![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trapezoid
|
Трапеция
|
|
|
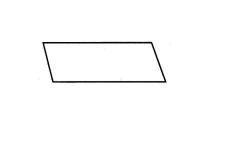
Parallelogram
|
|
|
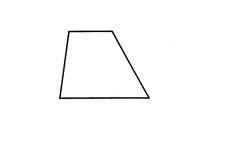
Trapezoid
|
|
|
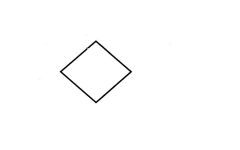
Rhombus
|
|
|
Opposite sides and opposite angles are equal.
|
Parallelogram
|
|
|
All angles are 90°, and opposite sides are equal.
|
Rectangle
|
|
|
All angles are 90°. All sides are equal.
|
Square
|
|
|
All sides are equal. Opposite angles are equal
|
Rhombus
|
|
|
One pair of opposite sides is parallel
|
Trapezoid
|
|
|
Note that a ... is a special type of parallelogram
that is both a rectangle and a rhombus. |
Square
|
|
|
Sum of interior angles of a polygon
|
(n-2)*180
|
|
|
Polygon
|
многоугольник
|
|
|
By the way, the corners of polygons are also known as ...
|
Vertices (singular: vertex)
|
|
|
Area of a TRIANGLE
|

(Base * Height) / 2
|
|
|
Area of a RECTANGLE
|
Length * Width
|
|
|
Area of TRAPEZOID
|

|
|
|
Area of any PARALLELOGRAM
|

|
|
|
Area of a RHOMBUS
|

|
|
|
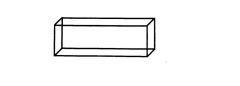
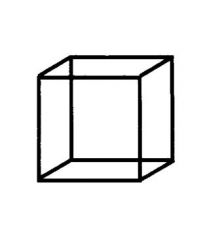
Rectangular solid
|
|
|
Cube
|
|
|
Volume of cube or rectangular solid
|
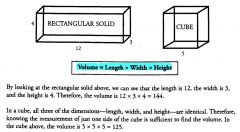
Length * Width * Height
|
|
|
Remember, when you are fitting 3-dimensional objects into other 3-dimensional objects, knowing the respective volumes is ...
|
Not enough. We must know the specific dimensions (length, width, and height) of each object to determine whether the objects can fit without leaving gaps.
|
|
|
The sum of the three angles of a triangle equals ...
|
180°
|
|
|
Angles correspond to ...
|
Their opposite sides. This means that the largest angle is opposite the longest side, while the smallest angle is opposite the shortest side.
|
|
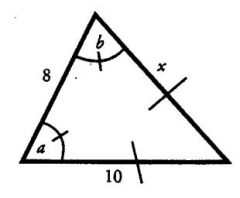
If angle a = angle b, what is the length of side x?
|
Since the side opposite angle b has a length of 10, the side opposite angle a must have the same length. Therefore, x = 10.
|
|
|
Mark equal angles and equal sides with a ...
|
Slash
|
|
|
The sum of any two sides of a triangle must be ...
|
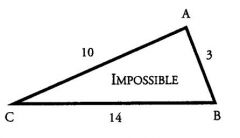
GREATER THAN the third side.
|
|
|
Note that the length cannot be as small as we wish. It must be greater than the difference between ...
|
The lengths of the other two sides.
|
|
|
If you are given two sides of a triangle, the length of the third side must lie between the ... and the ... of the two given sides.
|
Difference, sum.
For instance, if you are told that two sides are of length 3 and 4, then the length of the third side must be between 1 and 7. |
|
|
The hypotenuse is ... and is often assigned the letter c.
|
The side opposite the right angle
|
|
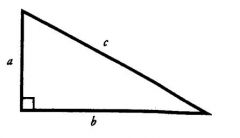
Pythagorean Theorem
|
a^2+b^2=c^2
|
|
|
What is a right triangle?
|
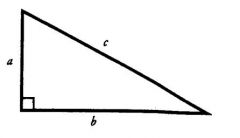
A right triangle is a triangle with one right angle
(90°). |
|
|
The most popular of all right triangles sides
|
3-4-5
3^2+4^2=5^2 Key multiples: 6-8-10 9-12-15 12-16-20 |
|
|
Also quite popular right triangle sides on the GMAT
|
5-12-13
Key multiples: 10-24-26 |
|
|
Less frequent right triangle sides
|
8-15-17
|
|
|
What is an isosceles triangle?
|
An isosceles triangle is one in which two sides are equal.
