![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
-prone vs supine?
-describe the anatomical position |
prone: lying with the face downwards. supine: lying on the back with the face upwards.
anatomical position: body is an erect, standing position, with arms at side, palms turned forward, the lower limbs parallel and the toes pointing forward. |
|
|
1) toward the head end of the body, or upper
2) toward the midline of the body or structure 3) toward the tail end of the body, or lower 4) toward the surface of the body 5) the front surface of the body 6) toward the midline of the body 7) away from a point of reference, usually the trunk or midline of the body, or the source of a part. 8) away from the midline of the body 9) near or toward a point of reference, usually the trunk or midline of the body, or the beginning source of a part. 10) the back surface of the body 11) the actual midline directly at the center. |
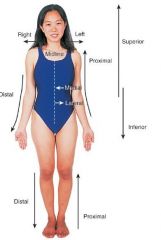
1) superior, cephalic, or cranial
2) deep, central, or internal 3) inferior or caudal 4) superficial or external 5) anterior or ventral 6) medial 7) distal. ex: the hand is located at the distal end of the forearm, the elbow at the proximal end. 8) lateral 9) proximal. 10) posterior or dorsal 11) median |
|
|
1) the vertical plane dividing the body into two apparently symmetrical halves
2) any lengthwise vertical plan running from front to back, dividing the body or any part of of it into right and left sides 3) any lengthwise vertical plane running from side to side, dividing the body or any part of it into anterior and posterior portions 4) a crosswise plane dividing the body or any part of it into upper and lower parts |
1) median
2) sagittal 3) frontal or coronal 4) transverse or horizontal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
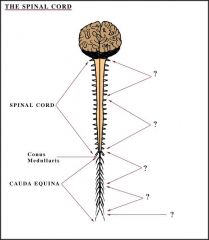
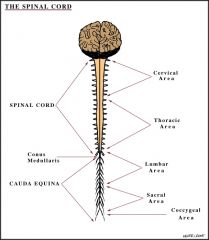
(insert number) cranial nerves and (insert number) spinal nerves form the (?).
-DESCRIBE the parts of central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) -Af- vs Ef-? |
12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves form the peripheral nervous system.
CNS= brain and spinal cord PNS= the spinal cord has two parts: 1) Afferent (sensory) system from receptors in periphery to CNS 2) Efferent (motor) system: from CNS to effectors in periphery The Efferent (motor) system breaks down into: A) Somatic nervous system (SNS): from CNS to skeletal muscles B) Autonomic nervous system (ANS): from SNC to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. We have no control over the ANS. The ANS then breaks down into: a) Sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) b) parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest) af-= toward ef-=away "SAME DAVE"="Sensory Afferent, Motor Efferent. Dorsal Afferent, Ventral Efferent." |
|
|
1) smooth vs striated? (how are they controlled in the PNS?)
2) define what a spinal nerve does? |
1) smooth-autonomic
striated-sensory, motor 2) it's a nerve that carries information to or from the body to the spinal cord (like a telephone) |
|
|
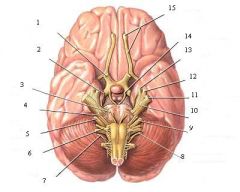
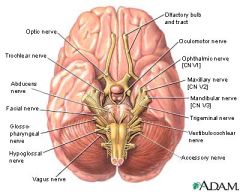
list the cranial nerves in order, with correct roman numeral, and what it controls (motor, sensory, or both). And correct initials/designations for each.
|
I Oh (Olfactory)
II Oh (Optic) III Oh (Oculomotor) IV To (Trochlear) V Touch (Trigeminal) VI And (Abducens) VII Feel (Facial) VIII Vagina (Vestibulocochlear aka Auditory) IX Gives (Glossopharyngeal) X Victor (Vagus) XI A (Accessory) XII Hard-on (Hypoglossal) I Some (Sensory) II Say (Sensory) III Marry (primarily Motor) IV Money, (primarily Motor) V But (Both) VI My (primarily Motor) VII Brother (Both) VIII Says (Sensory) IX Big (Both) X Boobs (Both) XI Matter (primarily Motor) XII More (primarily Motor) "You have I nose & II eyes" I - Olfactory n.; II - Optic n. Cranial nerves: CN I, CN II, CN III.... Spinal nerves a) cervical apical nerve: Cn1, Cn2... b) thoracic nerve: Tn1, Tn2.... c) Lumbar: Ln1, Ln2.... d) Sacral: Sn1, Sn2.... e) Coccygeal: Con1 |
|
|
sensory, motor, or both?
