![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does the fusion of spermatozoon and oocyte occur? What is the fusion called?
|
In the fallopian tube, called fertilization. Now called a Zygote, begins embryogenesis
|
|
|
What is a zygote classified as, as it is able to form a whole organism?
|
Totipotent blastomere
|
|
|
When are most of the organs formed by? What does this signify the beginning of?
|
8 weeks - the FETAL PERIOD
|
|
|
In traveling the fallopian tubes, what keeps the embryo from attaching to the oviduct?
|
The Zona pelliucida that coats it
|
|
|
Where does fertilization occur?
|
Oviduct
|
|
|
What significant event occurs after the 3rd round of cleavage?
|
Compaction of the cells into a 16-cell morula
|
|
|
When does cavitation occur? How does it occur? What is its result?
|
The trophoblasts secrete fluid to make a bastocoel (cavity) after the morula is formed, which is now a BLASTOCYST
|
|
|
Describe the polarity created by cavitation of the morula.
|
The blastocyst has an Embryonic pole (toward the cell mas) and Ab-embryonic pole (away from the cell mass)
|
|
|
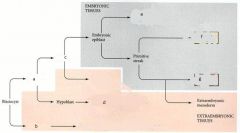
The 2 cells of the morula (Inner and Outer) each become what?
|
Outer - placenta. Inner - inner cell mass - become embryo/yolk sac/amnion/allantois
|
|
|
|
|
|
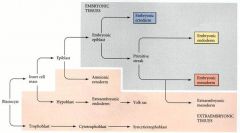
What is Gastrulation? What does it begin with?
|
Begins with formation of primitive streak (from the epiblast) The process of bilaminer disc becoming trilaminer disc
|
|
|
Which of the 3 trilaminer layers is formed 1st? How?
|
The epiblast cells migrate inward into the primitive groove to DISPLACE the hypoblast cells there and make the ENDODERM
|
|
|
Which of the 3 trilaminer layers is formed 2nd? How?
|
The next layer of cells migrates between the endoderm and epiblast migrates into the prim groove to form the MESODERM
|
|
|
Which of the 3 trilaminer layers is formed 3rd? How?
|
The remaining epiblast cells (did not migrate) form the ECTODERM
|
|
|
Where is Hensen's Node located? What does it become?
|
It is near the ANTERIOR or ROSTRAL end, which becomes foregut/Head mesoderm (CNS) and NOTOCHORD
|
|
|
What is the name of the DEEPEST area of the primitive groove, adjacent to Hensen's Node?
|
Primitive Pit
|
|
|
What is the Prochordal plate?
|
small aggregation of cells that migrates as part of hte 2nd wave htru Hensen's node
|
|
|
What is the primitive structure that becomes the oral cavity, located just rostral to the prochordal plate?
|
The buccopharangyeal membrane
|
|
|
How is the notochord formed?
|
The primiitve streak regresses caudally and lays down notochord
|
|
|
What is Neurulation? What other important formation occurs at this stage?
|
Formation of the neural tube from the neural groove in the ectoderm. Also, the mesoderm forms the somites
|
|
|
What protein supports development of the ectoderm? What inhibits it, thereby inducing development of NEUROectoderm?
|
Noggin and Chordin, also Shh which develops the Neural Tube
|
|
|
What is the TF secreted by neural crest cells? What does it do?
|
Slug - promotes cell migration
|
|
|
Which protein is thought to Help in neural fold fusion (closing the tube)
|
Pax3
|
|
|
Which genes help to specify the anterior-posterior positions of the embryo?
|
Hox genes
|
|
|
What is the term for the mesoderm lying laterally to the neural tube in early development? What is the next structure this gives rise to?
|
Paraxial Mesoderm---Somites
|
|
|
What are the 3 divisions of a somite?
|
Sclerotome = vertebrae/IV discs
Myotome - trunk muscles Dermatome - Dermis |
|
|
What is the term for the Mesoderm that is LATERAL to the PARAXIAL mesoderm (3 away from neural tube in early development) What does it give rise to
|
Lateral Plate mesoderm - Splanchnic (wall of the gut)
|
|
|
If the paraxial mesoderm does not become somites, what does it become?
|
The head:
1 Somitomeres - jaw muscles 2 occipital somites - layrng/pharyng muscles 3 prechordal mesoderm - eye muscles |
|
|
What genes can Counteract the inhibition by Shh genes? Where do they come from?
|
Wnt genes - from the dorsal neural tube
|

