![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Orientation of the Heart
|
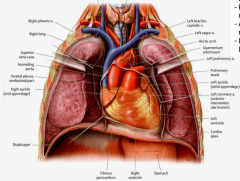
-Mostly on left -Apex pointed anteroinferiorly -Right surface is mostly right atrium -Anterior surface is mostly right ventricle -Left surface is mostly left ventricle
|
|
|
Layers of the Heart
|
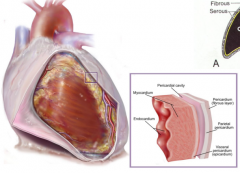
Fibrous pericardium Serous pericardium-continuous membrane that forms two layers separated by serous-filled pericardial cavity Parietal pericardium-adhered to deep surface of fibrous pericardium Visceral pericardium (epicardium)-outer layer of heart tissue Myocardium-thick middle layer of specialized cardiac muscle Endocardium-thin internal lining membrane of the heart that also lines the valves |
|
|
Right Atrium |
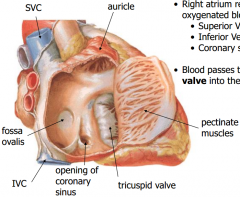
-Atria are the receiving chambers that pump blood into the ventricles -Right atrium receives poorly oxygenated blood from body -Superior Vena Cava -Inferior Vena Cava -Coronary sinus -Blood passes through tricuspid valve into right ventricle |
|
|
Right Atrium 2 |
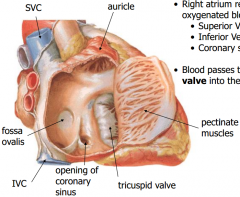
-The auricle and anterior part of atrium are lined with pectinate muscles -Fossa ovalis is a remnant of a fetal valve in atrial septum which shunted blood from the right atrium to the left atrium, bypassing the non-functioning lungs |
|
|
Right Ventricle |
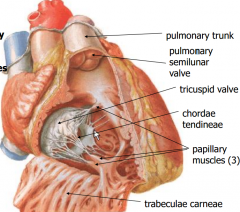
-Right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary valve -Into the pulmonary trunk -Pulmonary arteries carry low-oxygen blood to the lungs |
|
Left Atrium |
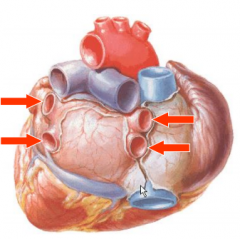
-4 pulmonary veins receive well-oxygenated blood from the lungs -auricle projects anteriorly -pectinate muscles -foramen ovale -blood leaves through mitral valve to left ventricle |
|
|
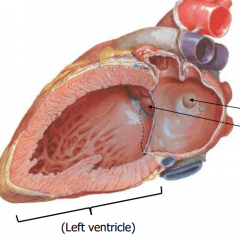
Left Ventricle |
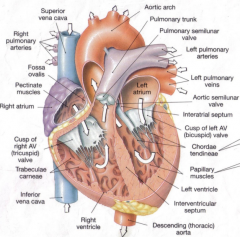
-mitral (bicuspid) valve -chordae tendineae -papillary muscles (2) -trabeculae carneae -pumps blood through aortic semilunar valve into aortic arch -very thick walls |
|
|
Heart Valves |
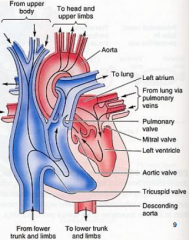
-tricuspid -pulmonary -mitral -aortic |
|
|
Tricuspid valve |
prevents backflow through right atrioventricular orifice |
|
|
Mitral (bicuspid) valve |
prevents backflow through left atrioventricular orifice |
|
|
Chordae tendinae and papillary muscles |
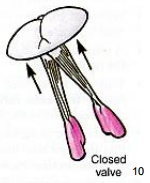
prevent cusps from inverting back into the atria due to pressure of blood in ventricles |
|
|
Pulmonary (semilunar) valve |
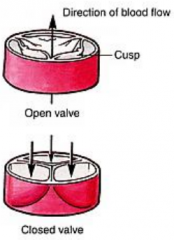
prevents blood from backflowing from pulmonary artery into right ventricle
-contains 3 cusps |
|
|
Aortic (semilunar) valve |
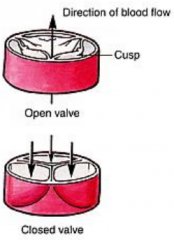
prevents blood from backflowing from aorta into left ventricle
-contains 3 cusps |
|
|
Coronary Arteries |
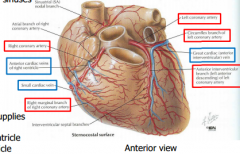
-Supply heart tissue itself -1st branch of aorta -Arises from aortic sinuses |
