![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
215 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Note
|
The governmental reporting standards established by GASB 34 (as amended) require presentation of basic FSs & RSI .
|
|
|
Note
|
Basic FSs are defined as:
1- GWFSs 2- Fund FSs 3- Notes to the FSs |
|
|
Note
|
Required & other supplementary information covers a wide range of data & presentations, including MD&A
|
|
|
Note
|
MD&A precede both the basic FSs & other schedules related to budget, pension, & infrastructure.
|
|
|
Note
|
Governmental reporting focuses on two important types of accountability:
1- Operational Accountability 2- Fiscal Accountability |
|
|
What is meant by Operational Accountability?
|
It is using the GWFSs to report the extent to which the government has met its operating objectives efficiently & effectively, using all resources available for that purpose, & the extent to which it can continue to meet its objectives for the future.
|
|
|
What is meant by Fiscal Accountability?
|
It is using the fund FSs to demonstrate that the government entity's actions in the current period have complied with public decisions concerning the raising & spending of public funds in the short-term.
|
|
|
What is the Governmental Financial Reporting Integrated approach?
|
It is the Financial accounting & disclosure of operational & fiscal accountability individually & the relationship between them through a reconciliation.
|
|
|
What is the Integrated approach Reporting Order?
|

|
|
|
What is the reason beyond reconciling the fund FSs to the GWFSs through the integrated approach?
|
To link the accountability objectives of the two levels of reporting.
|
|
|
Note
|
Reconciliation may appear on the face of the fund FSs or in the notes to the GWFSs.
|
|
|
When does the Reconciliation appear in the notes to the GWFSs?
|
When summarized aggregated information does not fully disclose the relationship of operational & fiscal accountability.
|
|
|
Note
|
Major funds are the focus of the fund statements, But Fund type summaries do not, in & of themselves, provide useful information.
|
|
|
Note
|
Major funds highlight the more significant components of governmental activities
|
|
|
What are the items REQUIRED for general purpose governmental units Reporting?
|
1- Management's Discussion & Analysis (MD&A)
2- GWFSs 3- Fund FSs 4- Notes to FSs 5- RSI other than MD&A 6- Other Supplementary Information |
|
|
Note
|
MD&A is a narrative analysis that explains through the eyes of management how they see the performance & where they see the company going.
|
|
|
Note
|
MD&A is considered RSI
|
|
|
What are the GWFSs?
|
1- Statement of Net Position
2- Statement of Activities |
|
|
Note
|
No Cashflows Statement in the GWFSs
|
|
|
Note
|
Fund FSs consist of:
1- Governmental Funds FSs 2- Proprietary Funds FSs 3- Fiduciary Funds FSs |
|
|
Note
|
On the Fund FSs each major fund is presented in a separate column, But Non-major funds are aggregated in one column
|
|
|
Note
|
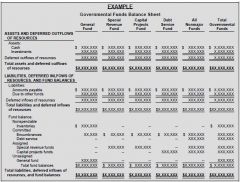
Example on Governmental Funds FSs
|
|
|
Note
|
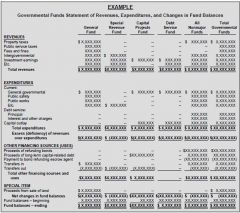
Example on Governmental Funds FSs
|
|
|
Note
|

Funds FSs
|
|
|
Note
|
RSI other than MD&A include:
1- Pension 2- Budget 3- Infrastructure |
|
|
What are the Pension information that are REQUIRED to be included in the "RSI other than MD&A" in reporting for the general purpose governmental units?
|
1- Sources of changes in net pension liability (last 10 years)
2- Information about the components of the net pension liability & related ratios (last 10 years) |
|
|
What are the Budget information that are REQUIRED to be included in the "RSI other than MD&A" in reporting for the general purpose governmental units?
|
Budgetary comparison schedules
|
|
|
What are the Infrastructure information that are REQUIRED to be included in the "RSI other than MD&A" in reporting for the general purpose governmental units?
|
1- Information about infrastructure (roads, bridges, etc.)
2- Assets for entities using the modified approach |
|
|
What are "Other OPTIONAL Supplementary Information" that are included in reporting for the general purpose governmental units?
|
1- Combining statements for non-major funds.