The two angles opposite those two sides will also be equal. |
|
|
An isosceles right triangle?
|
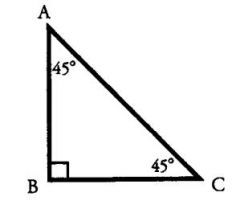
It has one 90°angle (opposite the hypotenuse) and two 45° angles (opposite the two equal legs). This triangle is called the 45-45-90 triangle.
|
|
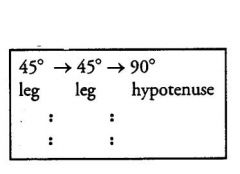
The lengths of the legs of every 45-45-90 triangle have a
specific ratio, which you must memorize: |
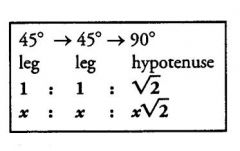
|
|
|
Thus, if you are given the ... of a square, you can use the 45-45-90 ratio to find the length of a side
of the square. |
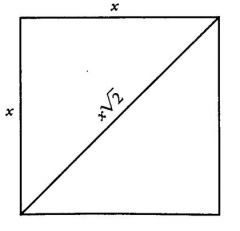
Diagonal
|
|
|
An equilateral triangle is ...
|
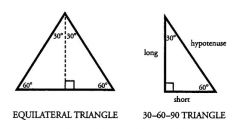
One in which all three sides (and all three angles) are equal. Each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60° (because all 3 angles must sum to 180°). A close relative of the equilateral triangle is the 30-60-90 triangle. Notice that two of these triangles, when put together, form an equilateral triangle.
|
|
|
The lengths of the legs of every 30-60-90 triangle have the following ratio, which you must memorize
|

|
|
|
Given that the short leg of a 30-60-90 triangle has a length of 6, what are the lengths of the long leg and the hypotenuse?
|
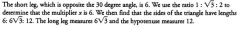
|
|
|
The diagonal of a square can be found using this formula
|

|
|
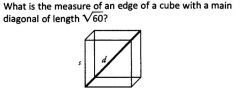
|
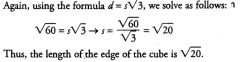
|
|
|
"Deluxe" Pythagorean Theorem
|
d^2=x^2+y^2+z^2
Where x, y, and z are the sides of the rectangular solid and d is the main diagonal. |
|
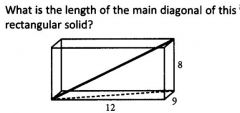
|
To find the diagonal of a rectangular solid, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem twice.
First, find the diagonal of the bottom face: 9^2+12^2=c^2 yields c = 15 (this is a multiple of a 3-4-5 triangle), so the bottom (dashed) diagonal is 15. Then, we can consider this bottom diagonal of length 15 as the base leg of another right triangle with a height of 8. Now we use the Pythagorean Theorem a second time: 8^2+15^2=c^2 yields c=17, so the main diagonal is 17. |
|
|
Triangles are defined as similar if all their corresponding angles are ... and their corresponding sides are ...
|
Equal, in proportion
|
|
|
If two similar triangles have corresponding side lengths in ratio a:b, then their areas will be in ratio ...
|
a^2 : b^2
|
|
|
For similar solids with corresponding sides in ratio a: b,
their volumes will be in ratio ... |
a^3 : b^3
|
|
|
Right triangles have three possible bases just as other triangles do, but they are special because their two legs are ...
|
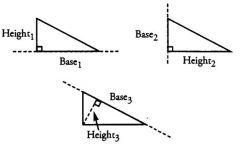
Perpendicular. Therefore, if one of the legs is chosen as the base, then the other leg is the height.
|
|
|
The area of an equilateral triangle with a side of length S is equal to
|
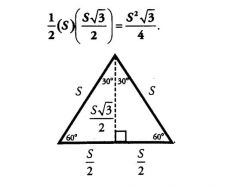
|
|
|
Any line segment that connects the center point to a point on the circle is termed ...
|
a radius of the circle
|
|
|
The formula for the circumference of any circle is
|
C=2(Pi)r
|
|
|
Pi is
|
a number that equals approximately 3.14. Pi = 22/7
|
|
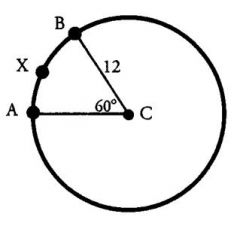
What is the length of arc AXB?
|
Arc AXB is the arc from A to B, passing through the point X. To find its length, first find the circumference of the circle. The radius is given as 12. To find the circumference, use the formula C = 2(Pi)r = 2(Pi)*12=24Pi.
