![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
requirements to be President |
35 years old Natural Born be a resident for at least 14 years |
|
|
Requirements for senator |
30 years old live in state representing live in that state for 9 years |
|
|
Requirements for Congressmen |
25 years old live in state representing 7 year resident of that state |
|
|
Checks and balances |
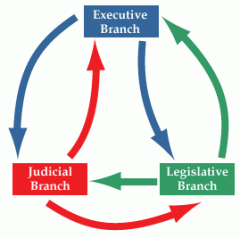
ensures no one branch gets too powerful |
|
|
1st amendment |
The right to Speech Petition Press Asembly Religion SPPAR |
|
|
2nd amendment |
The right to bear arms |
|
|
3rd Amendment |
No quartering solders |
|
|
4th amendment |
no unreasonable searches/seizures (need a warrent) |
|
|
5th amendment |
The right to remain silent (no self incrimination) No double jeopardy Due process of law |
|
|
6th - 12th amendments |
6 - rights of accused (speedy, Public trial) 7 - Trial by jury 8 - no excessive bail / cruel unusual punishment 9 - other rights 10 - Powers reserved to the states 11 - limits on lawsuits against states 12 - procedure of electing president / vice P |
|
|
13th Amendment |
Made slavery illegal |
|
|
14th amendment |
Protects the rights of citizens, originally protecting the rights of freed slaves |
|
|
15th amendment |
guaranteed the right to vote regardless of race |
|
|
16th amendment |
gives congress power to levy (collect) income tax
|
|
|
17th amendment |
provided for the direct election of senators |
|
|
18th |
prohibited the sale, transport, and production of alcohol (no alcohol allowed) |
|
|
19th |
gave woman the right to vote |
|
|
21st |
repealed the 18th amendment allowing alcohol |
|
|
22nd |
limited the president to 2 terms in office |
|
|
20th 23rd 24th 27th |
20 - changes dates of Pres/cong terms
23 - gives DC the right to vote 24 - Abolishes poll taxes 27 - congress pay raise next term |
|
|
25th |
provided the formal procedure for filling a vacancy in the oval office
|
|
|
26th |
moved the voting age to 18 |
|
|
Code of Hammurabi |
The first written code of law |
|
|
Justinian Code |
The result of an emperor simplifying Roman law into an orderly body of rules |
|
|
Napoleonic Code |
Code of law shaped by the Justinian Code and was eventually brought into all lands he conquered |
|
|
Common law |
a system of law based on precedent and customs |
|
|
Articles of the Constitution (part 1) |
1 - Legislative branch 2 - Executive Branch 3 - Judicial Branch |
|
|
Articles of the Constitution (part 2) |
4 - relationships between states 5 - Amendment process 6 - Supremacy clause 7 - Ratification (LEJSASR) |
|
|
Supreme Court Case (1) |
Brown v. Bored of education (1954) - overturned Plessy v. Ferguson, which said blacks and whites can be separate but equal |
|
|
Supreme Court Case (2)
|
Reed v. Reed - (1971) - ruled that state laws discriminating against woman was unconstitutional |
|
|
Supreme Court Case (3)
|
Miranda v. Arizona (1966) - suspects can't be questioned until them are read they're rights |
|
|
How a bill becomes a law* |
Proposed house 2 committee House 1 committee Floor debate floor debate basic majority basic majority vote president >>> President signs president pocket vetos W/ congress out of session |
|
|
How a bill doesn't become a law* |
denied at: committee 1 floor 1(not over 50% vote) committee 2 Floor 2 president vetos president pocket vetos W/ congress in session |
|
|
Great Compromise |
Agreement providing a dual system of congressional representation (2 house congress - 1 based on equality - 1 based on population) |
|
|
Three fifths compromise |
agreement providing that enslaved persons would count as three-fifths of other persons in determining representation in Congress |
|
|
Types of governemnt* |
Representative Democracy Authoritarian (Pick to rule for us) (total control) Republic (USA) Absolute Monarchy Constitutional Monarchy Dictatorship Totalitarian state |
|
|
Miranda Warning |
List of rights police must inform persons of before questioning, including the right against self incrimination and the right to council
|
|
|
Double Jepardy |
putting someone on trial for a crime for which he or she was previously acquitted
|
|
|
Types of Civil Law |
Contract law
property law family law personal injury law PPFC |
|
|
Delinquent Offenders |
a youth who has committed an offence that is punishing by criminal process
(illegal as an adult) |
|
|
Status Offenders |
a youth being charged with being beyond the control of his or her legal guardian
(only illegal as a child - running from home) |
|
|
Special District |
A unit of government that deals with a specific function, such as education, water supply, or transportation
(Bart or School district) |
|
|
Metropolitan area |
a large city and it's suburbs
|
|
|
Felonies |
type of crime more serious than a misdemeanor, punishable by over a year of jail time
|
|
|
Plaintiffs |
the person in a civil case who claims to have been harmed (the prosecution)
|
|
|
Defendants |
the person in a civil case who is said to have caused harm
|
|
|
Line- Item Veto |
vetoing a specific part of a bill
(only for the governor) |
|
|
trial court |
type of court in which a judge or jury listens to the evidence and reaches a verdict in favor of one party or another in the case |
|
|
Misdemeanors |
the least serious type of crime, punishable by less than a year of jail time
|
|
|
Reserved powers |
powers that the constitution does not give to the national government, and that are kept by the states
|
|
|
Concurrent powers |
powers shared by the state and federal governments
|
|
|
Enlightenment thinkers |
Baron be Montesquieu - separation of powers and checks and balances |
|
|
Enlightenment thinkers 2 |
John Locke - government by the consent of the people
|
|
|
Extending the right to vote |
15th amendment - Colored people can vote 19th - woman can vote 23rd - DC can vote 26th - 18 and up can vote |
|
|
Direct Primary |
an election in which voters choose candidates to represent each political party in a general election. The party chooses their representative to run for president ( they win the primaries and go to the general election) |
|
|
Closed Primary |
An election in which only the declared members of a political party are allowed to vote for that party's nominees
|
|
|
Open Primary |
an election in which voters need not declare their party preference
|
|
|
Plurality |
the most votes among all those running for a political office
|
|
|
Majority |
a number that is more than 50% of the total
|
|
|
Initiative |
a procedure by which citizens can propose new laws or state constitutional amendments
|
|
|
Refferendum |
a procedure by which citizens vote on state or local laws
|
|
|
Recall |
a special election in which citizens can vote to remove a public official from office
|
|
|
Electoral College |
a group of people named by each state legislature to select the president and vice president
|
|
|
Popular vote |
the votes cast by individual voters in a presidential election, as opposed to the electoral vote (we vote for people to vote for us) -purpose is to pick electors |
|
|
representative democracy |
a government in which citizens choose a smaller group to govern on their behalf |
|
|
republic democracy |
citizens have a role in choosing the person who will be head of state |
|
|
constitutional monarchy |
monarchy in which the power of the hereditary ruler is limited by the country's constitution and laws |
|
|
authoritarian regime |
a government in which one leader or group of people holds absolute power (power is held by a person or group not accountable to the people) |
|
|
totalitarianism |
describes a system in which government control extends to almost all aspects of peoples lives |
|
|
absolute monarchy |
a type of governemnt with no limit to their power |
|
|
dictatorship |
government with total control - but position is taken by force (overthrow existing gov) - Hitler |

