![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Whats do a plant cells and animals cells both have?
|
Cell membrane, Cytoplasm and Nucleus
|
|
|
Do Prokaryotes contain a nucleus?
|
No
|
|
|
Do Eukaryotes contain a Nucleus
|
yes
|
|
|
Are bacteria Prokaryote or Eukaryote cells?
|
Prokaryote
|
|
|
Which (prokaryote or eukaryote cells) 'Contains organelles that perform specialised functions'?
|
Eukaryote
|
|
|
In prokaryote cells is the DNA surrounded by an envelope?
|
No it isn't, they float around the cell.
|
|
|
Which cell (pro or eu) is considered to be more primitive?
|
Prokaryote.
|
|
|
Is the nucleaus of a Eu cell bound by one or two membranes?
|
2
|
|
|
Decribe what plasmosmata do? (3 main points)
|
They are strands of cytoplasm that protrude through the cell wall, connecting cells and transporting material.
|
|
|
Describe the role of the Vacuole? (3/4 points)
|
it's a water filled organism which pushes the cytoplasm outward against the cell wall giving rigidity or turgidity to the cell.
|
|
|
What are plasmids (2 points)
|
They have an intricate internal structure of folded membranes increasing the internal surface area on which chemical reactions occur.
|
|
|
Whats the main function of a mitrochondria (2 points)
|
Its the main sites of aerobic respiration.
energy release = ATP molecules |
|
|
What are crisie when talking about mitrochondria?
|
They are the inner folds of the mitrochondria
|
|
|
What shape are mitrochondria?
|
Sausage shape.
|
|
|
What 4 things do mitrochondria contain?
|
Mitochondria are filled with a jelly like matrix containing proteins, lipids, ribosomes and loops of DNA.
|
|
|
What happens in the Smooth ER?
|
Site of lipid, steroid and carbohydrate synthesis.
|
|
|
Which ER contains ribosomes?
|
Rough ER
|
|
|
Which ER is the site of protein synthesis?
|
Rough ER
|
|
|
What are CISTERNAE when discussing ER? (1 point)
|
Fluid filled spaces/sacs between the membranes.
|
|
|
What are Golgi apparatus made from?
|
Small pieces of Rough ER
|
|
|
Are golgi bodies smooth or rough?
|
Smooth
|
|
|
What is the function of the Goli body?
|
Modifies proteins after they are produced by the ribosomes.
|
|
|
What do ribosomes do? (1 point)
|
Synthesise proteins /enzymes
|
|
|
Are there lots of ribosomes in a cell or very few?
|
Lots.
|
|
|
What enzyme does lysosomes contain?
|
hydrolytic enzymes
|
|
|
Describe the function of a Lysosome? (2 points)
|
They destroy worn out organelles and completely break down cells after they have died.
|
|
|
Is the cell membrane on the inside or outside of the cell?
|
Inside
|
|
|
What does partially permeable mean?
|
It means that substances can pass through, both in and out of a cell.
|
|
|
Whats the main function of a chloroplast?
|
Site of Photosynthesis
|
|
|
What are the chlorophyll attached to?
|
The Thylakoids.
|
|
|
What is stroma when talking about chloroplast?
|
The fluid in the organ.
|
|
|
In the stroma are a series of flattened sacs called?
|
Thylakoids
|
|
|
These Thylakoids are stacked together to form...?
|
Grana
|
|
|
WHAT IS THE LARGEST CELL ORGANELLE?
|
Nucleus
|
|
|
Whats the function of a nucleus?
|
Its the 'control centre' of the cell
|
|
|
What is the Nucleolus? (2 points)
|
Its the ball in the middle of the nucleus that makes ribosomal RNA and assembles the ribosomes.
|
|
|
When refering to tissue what does meristematic mean?
|
Cells that are capable of cell division
|
|
|
How is an organ defined?
|
A collection of tissues with a specific function (flower, root, leaves)
|
|
|
What are the three types of tissue in a plant organ? (3 points)
|
Dermal, ground and vascular
|
|
|
What type of tissue is epidermis made out of?
|
Dermal tissue
|
|
|
What are the three types of ground tissue? (3 points)
|
Parenchyma, Collenchyma, sclerenchyma
|
|
|
Out of Parenchyma, Collenchyma and sclerenchyma, which has the thinest primary cell wall?
|
Parenchyma
|
|
|
Which ground tissue type is mainly found in the epidermis, pith and cortex?
|
Parenchyma
|
|
|
What is the main function of Collenchyma tissue?
|
As support
|
|
|
Is Collenchyma stronger or weaker than Parenchyma?
|
Stronger
|
|
|
Why is Collenchyma stronger than Parenchyma?
|
Has a second Cell wall layer with pectin.
|
|
|
Where is Chlorenchyma cells found?
|
In the palisade and spongy tissues in leaves and the stem.
|
|
|
Descrbe Sclerenchyma cells? (4 points)
|
Thickened, lignified secondary cell walls. They are the structural support, particularly in woody plants. Contains cellulose and lignin. Can be long stands of elongated cells
|
|
|
Typicall how thick is epidermis?
|
One cell thick
|
|
|
Desscribe what cutin is?
|
It's a waxy substance
|
|
|
What kind of tissue do the Xylem and Phloem make?
|
Vascular
|
|
|
Whats the Xylem and Phloems main function?
|
Transport water and solutes around the plant
|
|
|
Is the Xylem generally a one way or two way flow?
|
One way
|
|
|
is the Phloem generally a one way or two way flow?
|
Two way
|
|
|
What does the Xylem mainly transport around the plant? (2 points)
|
Water and dissolved minerals.
|
|
|
Does the Xylem or Phloem have lignin that supports it?
|
Xylem
|
|
|
What dos the Phloem transport?
|
Solutes e.g. sugars
|
|
|
How are the Solutes transported through the Phloem?
|
With energy prodived by the mitrochondria
|
|
|
When looking at a cross section of a vascular system, does the Xylem or Phloem appear larger?
|
Xylem
|
|
|
Draw a flower and label.
|
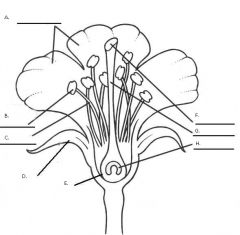
Label the parts of the flower from A to H.
A. Petals B. Anther C. Filament D. Sepal E. Ovary F. Stigma G. Style H. Ovule |
|
|
Draw and label the parts of the cross section of a leaf.
|
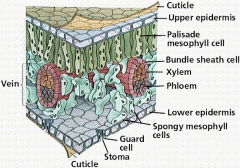
|
|
|
Draw and label the parts of a cross section of a grape berry.
|
http://www.thefullwiki.org/Grape
Check against this pic |