2- Variance between originally adopted & final amended budget. 3- Variance between final amended budget & actual. |
|
|
Note
|
Optional reporting format of the general purpose governmental units include a report called Comprehensive Annual Financial Report "CAFR"
|
|
|
What are the components of CAFR report ?
|
1- Introductory Section (unaudited)
2- Basic FSs & RSI (audited) 3- Statistical Section |
|
|
Note
|
Statistical section of CAFR report is not part of the basic FSs
|
|
|
What are the items included in the introductory unaudited section of CAFR report?
|
1- Letter of transmittal
2- Organizational chart 3- List of principal officers |
|
|
What are the "audited Basic FSs & RSI" included in the CAFR report ?
|
1- Management's discussion & analysis
2- GWFSs 3- Fund FSs 4- Notes to the FSs 5- RSI |
|
|
What are the items included in the statistical section of CAFR report?
|
1- Ten years of selected financial data
2- Ten years of economic data (e.g., millage rates, appraised values) 3- Other data |
|
|
What are the Government Financial Reporting Entities ?
|
1- Primary Government
2- Component Units |
|
|
Note
|
The focus of the GWFSs should be on the primary government.
|
|
|
What is the definition of the "Primary Government"?
|
It is all organizations that make up the legal government entity.
|
|
|
Note
|
The primary government is considered the nucleus of the financial reporting entity.
|
|
|
What are the Primary Government entities?
|
1- State governments
2- General purpose local governments 3- Special purpose local governments |
|
|
What are the examples on General purpose local governments?
|
1- City
2- County |
|
|
What is meant by Special purpose local governments?
|
It is a governmental unit that has a single or special purpose.
|
|
|
What are the examples on Special purpose local governments?
|
1- Hospital authority
2- School district |
|
|
What are the Criteria that should be met ALL in order for the state & local government to be considered as a "Primary Government Entity"?
|
1- Has a Separately-Elected governing body
2- Is Legally separate 3- Is Fiscally independent of other state & local governments. SELF |
|
|
Note
|
Special purpose governmental units that are not primary governments are organizations that are financially accountable to a primary government.
|
|
|
Note
|
Special purpose governmental units are typically entities engaged in:
1- Governmental activities 2- Business-type activities 3- Fiduciary activities 4- Governmental & business-type activities |
|
|
What are the "Component Unit" definitionS?
|
1- It is usually an organization that is legally separate & for which the elected officials of the primary government are financially accountable.
2- It is an organization that by its nature & the significance of its relationship with the primary government cannot be excluded from the primary government's FSs without making the primary government's FSs misleading or incomplete. 3- It is any organization (governmental, nonprofit, or for-profit) that does not meet the definition of a primary government. |
|
|
Note
|
Some component units are so intertwined with the primary government that they are, in substance, the same as the primary government, in these case blended presentation is preferred
|
|
|
What are Presentation types of financial information related to Primary Government & Component units?
|
1- Blended Presentation
2- Discrete presentation |
|
|
What is the "Blended Presentation"?
|
Blended presentation combines component units financial information with the primary government.
|
|
|
What are the circumstances that if one of them found, the Blended presentation method should be used?
|
1- A board of the component unit is substantively the same as that of the primary government.
2- The component unit serves the primary government exclusively or almost exclusively. 3- The component unit is not a separate legal entity. |
|
|
Note
|
If the blended presentation method is used, Financial information of the component units is NOT presented in separate columns.
|
|
|
What is the "Discrete Presentation"?
|
It is the presentation of Primary government SEPARATELY from component units' financial information
|
|
|
Note
|
Discrete presentation is used when the criteria for blended presentation are not met.
|
|
|
Note
|
Discrete presentation displays component units in separate columns.
|
|
|
Note
|
Most component units should use discrete presentation, its more common than blended presentation
|
|
|
Note
|
FSs of the reporting entity should provide an overview of the entity based on financial accountability.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
NFP organizations that provide ongoing support to a primary government or to a component unit of that primary government may also be a component unit of the primary government.
|
|
|
What are the examples on NFP organizations that are reported as a component unit of the primary government?
|
1- Private foundations associated with state universities
2- Private foundations associated with public health care facilities |
|
|
Note
|
Legally separate, NFP tax-exempt organizations should be reported as a discrete (separate column) component unit if they met some criteria.
|
|
|
What are those criteria that if met all, tax-exempt (NFP) organizations should be reported as a discretely presented component unit to the primary government?
|
1- Resources held by the tax-exempt organization are for the near-exclusive benefit of the primary government (benefit standard).
