![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tells us how resistive an object is to a force |
Inertial mass, m=F/a |
|
|
It tells us about the attractive force an object will experience due to another |
Gravitational mass, m=r^2F/GM |
|
|
The principle of equivalence states that |
Mass inertia = mass gravitational |
|
|
Is weight larger at the North Pole or at the equator and why |
It is large at the North Pole as at the equator there is an opposing radial acceleration which gives a lower recording of weight |
|
|
Calculate g... |
g=GM/r^2 |
|
|
Explain Cavendish torsion balance |

|
|
|
Potential energy formula... |
U(g) = - Gm(1)m(2)/r |
|
|
What is the flat earth approximation |
We can use mgy to find the potential energy if we imagine flat earth and have changed the potential zero point to be at the earth's surface. Only when y<<radius(earth) |
|
|
Kepler's first law |
The orbit of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at 1 Focus |
|
|
Kepler's second law |
As a planet moves around it's orbit it sweeps out equal areas in equal times |
|
|
Kepler's third law |
P^2 =a^3 |
|
|
Newton's version of Kepler's third law |
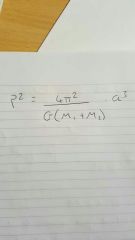
|
|
|
Satellite velocity |
V=sqrt(GM/r) |
|
|
What is the mechanical energy of a satellite in a circular orbit? |
1/2 * U(grav) |
|
|
Escape velocity and schwarzschild radius given by... |

|