Then, use the central angle to determine what fraction the arc is of the entire circle. Since the arc is defined by the central angle of 60 degrees, and the entire circle is 360 degrees, then the arc is 60/360 = 1/6 of the circle. Therefore, the measure of arc AXB = (1/6)*(24Pi) = 4Pi. |
|
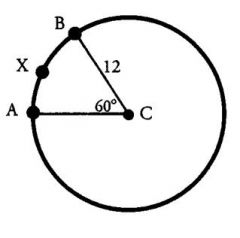
What is the perimeter of sector ABC?
|
In the previous example, we found the length of arc AXB to be 41Pi. Therefore, the perimeter of the sector is:
4Pi + 12 + 12 = 24 + 4Pi. |
|
|
The formula for the area of any circle is
|
A= Pi*r^2
|
|
|
An inscribed angle is equal to ... of the arc it intercepts, in degrees.
|
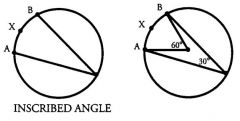
Half.
In this case, the inscribed angle is 30°, which is half of 60°. |
|
|
if one of the sides of an inscribed triangle is a DIAMETER of the circle, then the triangle MUST be a ...
|
Right triangle
|
|
|
Surface area of a cylinder ...
|
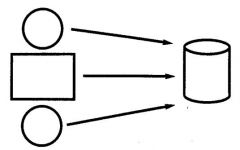
SA = 2 circles + rectangle = 2 (Pi*r^2) + 2Pi*r*h
|
|
|
The volume of a cylinder
|
V = Pi*r^2*h
As with finding surface area, determining the volume of a cylinder requires two pieces of information: (1) the radius of the cylinder and (2) the height of the cylinder. |
|
|
A rectangular box has the dimensions 12 inches * 10 inches * 8 inches. What is the largest possible volume of a right cylinder that is placed inside the box?
|

The radius of the cylinder must be equal to half of the smaller of the 2 dimensions that form the box's bottom. The height, then, can be equal to the remaining dimension of the box.
There is no general way to tell which way the cylinder will have the largest dimension; you must simply try all possibilities: |
|
|
Transversal
|
Поперечный; секущий.
(of a line) cutting a system of lines |
|
|
Interior angles that combine to form a line, sum
to 180°. These are termed ... |
Supplementary angles
|
|
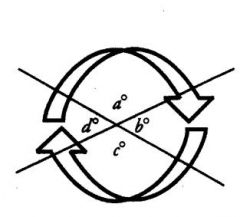
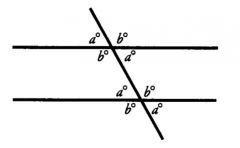
Angles found opposite each other where these two lines intersect are equal. These are called ...
|
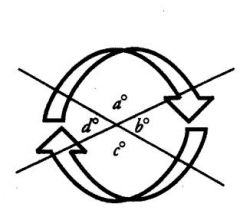
Vertical angles. Thus, in the diagram above, a = c, because both of these angles are opposite each other, and are formed from the same two lines. Additionally, b = d for the same reason.
|
|
|
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal in measure to the sum of ... of the triangle
|
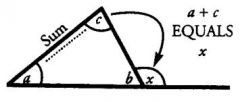
The two non-adjacent (opposite) interior angles.
|
|
|
Acute angle
|
Острый уголь. Less than 90°
|
|
|
Obtuse angle
|
Тупой уголь. Between 90 and 180 degrees.
|
|
|
Any acute angle is supplementary to any ...
|
Obtuse angle. Thus, a + b = 180°.
|
|
|
The point (0, 0), where the axes cross, is called ...
|
The origin
|
|
|
The slope of a line is defined as ...
|
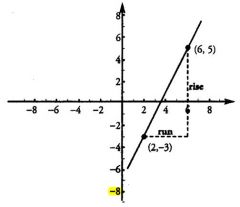
"rise over run" - that is, how much the line rises vertically divided by how much the line runs horizontally.