2- The primary government has access to a majority of the resources held by the tax-exempt organization (access standard). 3- Resources held by the tax-exempt organization are significant to the primary government (significance standard). |
|
|
Note
|
Legally separate, tax-exempt NFP organizations meeting the criteria of a financially integrated entity should be classified as a component unit of the primary government if their relationship to that government is so significant as to make the FSs misleading without component unit treatment.
|
|
|
Note
|
Organizations meeting the more generalized criteria associated with financial integration should be presented on either a blended or discrete basis depending on the circumstance.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
What is MD&A that is REQUIRED for general purpose governmental units Reporting?
|
It is a narrative that provides a brief, objective, & easily readable analysis of the government's financial activities based upon currently known facts, decisions, & conditions.
|
|
|
Note
|
MD&A provides the financial management of the government with the opportunity to present both a short-term & a long-term analysis of activities.
|
|
|
What are the issues that should be stated in MD&A?
|
1- Description of the FSs
2- Identity of the Primary Government & Discrete Component Units 3- Economic Conditions & Outlook 4- Major Initiatives |
|
|
What are the issues related to the FSs that should be included in MD&A?
|
1- An easily readable analysis
2- Condensed FS information 3- Analysis of overall financial position & results of operations 4- Analysis of balances & transactions of individual funds 5- Analysis of significant variations between original & final budget. 6- A description of the significant assumptions |
|
|
Note
|
Three years of Condensed FS information (derived from the GWFSs) are required if the basic FSs are comparative.
|
|
|
Note
|
In analysis of significant variations between original & final budget in MD&A, there is NO:
1- Variance analysis 2- Reconciliation of fund FSs to the GWFS |
|
|
Note
|
Major initiatives section of MD&A describes capital asset & long-term debt activity during the year.
|
|
|
What are the GWFSs?
|
1- Statement of Net Position
2- Statement of Activities |
|
|
Note
|
GWFSs aggregate information for all governmental & all business-type activities.
|
|
|
Note
|
GASB 34 requires the use of the economic resources measurement focus & the full accrual basis of accounting for GWFSs
|
|
|
Note
|
GWFSs include ALL assets & liabilities over which a government has Control or Responsibility, so fiduciary funds are excluded & the component units are included.
|
|
|
What is the format of Statement of Net position?
|
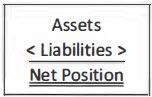
|
|
|
Note
|
Net position is divided into three components:
1- Net Investment in Capital Assets 2- Restricted Net Position 3- Unrestricted Net position RUN |
|
|
Note
|
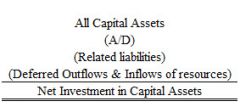
|
|
|
Note
|
Restricted net position consists of restricted assets reduced by liabilities & deferred inflows of resources related to those assets.
|
|
|
Note
|
Unrestricted net position includes the net amount of the assets, deferred outflows of resources, liabilities & deferred inflows of resources that are NOT included in the determination of Net investment in capital assets or the Restricted component of net position.
|
|
|
Note
|
The GASB 34 reporting model requires that capital assets, including infrastructure assets, be included in the GWFSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
The cost of capital assets should include all ancillary charges necessary to place the asset into its intended location & condition of intended use.
|
|
|
Note
|
Capitalization of construction period interest is NOT required for capital assets used in governmental activities.
|
|
|
What is meant by Infrastructure assets?
|
It is long-lived capital assets that normally are stationary in nature & normally can be preserved for a significantly greater number of years than most capital assets.
|
|
|
What are the examples on Infrastructure assets?
|
1- Roads
2- Bridges 3- Tunnels 4- Drainage systems 5- Water & sewer systems 6- Dams 7- Lighting systems |
|
|
Note
|
Prior to GASB 34, recording Infrastructure as capital assets in the GWFSs was optional, But Since implementation of GASB 34, infrastructure assets should be recorded as general capital assets
|
|
|
Note
|
Infrastructure assets are only reported on the GWFSs because of the incompatibility of recording these assets at the fund level with the governmental fund measurement focus & the fact that it would be difficult to allocate general assets to the individual funds.
|
|
|
What are the 2 approaches for assets capitalization & depreciation?
