![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the Herpes viruses
|

-
|
|
|
HHV-1 or HSV-1 causes what problem in children
|
Gingivostomatitis and Oral lesions
|
|
|
HHV-1 or HSV-1 causes what problem in adults
|
Pharyngotonsillitis, Esophagitis
and Oral lesions |
|
|
What type of virus is HHV-1 or HSV-1?
|
ds DNA virus; enveloped
|
|
|
What cells do HHV-1 or HSV-1 affect?
|
Lytic infections of fibroblasts and epithelial cells
|
|
|
for HSV-1 what are Primary Reactivation Events?
|
Febrile illness (common cold)
- Direct sunlight (UV-B) - Stress - Trauma - Menstruation - Spicy or acidic foods - Immunocompromise |
|
|
What are some complication of HSV-1 in Immunocompetent pts
|
Perinatal Infection (mostly HSV-2)
Necrotizing Encephalitis Keratoconjunctivitis Meningitis (mostly HSV-2) |
|
|
Leading cause of infectious blindness in US
|
Keratoconjunctivitis
|
|
|
What are some complication of HSV-1 in Immunodeficient pts
|
Pneumonia
Severe Mucocutaneous Infections |
|
|
By age 30, _____% individuals HSV-1 seropositive
|
50-80
|
|
|
Diagnostic for HSV-1:
Multinucleated cells AKA |
syncytia
|
|
|
Diagnositic for HSV-1:
____ bodies |
inclusion
|
|
|
DDx of HSV-1 lesions
|
Candidiasis
Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Aphthous ulcers (canker sores) Small, round (ovoid), recurrent ulcers with erythematous halo and yellow-gray floor |
|
|
Diet high in L_____ shown to reduce HSV recurrent infections
|
Diet high in Lysine shown to reduce HSV recurrent infections
|
|
|
Drug used for treatment of HSV-1
|
Acyclovir (Zovirax)
|
|
|
HHV5 or CMV is what type of virus?
|
ds DNA virus; enveloped
|
|
|
HHV-5 or CMV Replicates in ___________ and ___________ (salivary glands and kidneys)
|
HHV-5 or CMV Replicates in macrophages and fibroblasts (salivary glands and kidneys)
|
|
|
HHV-5 or CMV Establishes latency in _ cells and __ stromal cells
|
HHV-5 or CMV Establishes latency in T cells and BM stromal cells
|
|
|
Mononucleosis Syndrome (HHV-5 or CMV):
Fever, malaise, pharyngitis, blood atypical lymphocytes Monospot-________ test result (test for heterophile Ab) Duration: ~60d |
Mononucleosis Syndrome (HHV-5 or CMV):
Fever, malaise, pharyngitis, blood atypical lymphocytes Monospot-negative test result (test for heterophile Ab) Duration: ~60d |
|
|
What conditions are necessary for HHV5 or CMV to cause GI tract symptoms?
|
Immunocompromised Diseases
Disseminated disease in lungs, GI tract (esophagitis), liver, retina and CNS |
|
|
Only host for CMV
|
humans
50-100% seropositive in areas within the US Worldwide distribution |
|
|
Blood test for CMV
|
Peak viral titers 4-7wks after infection; measure anti-CMV IgM
|
|
|
DDX for CMV
|
Enteroviruses
HIV opportunistic infection Hepatitis A, B, D, E HHV6 EBV (mononucleosis) |
|
|
Prevention & Treatment
of CMV |
Prevention & Treatment
Gancicyclovir (Cytovene) or Foscarnet (Foscavir) – treat complications Gancicyclovir useful as a prophylactic prior to BM transplant |
|
|
type of virus of enterovirus
|
ss RNA virus; nonenveloped
Picornaviridae:Polioviruses, Coxsackie viruses A & B, Echoviruses, Hepatitis A |
|
|
Clinical Syndromes
Coxsackie virus A: |
Herpangina (3mo-16yrs)
Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease (<10yrs) |
|
|
Clinical Syndromes
Coxsackie virus B: |
Pleurodynia
|
|
|
Clinical Syndromes
Coxsackie viruses A & B (Echoviruses also): |
Aseptic Meningitis
Myocarditis (neonates, young children) |
|
|
Where does Enterovirus replicate?
|
peyer's patches
|
|
|
Echo virus affects what body parts?
