
1. telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres)
2. diencephalon |
|
|
What are the subdivisions of the brain stem?
|
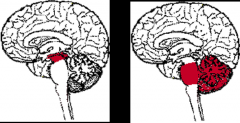
1. Mesencephalon
2. Rhombencephalon |
|
|
What are the subdivisions the rhombencephalon?
|
1. metencephalon
2. myelencephalon |
|
|
What cavity is associated with the telencephalon?
|
Lateral ventricle
|
|
|
What cavity is associated w/ the diencephalon?
|
3rd ventricle
|
|
|
What structures arise from the diencephalon?
|
1. Thalamus
2. Subthalamus 3. Hypothalamus 4. Epithalamus |
|
|
What structures arise from the telencephalon?
|
(cerebral hemispheres)
1. Cortex 2. White matter 3. Basal ganglia 4. limbic system 5. Olfactory system |
|
|
What structures arise from the mesencephalon?
|
Midbrain
|
|
|
What cavity Is associated with the mesencephalon?
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
|
|
What structures arise from the rhombencephalon?
|
1. Metencephalon
2. Myelencephalon |
|
|
What cavity is associated with the rhombencephalon?
|
4th ventricle
|
|
|
What structures arise from the metencephalon?
|
1. Pons
2. Cerebellum |
|
|
What structures arise from the myelencephalon?
|
Medulla
|
|
|
What is the clinical definition of the brain stem?
|
1. Midbrain
2. Pons 3. Medulla (NOT the cerebellum) |
|
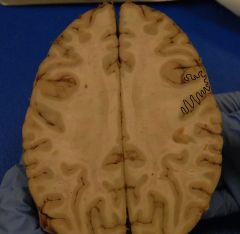
What is the area indicated by the squiggles?
|
The Cortex
|
|
|
What is the definition of the cortex?
|
The surface of the cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
What is a Gyrus?
|
A fold in the brain
|
|
|
What is a sulcus?
|
An intervening groove in the brain
|
|
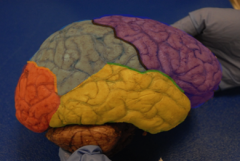
Who are we?
|
Purple = Frontal lobe
Yellow = Temporal lobe Grey = Parietal lobe Orange = Occipital lobe |
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of neurons w/in the brain?
|
In the cortex
|
|
|
Where is the "grey matter" of the brain?
|
In the cortex
|
|
|
Where is the "white matter" of the brain?
|
In subcortical regions
|
|
|
What is the white matter?
|
Myelinated axons of neurons
|
|
|
What is the difference b/e a sulcus and a fissure?
|
A fissure divides the large components of the brain
|
|
|
What is the inferior boundary of the frontal lobe?
|
The lateral or "sylvian" fissure
|
|
|
What is the posterior border of the frontal lobe?
|
The central sulcus
|
|
|
What region of the brain is located in the precentral gyrus?
|
Primary motor cortex
|
|
|
Where is the precentral gyrus?
|
Anterior to the primary motor cortex
|
|
|
What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
|
Responsible for the execution of voluntary movement
|
|
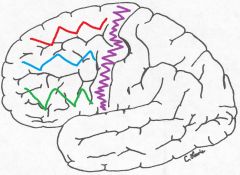
What are the squiggles?
|
Red = Superior frontal gyrus
Blue = middle frontal gyrus Green = inferior frontal gyrus purple = precentral gyrus |
|
|
What neurons does the middle frontal gyrus contain?
|
The saccadic gaze center (or frontal eye fields) which is responsible for fast (saccadic) horizontal eye movements.
|
|
|
What neurons does the inferior frontal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere contain?
|
Contains the motor or expressive language area (Broca's area) of the brain.
*dominant hemisphere is usually the left hemisphere in right handed people |
|
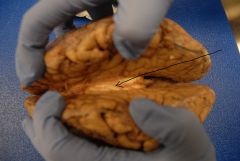
Who am I? What is my function?
|
Corpus Callosum; Connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
|
|
|
What does the medial surface of the frontal lobe lie on?
|
Lies on the corpus callosum
|
|
|
What is the area of the frontal lobe that lies on the corpus callosum?
|
The cingulate gyrus which makes up the medial surface of the frontal lobe
|
|
|
What makes up the corpus callosum?
|
Millions of myelinated nerve fibers
|
|
|
What is the paracentral lobule?
|
The cortex around the medial aspect of the central sulcus; which includes the medial portions of the pre-central and post-central gyruses
|
|
|
What does the inferior surface of the frontal lobe lie on?
|
Lies on the orbital frontal bone
|
|
|
What neurons does the inferior surface of the frontal lobe contain?
|
The olfactory bulb and tract
|
|
|
What neurons are located near the medial margin of the inferior surface of the frontal lobe?
|
The olfactory bulb and tract
|
|
|
Where is the gyrus rectus?
|
Lies medial to the olfactory sulcus
|
|
|
What lies anterior to the lateral surface of the parietal lobe?
|
Central sulcus
|
|
|
Where is the post-central gyrus? what neurons are located inside it? What do they do?
|
The post-central gyrus is located posterior to the central sulcus and contains the primary somatosensory cortex which receives most of the sensory information from the body.
|
|
|
What is the posterior border of the lateral surface of the parietal lobe?
|
The parieto-occipital sulcus
|
|
|
What lies inferior to the lateral surface of the parietal lobe?
|
The Sylvian or lateral fissure
|
|
|
What does the posterior parietal lobe consist of?
|
A superior and inferior parietal lobule
|
|
|
What do the superior and inferior parietal lobules contain?
|
The supramarginal gyrus and the angular gyrus
|
|
|
Where is the supramarginal gyrus located specifically?
|
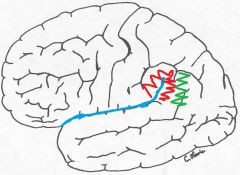
Around the most posterior portion of the sylvian fissure.