|
1- Required approach
2- Modified approach |
|
|
What does the Required Approach for the Depreciation of capital assets states?
|
All assets meeting capitalization requirements should be recorded & depreciated.
|
|
|
Note
|
According to Required Approach for the Capitalization of assets Depreciation expense that can be specifically identified with a functional category should be included in the direct expenses of that function (e.g., depreciation expense on police cars would be classified as public safety).
|
|
|
What does the Modified Approach for the Depreciation of capital assets states?
|
Infrastructure assets that are part of a network or subsystem of a network are not required to be depreciated provided the features of its two requirements are met.
|
|
|
What is meant by A network of assets?
|
It is a group of assets that provide a particular type of service for a government, Such as a dam composed of a concrete dam, a concrete spillway, & a series of locks.
|
|
|
What is meant by A subsystem of a network of assets?
|
It is composed of all assets that make up a similar portion or segment of a network of assets, Such as Interstate highways, state highways, & rural roads.
|
|
|
Note
|
All expenditures made to maintain Infrastructure capital assets under the modified approach would have to be expensed in the period incurred, while expenditures for additions & improvements would have to be capitalized.
|
|
|
What are those 2 requirements that should be met in order for the infrastructure capital assets NOT to be depreciated?
|
1- The Government's Asset Management System Meets Certain Conditions
2- The Government Documentation Should Include Data on Asset Preservation |
|
|
What are those conditions that Government's Asset Management System should met in order for Infrastructure assets NOT to be depreciated?
|
1- Inventory of eligible infrastructure assets is up-to-date.
2- A summarized condition assessment of the eligible infrastructure assets is performed & the results use a measurement scale. 3- Each year, an estimate is made of the amount necessary to maintain & preserve the eligible infrastructure assets at the condition level established & disclosed by the government. |
|
|
What are the data that should be included in the Government documentation on asset preservation?
|
1- A complete condition assessment of eligible infrastructure assets must be performed in a consistent manner at least every three years.
2- Reasonable assurance that the results of the three most recently completed condition assessments support assertions that the eligible infrastructure assets are being presented at (or above) the condition level established & disclosed by the government. |
|
|
Note
|
For Modified approach reporting, there are 2 schedules that must be presented as RSI as derived from the asset management system & documentation.
|
|
|
What are those 2 schedules that must be presented for modified approach reporting?
|
1- A schedule reporting the condition of the government's infrastructure,
2- A comparison schedule of needed & actual expenditures to maintain the government's infrastructure. |
|
|
Note
|
A change from the depreciation (required approach) to the modified approach should be treated as a change in accounting ESTIMATE.
|
|
|
Note
|
A change from the modified approach to the depreciation approach should also be treated as a change in accounting ESTIMATE.
|
|
|
Note
|
Governments are required to determine if impairment of an asset has occurred.
|
|
|
What is meant by asset Impairment according to GASB 42?
|
It is a significant, unexpected decline in the service utility of a capital asset.
|
|
|
Note
|
The events or changes in circumstances that lead to impairments are not considered normal & ordinary, That is, at the time the capital asset was acquired, the event or change in circumstance would not have been expected to occur during the useful life of the capital asset.
|
|
|
What is meant by the capital asset Service utility?
|
It is the usable capacity that a capital asset was expected to provide at its acquisition.
|
|
|
What are the most common indicators of potential impairment?
|
1- Physical damage
2- Enactment of laws & regulations 3- Obsolescence 4- Reduced utility |
|
|
What are the methods for calculating the amount of the impairment for assets that will remain in service?
|
1- Restoration cost approach
2- Service units approach 3- Deflated depreciated replacement cost approach |
|
|
What is the "Restoration cost approach"?
|
It is an approach that derives the amount of impairment from the estimated cost to restore the utility of the capital asset to its original condition, exclusive of any amount attributable to improvements & additions.
|
|
|
What is the "Service units approach"?
|
It is an approach that isolates the historical cost of the service utility of the capital that cannot be used due to the impairment, & estimates the total or maximum service units that the asset could have provided both before & after the impairment event, the percentage change in units would be applied to the carrying value of the capital asset to determine the amount of the impairment loss.
|
|
|
Note
|
Physical damage indicator of potential impairment could be measured using the Restoration cost approach.
|
|
|
What are the indicators of potential impairment that are measured using Service units approach?
|
1- Enactment of laws & regulations
2- Obsolescence 3- Reduced utility |
|
|
Note
|
As a GR, governments SHOULD capitalize works of art, historical treasures, & similar assets at their historical cost or fair value at date of donation (estimated if necessary) whether they are held as individual items or in a collection.
|
|
|
Note
|
Regardless of whether collection items are donated or purchased, governments may elect NOT to capitalize works of art when that collection meets some conditions.
|
|
|
What are those conditions that should be met ALL in order for governments to be able to elect NOT to capitalize works of art?
|
1- The collection is held for public exhibition, education, or research in furtherance of public service, rather than financial gain.