1) dorsal root 2) ventral root 3) spinal nerve 4) dorsal ramus 5) ventral ramus Ramus vs Root? |
1) sensory
2) motor 3) both sensory and motor 4) both sensory and motor (mixed) 5) both sensory and motor (mixed) Root=only sensory or motor Ramus=has mixed |
|
|
30 pairs of spinal nerves have both (mixed) sensory and motor fibers except...
|
except ONE: Cn1
the cervical nerve 1 only has motor fibers |
|
|
define Splanchnic nerves and list them
|
Nerves that synapse OUTSIDE the sympathetic chain
a) T5-T9 Greater Splanchnic-celiac ganglion b) T10-T11: Lesser Splanchnic- Superior mesenteric ganglion c) T12: Lowest Splanchnic- Aortico- Renal Ganglion d) L1-L2: lumbar splanchnic- Inferior mesenteric ganglion note: pelvic splanchnic nerves are located at sacral spinal nerves 2,3,4 ("sacral 234 keeps the penis off the floor") |
|
|
Where are the cell bodies located at in the cranial nerves?
|
CN III, VII, IX, and X and spinal nerves S2,3,4 which are the pelvic splanchnics
|
|
|
the autonomic nervous system consists of the parasympathetic system and the sympathetic system. the cell bodies for these systems are located in specific areas of the nervous system, list where they are located for both systems.
|
parasympathetic system- cell bodies located in cranial nerves III, VII, IX, and X, and sacral spinal nerves 2, 3, and 4 ("S2,3,4 keep the penis off the floor") which are the pelvic splanchnics (rest/DIGEST--hindgut, genitals, bladder, rectum, etc).
sympathetic system- also called the thoracolumbar part of the autonomic nervous system. it all occurs in thoracic and lumbar region: T1-L2 (L3) contribute fibers toward the formation. |
|
|
for the sympathetic nervous system the preganglionic __1__ fibers from the spinal cord enter the __2__ rami communicantes of the sympathetic trunk then:
1) synapse at the __3__ level (postganglionic sympathetic fibers leave through the __4__ rami communicantes). 2) go up the chain and synapse at a __5__ level (ex: superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglion) 3) passes through the sympathetic trunk __[with/without] synapsing but __[do/do not]__ synapse with other ganglia outside the chain...ex: a) T5-T9=______ b) T10-T11=_____ c) T12=_____ d) L1-L2=_____ |
1) myelinated
2) white 3) same 4) grey 5) different 6) without 7) do a) greater splanchnic- celiac ganglion b) lesser splanchnic- superior mesenteric ganglion c) lowest splanchnic- aortico-renal ganglion d) lumbar splanchnics-inferior mesenteric ganglion |
|
|
pre-ganglionic vs post-ganglionic
|
pre=fibers from the CNS to the ganglion
post=fibers from the ganglion to the effector organ *EVERY nerve has to synapse somewhere in the body. there are hundreds of fibers in these nerves, not just 1. some fibers synaps at one level and others at other levels. |
|
|
3 fibers of skin and functions of skin
|
elastic, collagen, reticular.
protection, reception, excretion/absorption (topicals), regulation of body temperature |
|
|
1) skin freely movable over superficial fascia, maybe wrinkled or pulled up into folds--except palm and soles. over joints.
2)skin is not smooth, geometric pattern of creases, follows bundle of collagen fibers in dermis of skin 3) found in palm of hand and sole of foot--alternate ridge and grooves and give finger and foot prints |
1) flexure lines
2) tension line or langer's lines 3) friction line |
|
|
1) what is a dermatome?