|
|
|
The slope is simple
|
rise / run or (y1-y2) / (x1-x2)
|
|
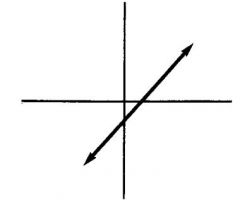
|
Positive slope
|
|
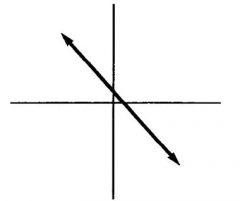
|
Negative slope
|
|
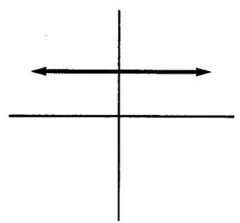
|
Zero slope
|
|
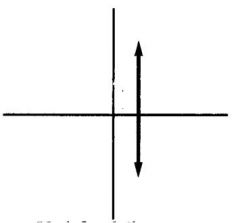
|
Undefined slope
|
|
|
A point where a line intersects a coordinate axis is called ...
|
An intercept. There are two types of intercepts: the x-intercept, where the line intersects the x-axis, and the y-intercept, where the line intersects the y-axis.
|
|
|
The x-intercept is the point on the line at which y =
|
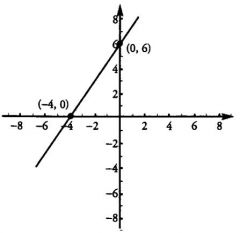
Zero. In this diagram, the x-intercept is (- 4), as expressed by the ordered pair (-4, 0).
|
|
|
The y-intercept is the point on the line at which x =
|
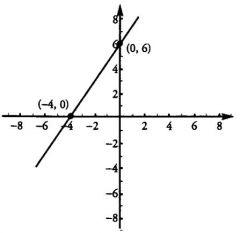
Zero.
In this diagram, the y-intercept is 6, as expressed by the ordered pair (0, 6). |
|
|
To find x intercept, plug in ... for ...
|
0 for y
|
|
|
To find y intercept, plug in ... for ...
|
0 for x
|
|
|
All lines can be written as equations in the form ...
|
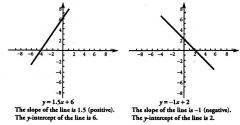
y = mx + b, where m represents. the slope of
the line and b represents the y intercept of the line |
|
|
Linear equations never involve terms such as ...
|
x^2, x^(1/2) or xy
|
|
|
What is the slope-intercept form for a line with the equation 6x + 3y = 18?
|
Rewrite the equation by solving for y as follows:
6x+ 3y= 18 3y= 18-6x y=6-2x y=-2x+ 6 Thus, the y-intercept is (0, 6), and the slope is -2. |
|
|
Find the equation of the line containing the points (5, - 2) and (3, 4)
|
FIRST: Find the slope of the line by calculating the rise over the run. The slope of the line is -3.
SECOND: Plug the slope in for m in the slope-intercept equation. y=-3x+ b THIRD: Solve for b, the y-intercept, by plugging the coordinates of one point into the equation. Either point's coordinates will work. Plugging the point (3, 4) into the equation (3 for x and 4 for y) yields the following: 4 = -3(3) + b 4=-9 + b b= 13 FOURTH: Write the equation in the form y = mx + b. y= -3x+ 13 This is the equation of the line. |
|
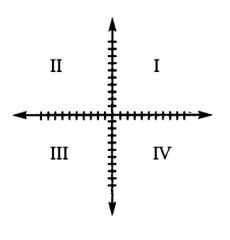
|
There are four quadrants in the coordinate plane, as shown in the diagram below.
Quadrant I contains only those points with a positive x-coordinate & a positive y-coordinate. Quadrant II contains only those points with a negative x-coordinate & a positive y-coordinate. Quadrant III contains only those points with a negative x-coordinate & a negative y-coordinate. Quadrant IV contains only those points with a positive x-coordinate & a negative y-coordinate. |
|
|
Which quadrants does the line 2x + y = 5 pass through?
|
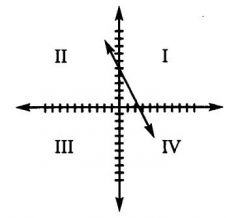
(1) First, rewrite the line in the form y = mx + b.