2- The collection is protected, kept unencumbered, cared for, & preserved. 3- The collection is subject to an organizational policy that requires the proceeds from sales of collection items to be used to acquire OTHER items for collections. |
|
|
Note
|
Elimination of interfund activities within major activity categories (e.g., governmental or business type activities) displayed for GW presentations should be prepared to avoid "grossing up" balances of assets & liabilities.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund receivables & payables displayed for GW presentations should be eliminated except for the net residual balances of amounts DUE & PAYABLE between governmental activities & business-type activities.
|
|
|
Note
|
For GW presentations Receivables & payables to fiduciary funds should be treated like assets & liabilities derived from external sources.
|
|
|
Note
|
Internal service funds should generally be reported in the governmental activities column.
|
|
|
Note
|
The GWFS includes all assets & liabilities over which a government has control or responsibility. It is important to note that:
• Fiduciary funds (PAPI) a re not included. • Component units are included. |
|
|
Note
|
Revenue & expenses are reported on the GW statement of activities using the full accrual basis.
|
|
|
What is the GW statement of activities "Program Approach"?
|
It is a net program cost format used in the preparation of GW statement of activities that provide cost information about the primary functions of the government & indicates each program's dependence on general revenues of the government. (i.e. Total costs by function are compared to program revenue associated with each function to arrive at the net cost that must be defrayed by tax revenues).
|
|
|
Note
|
The net expense or revenue for each function or program is classified into one of these categories:
1- Primary government governmental activities 2- Primary government business-type activities 3- Component units |
|
|
Note
|
Expenses category represents expenses directly associated with each of the functions or programs listed.
|
|
|
Note
|
Expenses are reported in the GW statement of activities by function on the full accrual basis.
|
|
|
Note
|
Program revenues are revenues directly associated with the function or program on the full accrual basis.
|
|
|
Note
|
Program revenues include Exchange & Non-exchange revenues
|
|
|
What are Program Revenue category types?
|
1- charges for Services
2- Operating Grants & Contributions 3- Capital Grants & Contributions SOC |
|
|
What are the program revenue "Charges for services"?
|
1- Charges for services to customers/applicants who directly benefit from goods/services (e.g., water & sewer fees, licenses, building permits, special assessments, etc.).
2- Charges for services to other governments (e.g., charges to housing prisoners, etc.). 3- Fines & forfeitures. |
|
|
What are the program revenue "Operating grants & contributions"?
|
It is Mandatory & voluntary non-exchange transactions with other governments, organizations, or individuals restricted for use in a particular program.
|
|
|
What are the program revenue "Capital grants & contributions"?
|
It is Mandatory & voluntary non-exchange transactions with other governments, organizations, or individuals restricted for use in a particular program.
|
|
|
Note
|
The net expense or revenue is presented in three categories & a total column:
1- Primary government governmental activities column 2- Primary government business-type activities column 3- Total column (1& 2) 4- Component unit column |
|
|
What are "General Revenues" on the GW statement of activities?
|
They are revenues that are NOT specifically associated with a functional expense
|
|
|
What are the examples on General revenues?
|
1- Taxes
2- Interest earnings 3- Other |
|
|
Note
|
General revenues are presented separately in three categories & a total column:
1- Primary government governmental activities column 2- Primary government business-type activities column 3- Total column (1& 2) 4- Component unit column |
|
|
What are "Special Items" on the GW statement of activities?
|
They are the unusual or infrequent (but not both) items
|
|
|
Note
|
Special items are within the control of management.
|
|
|
Note
|
Special items are reported separately.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
Generally, internal transactions that artificially "double up" on activity should be eliminated.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund services, such as water & other utilities, should not be eliminated.