2) (adjacent/nonadjacent) dermatomes overlap 3) __(#)__ contiguous spinal nerves are needed to be anesthesized during surgical intrusion of the skin 4) it is impt to know the dermatomes because they help detect ____ |
1) an area of skin supplied by the sensory fiber of a dorsal root through dorsal and ventral rami of the spinal nerves
"tome"=section "derma"=skin 2) adjacent 3) 3 3) neurological lesion (ex: chicken pox becomes shingles) |
|
|
during surgery always cut along _____. because if you cut ____ it does not heal and it scars.
|
cut along the collagen lines aka tension lines.
if you cut collagen fibers it does not heal and it forms scars. |
|
|
stetch marks vs keloid
|
stretch marks- seperation of the collagen fibers -- use oil to avoid stretch marks
keloid-excessive scarring, collagen secreted by fibroblast cells-- inject an antifibroblastic proliferation in area of scarring |
|
|
key dermatomes:
1) nipple 2) navel 3) above the pubic bone 4) hallux (big toe) 5) middle finger 6) little finger |
1) T4
2) T10 3) T12 4) L4 5) C7 6) C8 |
|
|
what is fascia and the diff b/w superficial and deep fascia
|
fascia=mixture of fat and connective tissue ("packaging material")
superficial fascia-usually contains more FAT than fibers--under skin deep- usually contains more FIBERS than fat |
|
|
1) the mammary gland is composed of what?
2) the breast is located b/w the ___ and ___ and between ribs ____ 3) nipple is in intercostal space ___ on top of the pectoralis major and minor muscles 4) a nipple is a ____ 5) the two major contents of breast are ___ and ___. a non-lactating breast is mostly ____ 6) 60% of carcinoma of the breast is located in the ______ quadrant |
1) breast and axillary tail
2) sternum and mid-axillary line between ribs 2-6 3) 4 (b/w ribs 4 and 5) 4) modified sweat gland 5) fat and glands. fat. 6) superolateral |
|
|
75% of the lympatic drainage of the breast is into the ____
-name the the other lymphatic drainages |
axillary lymph nodes--75%
transpectoral, parasternal (internal thoracic artery), to opposite breast, ligamentum teres (to liver) |
|
|
the lympatic drainages of the thorax/breast allow the spread of carcinoma to what 3 areas?
|
lungs, mediastinum (middle of sternum), and liver
|
|
|
in a radical mastectomy what is removed?
|
breast, axillary lymph nodes, muscles both major and mino pectoralis muscles, medial and lateral nerves, medial and lateral arteries, minor arteries, opposite breast
|
|
|
thoracic inlet starts and ends where and consists of what?
|
a) 1st rib, manubrium sterni, 1st thoracic vertebra
structures located in inlet: trachea esophagus nerves (vagus, phrenic) apex of lung |
|
|
probability of daughter getting breast cancer if mother or aunt has it?
|
mother-5x
aunt-3x |
|
|
thoracic outlet
|
T12, rib 12, costal margin
|
|
|
landmarks:
1) xiphoid process is at what level? 2) sternal angle is where? |
1) level of T10 or T11
2) lower border of T4 (impt in respiration bc it tells us the thoracic cage is NOT horizontal but is tilted forward and downward) |
|
|
how many ribs? identify true/false ribs and the typical/atypical ribs
|
12 pairs
Rib 1-7 articulate DIRECTLY through their costal cartilages with sternum aka TRUE RIBS Ribs 8-9-10 articulate with ADJACENT costal cartilage aka FALSE RIBS Rib 11-12 aka floating ribs aka FALSE RIBS end among the muscles of the body wall Typical ribs- Ribs 3-9 with head, neck, shaft, costal groove shelters the nerve, artery and vein (aka the neurovascular bundle). atypical- ribs 1,2 and 10-12 are unique for each one. RIBS DO NOT ARTICULATE WITH THE STERNUM DIRECTLY BUT THROUGH COSTAL CARTILAGE |
|
|
functions of thoracic cage
|
1) protects internal organs
2) attachment of muscle 3) assist in breathing |
|
|
muscles of thoracic wall and what ribs they go to
|
*1) serratus anterior ('serratus'='jagged')
-forms medial wall of axilla from ribs 1-8 -inserts in costal surface of scapula including: i: superior angle ii: inferior angle iii: medial border |
|
|
what nerve is found inside the AXILLA and what are its functions and what happens if you cut it?
