![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Distinguishing features and causes of plant |
Green- because chlorophyll Cannot move from place to place- because their roots are firmly in place |
|
|
Shoot system consists of |
Flower Stem Leaf Fruit |
|
|
Root system consists of |
Roots |
|
|
Differences between plants and animals |
Animals have many complex organ systems Plants make thier own food Plants dont have a digestive muscoskeletal or nervous system |
|
|
Similarities |
Exchange gas Internal transport system to move water and nutrients Reproducing |
|
|
3 types of tissue in plants** |
Ground tissue- all other tissue Dermal tissue- outer surface Vascular tissue- tranports water and nutrients
|
|
|
Root system |
Part of plant that typically grows underground that absorbs water and minerals using root hairs and stores food |
|
|
How are roots useful |
Stores nutrients Source of food Remedies |
|
|
Shoot system |
Conducts photosynthesis and reproduces sexually |
|
|
Function of leaf |
PHOTOSYNTHESIS support Protect Reproduce Atrract |
|
|
Structure of cell that performs photosynthesis |
Chloroplast contain thylakoid which a flat and disk like. Thylakoid are aranged in stacks called grana. Grana traps solar energy and begins converstion |
|
|
Function of flower |
Reproduce |
|
|
How is plant pollination is achieved |
The male reproductive structure produce pollen and the female reproductive structure produce eggs. When the eggs get fertilized by pollen; pollination occurs. |
|
|
Stem function |
Supports leaves flowers Medicine Path to transport materials Vascular tissue to carry substances Food storage Protects photosynthesis and reproduction |
|
|
Seed growth process |
Cells divide quickly and develop into an embryo where they differentiate into specific tissue |
|
|
Region of growth** |
Tips of roots and shoots Below the surface of the stem in woody plants |
|
|
Why does plant growth occur** |
Undifferentiated cells are actively growing and dividing. They specialize and develop features according to their location and future function |
|
|
Meristematic cell** |
Indifferentiated cell that can form a specialized cell |
|
|
Tissue in leaf diagram |

|
|
|
Tissue in stem diagram |
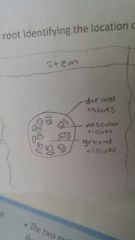
|
|
|
Tissue in root diagram |
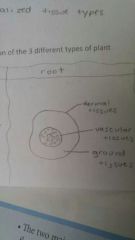
|
|
|
Dermal tissue |
Covers the entire outer surface of plant and includes the epidermal and periderm tissue |
|
|
Vascular tissue |
Joins plant parts and transportation system for water minerals and other chemicals |
|
|
Ground tissue |
All internal tissue in the root stem and leaves |
|
|
Epidermal tissue |
Thin layer of the cells that covers the surface of leaves stems and roots |
|
|
Periderm |
Forms bark on stems and large roots om woody plants |
|
|
Xylem** |
Made up of elongated cells. It transports dissolved minerals, water and nutrients upward starting at the the roots |
|
|
Phloem** |
Tissue that transports solutions of sugar produced by photosynthesis and other dissolved nutrients and hormones. They can be transport either downward starting at the leaf or upward starting from the root. |
|
|
Ground tissue** |
Filter between dermal and vascular tissue In green plants: manufacture nutrients by photosynthesis In roots: store carbohydrates In stems: provide energy and support |
|
|
Remaining sugar is called |
Starch |
|
|
Palisade layer |
A type a ground tissue located below the upper suface of a leaf that are closely packed woth chloroplasts |
|
|
Spongy mesophyll |
Loosely packed cells containing chloroplasts in the middle of a leaf |
|

Leaf cross section |

|
|
|
Cuticle |
Layer of wax that blocks gas and water diffusion |
|
|
Stomate |
Opening in surface of the leaf that allows gas exchange |
|
|
Guard cell |
One of a pair of cells in the epidermis that surrounds and controls the opening and closing of each stomate |
|
|
Obtaining water process |
Root hairs exend from the roots into the soil. These root hairs absorb water through osmisis. The water travels from the roots up to the stem through the leaf via the xylem |
|
|
Obtaining food and transporting it within an ANIMAL orgamism |
The nervous system and musculoskeletal system allow the body to obtain the the food. Then the digestive system digests it and the circulatory system transport the nutrients via blood vessels |
|
|
Obtaining food and transporting it with a PLANT tissue |
The entry of carbon dioxide water and light energy is controlled by the dermal tissue. Then the ground tissue cells in leaves produce sugar (their food). Then the vascular system transport the food i the phloem |
|
|
Cell division in plants |
Only in certain areas and once it has differentiated it does not divude any further |
|
|
How do plants grow |
By Using unspecialized cells called meristem |
|
|
Apical meristem |
Undifferentiated cells at the tips of the roots and shoots |
|
|
Lateral meristem |
Undifferentiated cells under the bark in the stems and roots of woodu plants |
|
|
Where and how does cell division occur in a plant |
In the apical meristem the cells elongaterhen differentiate into various kinds of specialized tissue and mature |
|
|
Growth in diameter |
The outer meristem produces new dermal tissue called cork to replace old epidermal cells. The inner lateral meristem produces new phloem on its outer surface and new xylem on its inner surface. |
|
|
Vegetation reproduction process |
Runners are shoots that grow away from parent plant. Once they touch the ground they put down roots and form an identical plant |
|
|
Vegetation reproduction |
Process where plants produce genetically identical offsprings from its roots or shoots |
|
|
Vegetation reproduction |
Process where plants produce genetically identical offsprings from its roots or shoots |
|
|
Tissue culture propagation |
Method of breaking down a piece of root into individual cells growing them into calluses thn treated chemically to create a whole new plant |