|
|
|
Note
|
Internal activity associated with blended component units should be reclassified as interfund activity
|
|
|
Note
|
Internal activity associated with discretely presented component units should be reported as external transactions.
|
|
|
Note
|
Internal service fund activity should generally be reported in the governmental activities column.
|
|
|
Note
|
The GW statement of activities is the operating statement of the government.
|
|
|
Note
|
The basis of accounting in the GWFS is full accrual-identical to commercial accounting.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
GASB 34 emphasizes reporting by major fund rather than fund type, because Reporting by major fund provides more meaningful information.
|
|
|
What are the criteria that if met ALL, the fund will be considered a MAJOR fund?
|
1- Individual GRaSSP funds/Enterprise funds =10% or more of the total of all governmental funds/enterprise funds (corresponding Revenues-Expenditures/Expenses-Assets & deferred outflows of resources –Liabilities & deferred inflows of resources)
2- Individual GRaSSP funds/Enterprise funds =5% or more of BOTH the total of all governmental funds AND enterprise funds (corresponding Revenues-Expenditures/Expenses-Assets & deferred outflows of resources –Liabilities & deferred inflows of resources) |
|
|
Note
|
Government officials may elect to report a fund as major if they believe that the public interest is served by the reporting, regardless of the quantitative criteria.
|
|
|
Note
|
The general fund is always considered a major fund.
|
|
|
Note
|
Internal service funds are not considered in the evaluation of major & non major funds. The only proprietary funds used in the determination of major & non major funds are the enterprise funds.
|
|
|
Note
|
When determining if a fund qualifies as a major fund, remember that aggregate fund balance/equity is not used in either test.
|
|
|
Note
|
The differences between governmental fund & GWFSs are the result of differences in:
1- Measurement Focus Differences 2- Basis of Accounting Differences |
|
|
Note
|
Reconciliation of governmental fund FSs to the GWFSs involves elimination of the impact of using the current financial resources measurement focus for governmental fund FSs instead of the economic resources measurement focus used in GWFSs
|
|
|
What are the Measurement focus differences that should be adjusted in order to make the reconciliation between the governmental fund FSs & the GWFSs?
|
1- Loan proceeds (net of principal payments on debt) must be eliminated from resource inflows on the governmental fund operating statement & the related long-term debt must be added to the balance sheet.
2- Current period capital expenditures (net of depreciation expense) must be eliminated from resource outflows on the governmental fund operating statement & the related capital assets (net of accumulated depreciation) must be added to the balance sheet. |
|
|
Note
|
Reconciliation of governmental fund FSs to the GWFSs involves elimination of the impact of using the modified accrual basis of accounting in governmental fund FSs instead of the full accrual basis of accounting used in GWFSs.
|
|
|
What are the Basis of Accounting differences that should be adjusted in order to make the reconciliation between the governmental fund FSs & the GWFSs?
|
1- Increasing revenues to show revenues earned rather than only those measurable & available
2- Recognizing expenses when incurred rather than expenditures of current resources. |
|
|
Note
|
During reconciliation of governmental fund FSs to the GWFSs there must be reconciliation to the following:
1- Fund balances of governmental funds Vs net position in GWFSs 2- Net change in fund balances of governmental funds Vs change in net position for GOVERNMENTAL activities. |
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
Reconciliation of activity by fund type to the GWFSs can be presented on either the face of the FSs or the notes to the FSs.
|
|
|
What are the differences in Cashflows statement preparation between the Commercial business enterprises & the Proprietary funds?
|
1- The direct method is required (indirect method is not permitted).
2- A reconciliation of operating income (not net income) to net cash provided by operations is required. 3- There are four categories (instead of the three categories in commercial accounting) 4- The order of financing & investing activities categories are reversed, where Governmental entities present the financing category before investing, while Commercial entities present the investing category before financing. 5- Interest income/cash receipts are reported as "investing activities" (not as operating activities). 6- Interest expense/cash payments are either Capital/Non-capital financing activities (not Operating activities) 7- Capital asset purchases are reported as "financing activities" (not as investing activities). |
|
|
What are the 4 categories of the Proprietary funds Cashflows statement?
|
1- Operating activities
2- Capital & related financing activities 3- Noncapital financing activities 4- Investing activities |
|
|
What are the transactions included in the Proprietary funds Cashflows statement "Operating Activities"?