|
LONG THORACIC NERVE
fcn: rotates scapula, abductor of arm and elevation above the horizontal plane and respiration cut nerve? -winging of scapula -loss of elevation -problems in respiration |
|
|
what are the 3 muscle intercostals and their attachment, fcn, and corresponding nerve
|
1) EXTERNAL INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE
attachment: lower borders of the ribs 1-11 to the upper borders of ribs 2-12 -*fibers run down and forward at the costochondral joint are replaced by the external intercostal membrane fcn: elevate the rib cage--muscle of inspiration nerve: corresponding intercostal nerves 2) INTERNAL INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE -*fibers run down and backward -attachment: same as external intercostal muscle -internal intercostal membrane is near the vertebrae fcn: muscle of expiration -nerve: corresponding intercostal nerve 3) INNERMOST INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE has 3 parts: i) the innermost intercostal per se. it is mostly membrane ii) subcostalis muscle--found at the ANGLE OF RIB ONLY; attachment- b/w the ribs posteriorly and may cross 1 or 2 ribs and attach to the third rib; fcn- expiration iii) sternocostalis muscle (transversus thoracis muscle)- attachment- back of xiphoid process and sternum; inserts- in the cotal cartilages; nerve-intercostal nerves; fcn- expiration *INNTERMOST INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE FIBERS RUN DOWN AND BACKWARD ALSO |
|
|
nipple of the breast is in intercostal space __
|
4
|
|
|
how many intercostal spaces are there?
|
11 intercostal spaces--space below the 12th rib is the subcostal space
|
|
|
posterior intercostal neurovascular bundle is bw the _____ and ____
|
internal intercostal muscle and the innermost intercostal muscles
|
|
|
what is the arterial blood supply of the anterior aspect of intercostal spaces?
|
internal thoracic artery (a branch from the subclavian artery)
|
|
|
what is the arterial blood supply of the posterior aspect of the intercostal spaces?
|
a) 1st intercostal space- highest intercostal artery (from the costocervical trunk which is a branch from the subclavian artery)
b) 2-11- by posterior intercostal arteries (from thoracic aorta directly) c) subcostal space ("12th")- by the subcostal artery (from the thoracic aorta directly) |
|
|
what is the venous blood supply of the anterior aspect of the intercostal spaces?
|
internal thoracic vein drains into the brachiocephelic vein
|
|
|
what is the venous blood supply of the posterior aspect of the intercostal spaces?
|
the right and left side are different and examined seperate:
RIGHT SIDE -1st intercostal space- highest intercostal vein drains into the brachiocephalic vein 2-3- higher intercostal drains into azygos (right side) 4-11- intercostal veins drain directly into the azygos vein subcostal vein (12) drain directly into the azygos vein NOTE: THE AZYGOS VEIN DRAINS INTO THE SUPERIOR VENA CAVA LEFT SIDE: 1st- highest intercostal vein drains into the brachiocephalic vein 2-3-4 intercostal veins join to give the Accessory Hemiazygos Vein 5-11 intercostal veins and the subcostal vein (12) join together to give the Hemiazygos vein. NOTE: THE ACCESSORY HEMIAZYGOS AND THE HEMI-AZYGOS CROSS OVER TO THE RIGHT SIDE INDEPENDANTLY OR JOIN AS A SINGLE UNIT AND DRAIN INTO THE AZYGOS VEIN NOTE: THE ACCESSORY HEMI-AZYGOS MAY DRAIN INTO THE BRACHIOCEPHALIC VEIN ALSO |
|
|
what are the layers of penetration in the mid-axillary line (in order)?
|
1) skin
2) superficial fascia 3) deep fascia 4) serratus anterior 5) external intercostal muscle 6) internal intercostal muscle 7) innermost intercostal muscle 8) endothoracic fascia 9) parietal pleura 10) pleural cavity 11) visceral pleura 12) lungs note: fascia is not a muscle, it is fat and connective tissue |
|
|
1) what is the fcn of endothoracic fascia?
2) thickening of the fascia over the apex of the lung is called ____ |
1) to prevent parietal pleura (surrounds lungs) from rubbing against the innermost intercostal muscles
2) Sibson's Fascia |
|
|
what does the thoracic cavit contain?