2x+y=5 y=5-2x y=-2x+ 5 (2) Then sketch the line. Since b = 5, the y-intercept is the point (0, 5). The slope is -2, so the line slopes downward steeply to the right from the y-intercept. Although we do not know exactly where the line intersects the x-axis, we can now see that the line passes through quadrants I, II, and Iv. Alternatively, you can find two points on the line by setting x and y equal to zero in the original equation. In this way, you can find the x- and y- intercepts. x=0 2x+y= 5 2(0) +y = 5 y=5 y=0 2x+y=5 2x+(0) = 5 x=2.5 The points (0, 5) and (2.5, 0) are both on the line. Now sketch the line, using the points you have identified. If you plot (0, 5) and (2.5, 0) on the coordinate plane, you can connect them to see the position of the line. Again, the line passes through quadrants I, II, and IV. |
|
|
Perpendicular bisector
|
Перпендикуляр, делящий отрезок пополам. The perpendicular bisector of a line segment forms a 90° angle with the segment and divides the segment exactly in half
|
|
|
The perpendicular bisector has the ... of the line segment it bisects.
|
Negative reciprocal slope. That is, the product of the two slopes is -1. (The only exception occurs when one line is horizontal and the other line is vertical, since vertical lines have undefined slopes)
|
|
|
Parallel lines have ... slopes
|
Equal. m1 = m2
|
|
|
Perpendicular lines have ... slopes
|
Negative reciprocal. -1/m1=m2, or m1*m2=-1
|
|
|
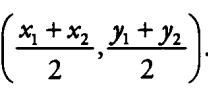
|
|
|
If two lines in a plane do not intersect, then the lines are ...
|
Parallel. If this is the case, there is NO pair of numbers (x, y) that satisfies both equations at the same time.
|
|
|
The two equations might represent the same line. In this case...
|
Infinitely many points (x, y) along the line satisfy the two equations (which must actually be the same equation in two disguises)
|
|
|
Of all quadrilaterals with a given perimeter, the ... has the largest area
|
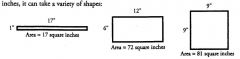
SQUARE
|
|
|
Of all quadrilaterals with a given area, the ... has the minimum perimeter.
|
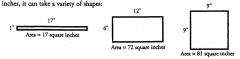
SQUARE
|
|
|
If you are given two sides of a triangle or parallelogram, you can maximize the area by placing those two sides ... to each other.
|
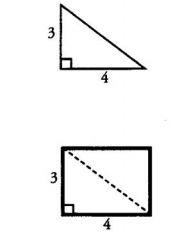
PERPENDICULAR
|
|
|
Any function of the form f(x) = ax^2 +bx +c, where a, b, and c are constants is called a quadratic function and can be plotted as a ... in the coordinate plane.
|
Parabola
|
|
|
Quadratic formula
|
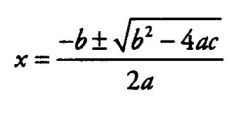
|
|
|
If b^2 -4ac > 0, then the square root operation yields a ...
|
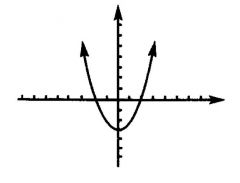
Positive number. The quadratic formula produces two roots of the quadratic equation. This means that the parabola crosses the x-axis twice and has two x-intercepts.
|
|
|
If b^2 -4ac = 0, then the square root operation yields ...
|
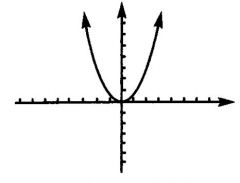
Zero. The quadratic formula only produces one root of the quadratic equation. This means that the parabola just touches the x - axis once and has just one x-intercept.
|
|
|
If b^2 -4ac < 0, then the square root operation yields ...
|
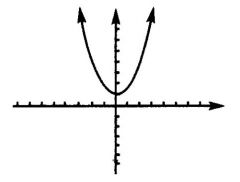
Cannot be performed. This means that the quadratic formula produces no roots of the quadratic equation, and the parabola never touches the x-axis (it has no x-intercepts)
|
|
|
Given coordinates of two points, distance D between two points is given by:
|
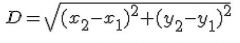
|
|
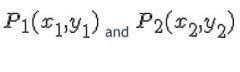
The slope equation of a straight line passing through points
|
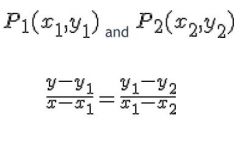
|
|
|
If the equation of the line is given in the General form: ax+bx+c, then the slope is ... and y intercept is
|
-(a/b)
-(c/b) |
|
|
if any point O(x,y) divides distance between two point A(x1,y1) and B(x2,y2) in the ratio m1:m2 coordinates of the point O is
|
x=(m1*x2+m2*x1)/(m1+m2) and y=(m1*y2+m2*y1)/(m1+m2)
|
|
|
The perpendicular bisector has the negative reciprocal slope of the line segment it bisects. That is, the product of the two slopes is -1. The only exception occurs when one line is ... and the other line is ..., since ... lines have undefined slopes
|
Horizontal, vertical
|