|
1- Cash inflows from sales of goods & services
2- Cash outflows to suppliers or employees 3- Cash inflows from interfund reimbursements & exchanges including payments in lieu of taxes. 4- Cash transactions not meeting the definition of the other categories |
|
|
What are the transactions included in the Proprietary funds Cashflows statement "Investing Activities"?
|
1- Cash inflows & outflows associated with loans to others
2- Cash inflows & outflows associated with equity transactions |
|
|
What are the transactions included in the Proprietary funds Cashflows statement "Capital & related financing activities"?
|
1- Cash flows from issuing debt associated with capital assets
2- Cash inflows from capital grants 3- Cash inflows from contribution activity associated with capital assets 4- Cash activity related to special assessments associated with capital assets |
|
|
What are the transactions included in the Proprietary funds Cashflows statement "Noncapital financing activities"?
|
1- Cash receipts from grants or subsidies
2- Cash received from property taxes (not restricted for capital use) 3- Operating transfers |
|
|
Note
|
Notes to the FSs are essential to fair presentation & considered INTEGRAL to the FSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
Notes to the FSs should focus on the primary government, specifically:
1- Governmental activities 2- Business-type activities 3- Major funds 4- Non major funds in the aggregate 5- Additional information regarding discretely presented component units |
|
|
Note
|
Notes to the FSs are classified into:
1- Generic Governmental Disclosures 2- Specific Governmental Disclosures (GASB 38) |
|
|
What are the Generic Governmental disclosures?
|
1- A description of GW activities, noting the exclusion of fiduciary funds.
2- Policies relating to elimination of internal activity. 3- Description of the modified approach for reporting infrastructure, if used. 4- Segment information on enterprise funds |
|
|
Note
|
Segment information on enterprise funds should meet the following definition of a segment:
1- Enterprise represents an identifiable activity. 2- Enterprise has one or more debt issues outstanding with revenue streams pledged in support of that debt. 3- Enterprise is accounted for separately. |
|
|
What are the Specific Governmental disclosures?
|
1- Description of activities for Major funds - Internal service funds - Fiduciary funds
2- The length of time used to define "available" in determining revenue recognition under the modified accrual basis (measurable & available). 3- Actions taken to correct material non-compliance with finance-related or legal compliance. 4- A schedule of short-term debt & the purpose for which the short-term debt was issued. 5- Analysis of interfund account balances 6- Analysis of accounts receivable & accounts payable |
|
|
Note
|
Analysis of interfund account balances would be by the following criteria:
1- Maturity (current & non-current) 2- Purpose 3- Individual major fund 4- Non major funds in the aggregate 5- Internal service fund 6- Fiduciary fund types |
|
|
Note
|
Analysis of A/R & A/P would be by the following criteria:
1- Maturity (current & non-current) 2- Type, If receivables (taxes & special assessments), If payables (vendors, salaries & benefits) 3- Activity & fund whether Governmental activities (GRaSPP) & internal service or Business-type activities (enterprise funds) |
|
|
Note
|
RSI includes information that precedes the FSs (the MD&A) & information included after the basic FSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
Significant information that follows the basic FSs includes:
1- Budgetary Information 2- Infrastructure Information 3- Pension Information |
|
|
Note
|
Budgetary comparison schedules MUST be prepared for:
1- General fund 2- Each major special revenue fund that has a legally adopted annual budget & may be presented as either RSI or in the basic FSs. |
|
|
Note
|
Budgetary comparison schedules MUST show the following:
1- Original Budget 2- Final amended Budget 3- Actual amounts |
|
|
Note
|
Computation of variances (Inflows/Outflows & Balances) between budget & actual is OPTIONAL.
|
|
|
Note
|
Computation of differences between original & final amended budget is OPTIONAL.
|
|
|
Note
|
Computation of differences between original & final amended budget is by using Budgetary basis
|
|
|
Note
|
Budgetary comparison may use either GAAP or budgetary formats, or basis of accounting, but must include a reconciliation to GAAP.
|
|
|
Note
|
Notes to RSI should disclose excess of expenditure over appropriations in individual funds presented in the budgetary comparison.
|
|
|
What did the disclosures schedules in RSI for all eligible infrastructure assets reported using the modified approach SHOULD include?
|
1- Assessed condition of infrastructure
2- Estimated annual amount to maintain & preserve infrastructure for each of the past five years. |
|
|
What are the ADDITIONAL disclosures in RSI related to infrastructure?
|
1- The basis for condition measurement,
2- The condition level at which the government plans to maintain its infrastructure. |
|
|
Note
|
Pension information disclosed in the RSI should cover the most recent 10 fiscal years
|
|
|
What are those pension information that SHOULD be disclosed in the RSI for each of the most recent 10 fiscal years?
|
1- Sources of changes in the net pension liability.