|
skin, muscle, meninges
|
|
|
Cox a and B affects what body parts
|
muscle
|
|
|
Cox A affects what body parts
|
skin and muscle
|
|
|
Complications of Enterovirus
|
Complications
Acute Hemorrhagic Conjunctivitis Secondary bacterial infections Coma (Aseptic Meningitis) |
|
|
Enterovirus is nonenveloped and is resistant to pH and _____.
|
detergents
|
|
|
DDX of Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
|
DDX of Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
HSV-1 infection Varicella |
|
|
DDX of Aseptic Meningitis
|
DDX of Aseptic Meningitis
Arbovirus infection Lyme disease Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Erhlichiosis |
|
|
DDx of Pleurodynia
|
DDx of Pleurodynia
Pneumonia Acute abdomen |
|
|
DDx of Herpangia
|
DDx of Herpangia
Bacterial or other viral tonsillitus |
|
|
Treatment and Prevention of enterovirus
|
Prevention through adequate sanitation practices
Treat symptomatically |
|
|
_______ esophagitis is by far the most common esophageal infection
|
Candida esophagitis is by far the most common esophageal infection
|
|
|
Conditions predisposing to Candida esophagitis in the normal host include:
A_________ use Inhaled or ingested c_________________, Antisecretory therapy or hypochlorhydric states D_______ ________. _______ism, malnutrition, and advanced age |
Conditions predisposing to Candida esophagitis in the normal host include:
Antibiotic use Inhaled or ingested corticosteroids, Antisecretory therapy or hypochlorhydric states Diabetes mellitus. Alcoholism, malnutrition, and advanced age |
|
|
Symptoms of Infectious Gastroenteritis
|
Diarrhea
Nausea Vomiting Important complications: Dehydration Malnutrition Electrolyte imbalances Death |
|
|
Main cause of childhood viral gastroenteritis
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
Rotavirus is what Type of virus
|
ds RNA virus; nonenveloped
Reoviridae family |
|
|
Rotavirus lyses the cell:
Loss of villus epithelial cells results in Decreased __ absorption Decreased level of intestinal ___________ases Decreased absorption of ____ose and other macromolecules Increased water enters lumen |
Rotavirus lyses the cell:
Loss of villus epithelial cells results in Decreased Na absorption Decreased level of intestinal disaccharidases Decreased absorption of lactose and other macromolecules Increased water enters lumen |
|
|
nonenveloped viruses: what is the worry?
|
they are resistant to acid, detergents, and disinfectants
can use 95% EtOH and chlorine to kill them |
|
|
Diarrhea from rotavirus also results from viral protein (____) which acts as enterotoxin- causes excess ________ secretion
|
Diarrhea from rotavirus also results from viral protein (NSP4) which acts as enterotoxin- causes excess chloride secretion
|
|
|
How does rotavirus bind to villus epithelial cells
|
Viral capsid protein (vp4) binds to glycolipids on the membrane of villus epithelial cells in the small intestine
|
|
|
Describe ORT for rotavirus dastroenteritis
|
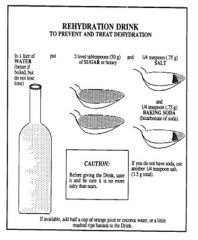
-
|
|
|
Again, describe ORT for gastroenteritis:
|
By providing a 1:1 proportion of Na to glucose, classic oral rehydration solution (ORS) takes advantage of a specific Na-glucose transporter (SGLT-1) to increase the reabsorption of Na, which leads to the passive reabsorption of water.
Alternatively, rice- and cereal-based ORS take advantage of Na-amino acid transporters to increase reabsorption of fluid and electrolytes |
|
|
Enteric _____viral infections are clinically and pathologically similar to rotavirus
|
Enteric adenoviral infections are clinically and pathologically similar to rotavirus
|
|
|
Ship sickness?
|
Norovirus
|
|
|
Norovirus is what type of virus?
|
ss RNA virus; nonenveloped
Caliciviridae family: Calicivirus, Astrovirus, Norwalk virus Resistant to freezing and temps up to 140ºF and chlorine reagents |
|
|
Rotavirus:
Greatest risk – 6-24mo Norovirus: Greatest risk – Adults and children >____ |
Rotavirus:
Greatest risk – 6-24mo Norovirus: Greatest risk – Adults and children >4yrs |
|
|
Rotavirus is most commonly infectious in what places?
|
Most common infections seen in day care centers, cruise ships, camps, institutions, military bases
|