|
1) a) two pleural cavities, seperate and enclosed spaces (has pleural fluid) and one
b) mediastinum Other structures inside the thoracic cavity include: 1) heart 2) lungs 3) trachea 4) esophagus 5) vagus and phrenic nerves, etc |
|
|
pleural reflections:
1) fcn of pleural fluid? 2) ___ is not covered by pleural membrane 3) remove fluid with ____ 4) ___ lines the muscle wall 5) ___ covers the organ 6) ___ is an area of parietal pleura reflected on apex of lung |
1) minimize friction bw the parietal pleura and visceral pleura
2) root of lung 3) mid-axillary tap 4) parietal pleura 5) visceral pleura 6) cupola |
|
|
pleural recess':
____ is found at the junction of the costal and diaphragmatic parietal pleura near the mid axillary line. a pleural cavity tap can be done here in the intercostal space #___ what is the fcn of these recess'? |
costo-diaphragmatic recess (space). intercostal space 9
other 2: costo-mediastinal recess and costo-vertebral recess fcn: it allows expansion of the lungs during inspiration |
|
|
pleural blood and nerve supply:
1) parietal- 2) visceral- 3) nerve- 4) visceral pleural- 5) phrenic- |
1) parietal- intercostal artery, internal thoracic artery
2) visceral--bronchial artery (supply the lung) 3) nerve--parietal pleura--*VERY sensitive to pain, supplied by intercostal nerves T1-T11, subcostal and phrenic nerve (Cn 3,4,5) 4) Visceral pleural--*insensitive to pain. no sensory innervation 5) phrenic- motor nerve to the diaphragm |
|
|
what is the mediastinum?
|
the medial region bw the two pleural cavities contains all the structures in the chest except the lungs and pleural sacs
|
|
|
*sternal angle is at what level?
|
T4 level- a line through the sternal angle divides the mediastinum into superior above and inferior below
|
|
|
contents of superior mediastinum
|
1) arch of aorta and branches
these brances are: brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid, left subclavian 2)*brachiocephalic vein(s) is formed by the joining of the subclavian vein and internal jugulary vein 3) superior vena cava is formed by the joining of the right and left brachiocephalic veins 4) thymus (children) becomes fat in adults 5) esophagus 6) trachea 7) thoracic duct (bile and fat) |
|
|
contents of inferior mediastinum
|
3 compartments:
1) anterior mediastinum- from the posterior surface of the sternum to the anterior surface of the pericardial sac contents: fatty tissue, thymus, lymph nodes 2) middle mediastinum contents: heart, pericardium, main bronchi, great vessels, 3)*POSTERIOR MEDIASTINUM-- TO PERICARDIAL SAC AND DIAPHRAGM AND ANTERIOR TO THE THORACIC VERTEBRAE (5-12) LOWER EIGHT. contents: esophagus, thoracic aorta, azygos system, thoracic duct, vagus nerve, splanchnics nerves are from the sympathetic chain |
|
|
1) the posterior mediastinum goes from the pericardial sac and diaphragm and anterior to the thoracic vertebra #____.
2) is the trachea in the posterior mediastinum? 3) _____ is formed by the joining of the subclavian vein and internal juglar vein 4) ___ is formed by the joining of the right and left brachiocephalic veins 5) splanchnics nerves are from the ____ |
1) 5-12
2) no 3) brachiocephalic vein 4) superior vena cava 5) sympathetic chain. the sympathetic chain is NOT in the posterior mediastinum only the splanchnics |
|
|
mediastinoscopy?
|
to remove tissue from the anterior and superior mediastinum to examine the lymph nodes. incision is made at the jugular notch
|
|
|
trachea:
1) how many C bars of cartilage? 2) begins in the neck at what location? 3) bifurcates at ____ into right and left main bronchi |
1) 15-20. 9-15cm long and 2.3 cm in diameter
2) CV6 3) sternal angle (TV4) |
|
|
compare the right and left bronchus
|
right: wider-shorter and more in vertical plan then left bronchus. divides into superior lobar bronchus, middle and inferior lobar bronchi (3 branches!)
left bronchus: narrower, l onger, and more horizontal plane than that of the right bronchus. passes in front (anterior to) of the exophagus. divides into superior and inferior lobar bronchii (TWO branches) |
|
|
*lateral view of the lungs:
-what are the fissures of the lungs? (levels) how many lobes and segments in the lungs? |
fissures-OBLIQUE begins 2.5" from the apex of lung and ends at COSTAL CARTILAGE 6
horizontal-costal cartilage LEVEL 4. found ONLY in the RIGHT lung the right lung has 3 lobs where as the left has only 2. the right lung has 10 segments and the left lung has 8 segments. |
|
|
lobes of the lung:
1) the ___ lobe is found above the horizontal fissure 2) the middle lobe is found bw the ___ and ___ fissures 3) inferior lobe is found below the ____ fissure |
1) superior lobe
2) oblique and horizontal fissures 3) oblique fissure |