*red in the picture |
|
|
Where is the angular gyrus located?
|
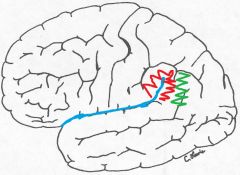
Just posterior to the supramarginal gyrus
*green in the pic. |
|
|
What neurons do the supramarginal gyrus and the angular gyrus contain in the dominant hemisphere?
|
The receptive language area (Wernicke's area); which is necessary for the perception and interpretation of spoken and written language.
|
|
|
What is the posterior portion of the medial surface of the parietal lobe?
|
The postcentral gyrus
|
|
|
Where is the precuneous located
|
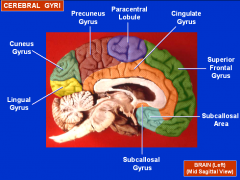
B/e the paracentral lobule and the parieto-occipital sulcus
|
|
|
What is the superior border of the lateral surface of the temporal lobe?
|
The sylvian (lateral) fissure
|
|
|
What gyri does the lateral surface of the temporal lobe contain?
|
The superior, middle and inferior temporal gyruses
|
|
|
What forms the floor of the sylvian fissure?
|
The superior temporal gyrus
|
|
|
What lies on the inner surface of the superior temporal gyrus?
|
Heschl's gyrus
|
|
|
What is the function of Heschl's gyrus?
|
The primary auditory cortex (sense of hearing).
|
|
|
Where is the most important part of the language receptive cortex (Wernicke's area) located?
|
In the superior temporal gyrus
|
|
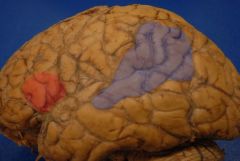
Who are we?
|
Red = Broca's motor or expressive speech area
Grey = Wernicke's area |
|
|
What gyrus does the medial portion of the temporal lobe consist of?
|
The parahippocampal gyrus
|
|
|
What is the most medial portion of the parahippocampal gyrus?
|
The uncus
|
|
|
What is the function of the uncus?
|
A major part of the primary olfactory cortex (sense of smell)
|
|
|
Where would a seizure have originated if the patient experiences a foul smelling odor as the first symptom?
|
The uncus
|
|
|
If a patient has increased intracranial pressure from a subdermal hematoma what symptom could be caused by compression of the uncus?
|
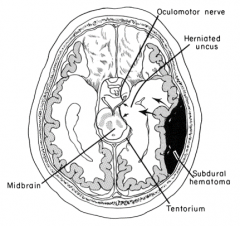
CNIII palsy from compression by the already compressed uncus. This would cause abnormalities in eye movements.
|
|
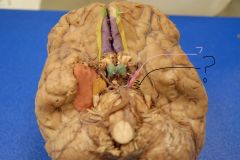
Who are we?
|
Pink = CN III (oculomotor nerve)
Black = Uncus Orange = Parahippocampal gyrus |
|

|
Brrraaaaaiiiiinnnnsssss.....
|
|
|
What separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe?
|
The parieto-occipital sulcus
|
|
|
What sulcus lies on the the medial surface of the occipital lobe?
|
The calcarine sulcus
|
|
|
What does the calcarine sulcus do?
|
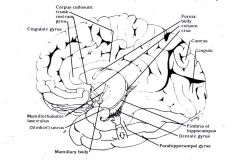
Separates the cuneus from the lingula
|
|
|
What lies superior to the calcarine sulcus?
|
The cuneous
|
|
|
What lies inferior the calcarine sulcus?
|
The lingula
|
|
|
What is the cortex around the calcarine sulcus?
|
The primary visual cortex (striate cortex) which receives visual pathways from the retina known as optic radiations.
|
|
|
What does the inferior surface of the occipital lobe rest on?
|
The cerebellar tentorium, which is a reflection of the dura.
|
|
|
Where are the insular and limbic lobes located? what are they derived from?
|
On the medial surface of the brain and are derived from the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes.
|
|
|
What is the insular lobe?
|
The portion of the cortex that lies buried w/in the sylvian fissure.
|
|
|
Insular lobe
|
|
|
What area of the brain can only be observed by spreading apart the frontal, parietal and temporal opercula?
|
The insular lobe
|
|
|
What Sy would pts with acute infarction of the insular lobe have?
*especially on the right side |
Cardiac complications such as atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias.
|
|
|
Where do ascending pain pathways that relay through the thalamus transmit nociceptive (pain related) signals to?
|
Both the anterior cingulate gyrus and to the insula.
|
|
|
What regions of the brain are responsible for the placebo effect?
|
The anterior cingulate gyrus, the insula and the amygdala
|
|
|
What is located in the anterior portion of the insula?
|
The insular taste cortex
|