|
|
Left coronary artery supplies... |
-left atrium -most of left ventricle -part of right ventricle |
|
|
Right coronary artery supplies... |
-right atrium -most of right ventricle -part of left ventricle |
|
|
Anastomosis of coronary arteries |
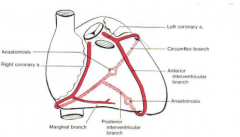
Coronary circulation is extremely variable in detail. In most cases, the right and left coronary arteries share equally in blood supply to the heart. In ~15% of hearts, the left coronary artery is said to be dominant in that the posterior interventricular branch comes off the circumflex |
|
|
Cardiac veins |
-most cardiac veins drain into coronary sinus -coronary sinus then drains into right atrium
-coronary sinus -great cardiac (anterior interventricular) vein -middle cardiac (posterior interventricular) vein -small cardiac vein |
|
|
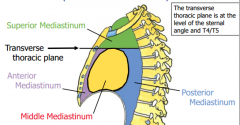
Mediastinum |
-interpulmonary space (the area between the pulmonary cavities) -contains all the thoracic viscera and structures except for the lungs -extends from superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm, and from the sternum to the thoracc vertebrae (4 divisions) |
|
|
Divisions of the Mediastinum |
|
|
|
Anterior Mediastinum |
-Between body of sternum and pericardium CONTAINS: -remnants of thymus gland -internal thoracic a. & branches -lymph nodes -fat -connective tissue -thymus (inferior part) -internal thoracic arteries and veins (deep branches) |
|
|
Middle Mediastinum |
-Between right and left pulmonary cavities CONTAINS: -pericardium -right main bronchus -heart -arch of azygos vein -ascending aorta -pulmonary trunk -superior vena cava |
|
|
Superior Mediastinum |
-From superior thoracic aperture to transverse thoracic plane CONTAINS: -brachiocephalic veins -thymus gland (early childhood) -superior vena cava -vagus nerve -arch of aorta & branches (ABCS) -left recurrent laryngeal nerve -trachea -phrenic nerve -esophagus -ligamentum arteriosum* -thoracic duct
|
|
|
Great Vessels of Mediastinum |
-right common carotid -left common carotid artery -right subclavian artery -left subclavian artery -right brachiocephalic vein -left brachiocephalic trunk -brachiocephalic trunk -aortic arch -superior vena cava |
|
|
Posterior Mediastinum |
-Between pericardium and T4-12 vertebrae CONTAINS: -esophagus -descending thoracic aorta -thoracic duct -azygos and hemiazygos veins -vagus nerves -thoracic sympathetic trunk |
|
|
Veins of Thorax |
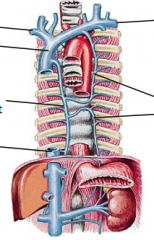
-brachiocephalic v -superior vena cava -azygos v (drains right thorax) -hemiazygos v (drains left thorax) -inferior vena cava |
|
|
Lymphatic System |
-returns excess tissue fluid (lymph) to the bloodstream -lymph nodes filter foreign materials, trigger immune system MAJOR LYMPH VESSELS: Thoracic duct- drains 3/4 of body, empties into left subclavian vein Right lymphatic duct- drains upper right quadrant, empties into right subclavian vein |