2- Information about the components of the net pension liability & related ratios 3- Significant methods & assumptions used to calculate the actuarially determined contributions. 4- Annual money-weighted rate of return on pension plan investments for each of the ten years presented. 5- Explanation of trends in amounts reported in the supplementary schedule |
|
|
What are the information about the components of the net pension liability & related ratios that SHOULD be disclosed in the RSI?
|
1- The pension plan's fiduciary net position as a percentage of the total pension liability.
2- The net pension liability as a percentage of the covered-employee payroll. 3- Actuarially determined contributions. 4- The amount of contributions. |
|
|
What are the Explanation of trends in pension amounts reported in the supplementary schedule that SHOULD be disclosed in the RSI?
|
1- Changes in benefit terms.
2- Changes in the population. 3- Changes in assumptions. |
|
|
What is meant by the "Interfund Activity"?
|
It is the flow of resources between funds & between the primary government & its component units.
|
|
|
Note
|
The accounting associated with interfund activity can be classified as follows:
1- Reciprocal interfund activity 2- Non-reciprocal interfund activity |
|
|
Note
|
Interfund activity is subject to SPECIFIC requirements related to FS display & disclosure.
|
|
|
Note
|
Reciprocal interfund activity includes exchange-type transactions between funds.
|
|
|
What are the types of Reciprocal interfund activity?
|
1- Interfund Loans
2- Interfund Services Provided & Used |
|
|
What are the "Interfund Loans"?
|
Interfund loans represent temporary extensions of credit to other funds that are expected to be repaid & are accounted for as interfund receivables & payables (due from/due to).
|
|
|
Note
|
Unrealizable Reciprocal interfund loans balances are reclassified as transfers.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund services represent sales & purchases between funds at external pricing.
|
|
|
What are the examples on "Interfund Services"?
|
Sales of water & sewer services by an enterprise fund to the city & internal service fund activities.
|
|
|
Note
|
Transactions of Interfund services are accounted for as revenues & expenses/expenditures.
|
|
|
Note
|
Generally, non-reciprocal interfund activity represents non-exchange transactions between funds.
|
|
|
What are the types of Non-reciprocal interfund activity?
|
1- Interfund Transfers
2- Interfund Reimbursements |
|
|
What are the "Interfund transfers"?
|
It is the Flow of assets between funds without the exchange of equivalent value.
|
|
|
What are the examples on "Interfund transfers"?
|
1- Payments in lieu of taxes made by a proprietary fund to the general fund
2- Budgeted transfer of pledged revenues from a special revenue fund to a debt service fund to meet bond covenant requirements |
|
|
Note
|
Transfers are normally displayed in the fund FSs as other financing sources & uses after non-operating revenues & expenses.
|
|
|
What are the "Interfund Reimbursements"?
|
Payments of expenses made by one fund on behalf of another fund.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund reimbursements serve to reclassify the expenditure or expense associated with the original transaction to the fund ultimately responsible for the obligation satisfied.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund reimbursements are NOT displayed in the fund FSs as interfund transactions.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund activity within the governmental activities column of the GWFSs should be ELIMINATED.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund activity within the business-type activities column of the GWFSs should be ELIMINATED.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund activity between the governmental activities & business-type activities displayed on the GWFSs should be ELIMINATED.
|
|
|
Note
|
Interfund activity between the primary government & its fiduciary funds should be REPORTED as if between external parties.
|
|
|
What are the FS disclosures related to Interfund Loans & Transfers?
|
1- Due to/from individual major fund.
2- Due to/from non major funds in the aggregate. 3- Due to/from internal service funds in the aggregate. 4- The purpose/description of each loan or transfer. |
|
|
Note
|
Disclosures specific to Interfund loans include Any amounts not expected to be repaid within a year.
|
|
|
Note
|
Disclosures specific to Interfund transfers include:
1- Any transfers that do not occur on a routine basis. 2- Transfers not consistent with the activities of the fund making the transfer. |

