![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
observation/inference |
observation: quantitative and qualitative qualitative:using your senses, qualitative: numerical, involves measurment inference: are conclusions that you make based on observations |
|
|
variables Independent |
Independent variable is the variable that you adjust or change,
|
|
|
examples of variable independent/dependent and control |
lights(independent variables) growth rate(dependent variable) pots,location,soil,species of plant,brand of light,conditions,temperature(constant variable) |
|
|
PARTICLE THEORY |
particle theory states that all matter consists of many small particles which are constantly moving or are in a continual state of motion. |
|
|
FIVE POINTS OF THEORY |
1. all matter is made up of tiny,invisible particles 2. particles have empty spaces between them 3. particles move faster and further apart when they are heated 4. particles attract each other, so they tend to stick together rather than fly apart |
|
|
states of matter |
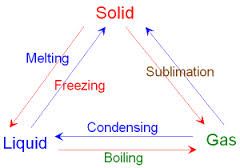
solid , liquid , gas |
|
|
physical and chemical properties |
physical property: is observed with senses and is determined without destroying matter chemical property: indicates how a substance reacts with something else and that the matter will be changed into a new substance after the reaction |
|
|
physical properties |
melting point, boiling point, viscosity, ductility,malleability, density, solubility |
|
|
chemical properties |
combustibility, reaction with acid, flammability, light sensitivity |
|
|
physical/chemical change |
physical change occurs when thee substance changes is size,shape or form and no new substance is formed chemical change occurs when there is a change in the physical and chemical properties, and a new substance is formed (5 indicators are odour,colour,temp.,gas bubbles and precipitate) |
|
|
matter |
anything that has volume and mass |
|
|
classification of matter |
Matter can be classified into two basic categories. Matter is either a mixture or it is a pure substance. We can classify mixtures into two categories - Homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. We can also classify pure substances into two categories - Elements and compounds. |
|
|
element(s) |
element = a pure type of matter composed of all the same atoms
|
|
|
atoms and molecules |
atoms: is the basic unit of a chemical element
molecule: combination of atoms (same element or different) joined chemically.
|
|
|
compound |
compound = pure substance made of 2 or more elements by a chemical reaction (different elements) Example: HCl or H2O all compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. compounds are made up of elements |
|
|
mixture |
mixture = combining substances in such a way that no chemical reaction occurs (different parts can still be picked out). |
|
|
law of definite proportions |
The Law of definite proportions states that no matter how you make a chemical compound, it's got the same ratio of elements. An example: Whether you make water by combining hydrogen and oxygen or by decomposing hydrogen peroxide, the resulting water will still be 1 part by mass of hydrogen to eight parts by mass of oxygen. |
|
|
proton |
is relatively large has a positive charge and is found in the nucleus |
|
|
neutron |
has a no charge,so it is neutral charge , found in the nucleus and is relatively large |
|
|
electron |
has a negative charge, is very small and is found outside of the nucleus |
|
|
atomic mass and number |
Atomic mass is the sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom, or the average mass, in a group of atoms.
Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table |
|
|
Bohr Rutherford diagram |

|
|
|
lewis dot diagram |

|
|
|
general atomic theory |
dalton proposed all matter consisted of tiny particles called atoms
Thomson's model of the atom is 'plum pudding'
Rutherford's model of the atom is called planetary model
Bohr-Rutherford model is the refined version of the original Putherford model. Schrodinger showed that electrons move in a region on space which is often represented visually as a cloud. |
|
|
STRUCTURE OF THE PERIODIC TABLE |
1. each element has a box 2. ordered by the atomic number 3. the columns are called groups, same valence electrons(outer shell) 4. the rows are called periods, same energy levels(shell number) 5. special groups 1,2,17,18 Alkali metals, Alkaline metals, Halogens, Nobel Gas 6. metal/non metals/ metalloid location is the 'staircase' 7. reactivity/ trends |
|
|
dependent variable |
Dependent variable is the responding variable,the outcome |
|
|
constant |
Constant: factors in the experiment which do not change throughout the entire experiment |
|
|
control |
Control variable that gets tested without change, does NOT have the experimental variable |

