![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Abiotic Factors |
A non-living factor within an ecosystem e.g. weather, pollution |
|
|
Biotic Factors |
A living factor within an ecosystem e.g. animals, plants |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Science of classification |
|
|
Order of Taxons |
Domain -- Kingdom -- Phylum -- Class -- Order -- Family -- Genus -- Species |
|
|
Community |
The sum of living organisms in a habitat |
|
|
Environment |
The abiotic and biotic components of an environment |
|
|
Ecosystems |
The interactions between the environment and the community |
|
|
Terrestrial Environments |
Land based e.g. tundra, deserts, forest, grasslands |
|
|
Aquatic Environments |
Photic zone e.g. marine and freshwater |
|
|
Niche |
A specific area |
|
|
Fundamental Niche |
The potential area an organism could inhabit if it was not under threat from other organisms |
|
|
Realised Niche |
The actual niche a species inhabits |
|
|
Environmental Niche |
The way a species functions in a niche |
|
|
Resource Partitioning |
Where the resources go – controls a realised niche |
|
|
Intraspecific Collaborations |
Between members of the same species |
|
|
Interspecific Collaborations |
Between members of different species |
|
|
Parasitism |
One species benefits at the expense of another |
|
|
Mutualism |
Two organisms live together and help each other |
|
|
Keystone Species |
One species that an ecosystem relies on the balanceresources and population |
|
|
Biological Complexity Order |
Biosphere -- Biome -- Ecosystem -- Community -- Population -- Individual |
|
|
Biosphere |
All living things on Earth e.g: lithosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere |
|
|
Biome |
Largest geographic communities that can be recognised, categorised by physical factors. |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Living things and physical environment; classified by abiotic and biotic factors |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Produces food that an ecosystem is based around through photosynthesis |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
Get energy and matter from autotrophs |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
Transfer of light energy into chemical energy by plants |
|
|
Energy Process |
Inputs -- Processing -- Outputs (& storage) |
|
|
Trophic Level |
Each link in a food chain |
|
|
Trophic Level Orders |
Producer -- 1st Order Consumer -- 2nd Order Consumer -- 3rd Order Consumer -- Apex Predator |
|
|
Amount of Energy lost from each Trophic Level |
10% |
|
|
Food Web |
Feeds on a variety of animals |
|
|
Ecological Pyramids |
Number of creatures and amount of organic matter; shows the amount of energy transferred |
|
|
Carbon Cycle |
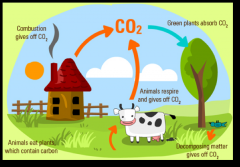
|
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle |
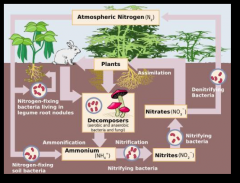
|
|
|
Biological Species Concept |
A species continues because it can interbreed |
|
|
Hybrid |
An organism created when two different species interbreed |
|
|
Morphological Species Concept |
A species based on physical characteristics |
|
|
Domain |
1. Archaea and Bacteria 2. Eukarya |
|
|
Competitive Exclusion Principle |
Two species cannot live in the same niche for a long time |
|
|
Kingdom |
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia |
|
|
Phylogenetic Species Concept |
The smallest group of individuals sharing a common ancestor |
|
|
Commensalism |
One animal benefits while the other is not impacted |

