![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What nerves supply the smooth muscle of the Enteric nervous system?
|
Vagus, Sacral 2-4. which are parasympatheic
|
|
|
What nerves supply blood vessels:
1 of Body wall and limbs? 2 of Guts/viscera/Splanchna? |
1 sympathetic via paravertebral ganglia
2 sympathetic via pre-vertebral (anterior to the aorta) ganglia via enteric nervous system |
|
|
What are the 3 vascular divisions of the GI tract?
|
1 the foregut, supplied by celiac trunk
2 the midgut, by superior mes artery 3 - the hindgut - by inferior mes artery |
|
|
What are the components of the 3 vascular divisions of the GI tract?
|
1 - foregut: lower esophagus to 2nd part of duodenum
2 - midgut - remaining duodenum to 2/3 of TRANSVERSE colon 3 - hindgut - FInal 1/3 of trans colon thru rectum |
|
|
What are the innervations of the 3 vasculature components of the gut?
|
1 - foregut: thor splanchnic nerve, vagus nerve
2- midgut - thor splanchnic nerve, vagus nerve 3 - hindgut - Para: Pelvic splanchnics S2,3,4 and sympa: lumbar splanchnics |
|
|
Classify each of the following in terms of fore/mid/hind gut
1 - liver 2 - gall bladder 3 - bile duct 4 - pancreas/panc duct |
1 - fore
2 - fore 3 - fore 4 - fore and mid |
|
|
How is the innervation of visceral and parietal peritoneum different?
|
Visceral is supplied via para/sympa nerves, whereas the parietal is via somatic nerves
|
|
|
What is retroperitoneal? What organs are such(4)?
|
Attached to visceral peritoneum ONLY VIA the anterior side, on posterior it is attached to the body wall.
INCLUDES: middle half of duodenum, pancreas, ascending/descending colons |
|
|
How does one define the transpylorc plane?
|
It is 1/2 between jug notch and pubic symph, or xiphoid and umbilicus
|
|
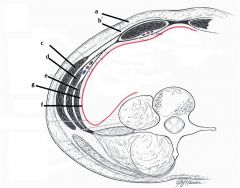
|
A - Camper's fatty fascia
B - scarpa's membranous fascia C - ex oblique D - Int oblique E - transverus abdominus F - Parietal peritoneum G - Transversalis fascia |
|
|
Which organ removes damaged blood cells from circulation?
|
Spleen
|
|
|
Which organ secrets trypsin?
|
Pancreas
|
|
|
How is the pancreas supplied? (vascularly)
|
via the Celiac trunk and via the superior mesenteric artery
|
|
|
What does the liver attach to superiorly? via what?
|
The diaphragm, via the falciform ligament
|
|
|
What is significant about the liver's inferior surface?
|
The gallbladder
|
|
|
What are the vascular supply divisions of the liver?
|
The right is supplied by right hepatic artery,
Left, quadrate and caudate supplied by Left hepatic artery AND PORTAL VEIN: for procesing |
|
|
Where is the gallbladder aligned?
|
The mid-clavicular line (right side)
|
|
|
Where does blood from the liver go?
|
3 hepatic veins to the IVC
|
|
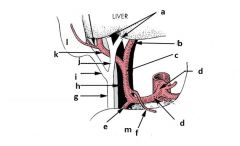
|
A - r/l hepatic ducts
b - l hepatic artery c - proper hepatic artery d - celiac trunk d - common hepatic artery e - gastroduodenal artery f - r gastric artery g - bile duct h - portal vein i - cystic duct j - common hepatic duct k - right hepatic artery l - gall bladder m - duodenum |
|
|
Thru what and where is bile released into the duodenum?
|
At the duodenal papilla, the common bile duct and main pancreatic duct combine and enter
|
|
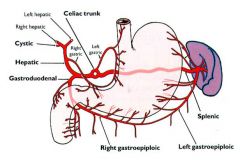
|
A - right gastric artery
B - left gastric artery C - gastroduodenal artery D - right and left gastro-omental arteries E - splenic artery |
|
|
What is significant of the muscles of the stomach wall? I
|
It has 3 (vs2) w/ longitudinal, circular and a 3rd oblique layer
|
|
|
What are the duodenal divisions? Which are retroperitoneal?
|
1st = bulb, receives acid
2nd = where pancreas/liver open, IS RETRO 3rd - Jejunum 4th - Ileum |
|
|
what is the ileocecal junction?
|
Of small/large bowel
|
|
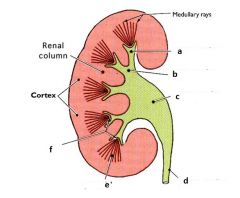
|
A - minor calyx
B - major calyx C - renal pelvis D - uretur E - pyramid F - papilla |
|
|
What arteries supply adrenal glands?
|
Phrenic arteries and renal arteries And direct branches of aorta
|

