![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is our only source for energy for moving, breathing and cardiac cycle
|
Diet
|
|
|
Nutrients obtained from diet have one of three possible fates, what are they?
|
-Supply energy
- serve as building blocks ( proteins, hormones and enzymes) -stored for future use (Glycogen, fats etc..) |
|
|
What is catabolism
|
Breaking down of complex molecules
|
|
|
Define anabolism
|
Endergonic rxns which involve Building of complex molecules
|
|
|
What's Metabolism and what organs regulate it
|
- Balance between energy inputs and outputs of anabolism and catabolism
-primarily regulated by brain liver and adipose tissue |
|
|
Which molecules have a finite lifespan and why
|
Anabolic molecules because they undergo catabolism
|
|
|
Which rxns use ATP, which make it
|
Anabolic- use it
Catabolic- make it |
|
|
What percentage of energy is used from catabolism for cellular function?
-what happens to the rest? |
-40%
-lost as heat |
|
|
Coupling catabolism by ATP
|

|
|
|
What is glycolysis
|
The breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6) to make 2 molecules pyruvate and 2 molecules of ATP
|
|
|
What are plasma glucose regulated to?
|
90/100mg/ dl
2-3 grams |
|
|
Describe the first step of glycolysis
|
- it's a phosphorylation rxn
- (6C molecule) glucose (C6H12O6) is phosphorylated by hexokinase (gkucokinase in liver) -makes glucose-6-phosphate ( C6H11O6P1) -uses 1 ATP - make 1 ADP |
|
|
Describe the second stage of glycolysis
|
-isomerisation rxn of g-6-p
-enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase -makes fructose-6-phosphate (6 carbon sugar) |
|
|
Describe third stage of glycolysis
|
Phosphorylation
F-1,6-P is phosphorylated to F-6-B ( C6H10O6P2) Enzyme- phosphofructokinase Uses 1 ATP Gain ADP |
|
|
4th stage of glycolysis
|
Destabilisation
-F1,6B is split into two sugars dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. -By aldolase -dihydroxyacetone can be converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by triosephosphate isomerase. |
|
|
5th step
|
Dihydroxyacetone can be changed to by triosephosphate Isomerase into Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
|
|
|
6th step
|
G-3-P is dehydrohenated by glyceraldehyde-3-dehydrogenase into 1,3bisphosphogylcerate.
-1 NADH and H |
|
|
7th step
|
-1,3 bisphosphoglycerate is changed to 3-phosphoglycerate by enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase.
-ATP gained |
|
|
8th step
|
3-phosphoglycerate is changed into 2-phosphoglycerate by
phosphoglycerate mutase |
|
|
9th step
|
-2-phosphoglycerate is changed into - phosphoenol pyruvate by enolase
Water is gained - |
|
|
10 step
|
Phosphoenolpyruvate is turned to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase
-2 ATP gained |
|
|
How does glucose get into the Gi tract
|
-By secondary active transport
|
|
|
How does glucose get into most other cells?
|
Facilitated diffusion through GlutT molecules
|
|
|
On which cells does insulin increase expression of GlutT
|
Muscle and adipose
|
|
|
which cells have GLUT1 and is it affected by insulin
|
-Nerve cells and hepatocytes
-no GLUT1 is always open |
|
|
What are the gains of glycolysis
|
2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 2 molecules of ATP, 2 NADH and 2H+
|
|
|
What's the purpose of formation for Acytyl Co enzyme? And what's the gain
|
-To prepare pyruvate for entry into the krebs cycle
-produced NADH and H and CO2 |
|
|
What happens in the krebs cycle rxn
|
Acytyl coenzyme A is oxidised to produce ATP, CO2, NADH, H+, and FADH2 and transfers their electrons through electron carriers
|
|
|
What exactly happens in glycolysis in summary
|
-Glucose is split into 2 3-carbin molecules of pyruvic acid
-consumes 4 ATPs but uses 2 -fate of pyruvic acid depends on oxygen availability -if oxygen is lacking then it is turned to lactic acid -if oxygen is plentiful then it is converted to Acytyl coenzyme A |
|
|
What's the key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis
|
Phosphofructokinase
|
|
|
What happens in steps 1-5 of glycolysis
|
-energy is invested in form of ATP
-6-C glucose is split into 2 3-carbon molecules glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate -PFK activity is high when ADP levels are elevated. |
|
|
What happens when PFK is low
|
-Glucose is shunted away from glycolysis to glycogen storage pathway
|
|
|
Overall what happens in steps 8-10 of glycolysis
|
-2 glyceraldehyde molecules are converted to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and ATP is gained
-NADH and H+ generated in step 6 is used to generate 4 ATPs in the electron transport chain. Hepatocytes and cardiac muscle generate 6 ATPs. From them. |
|
|
What's Gluconeogenesis
|
Formation of glucose from non-carbohydrates such as lactate, glycerol, and aas
|
|
|
Glycogenesis
|
Formation of Glycogen from glucose and (fructose)
|
|
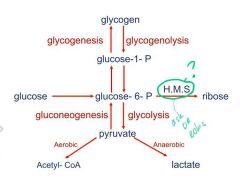
What's glycogenolysis
|
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose (G-1-phosphate)
|
|
|
Gluconeogenesis
|
Breakdown of fats, amino acids to form glucose
|
|
|
What tissues have an absolute requirement of glucose per day and what are they?
|
Brain - 120g/day
Erythrocytes - 40g/day |
|
|
What are the key organs involved in carbohydrate Metabolism?
|
Liver
Pancreas |
|
|
What's the role of the liver in CM
|
-Acts as body's sink for glucose
-major site for glucose storage -site for Gluconeogenesis |
|
|
What's the role of the pancreas in carbohydrate Metabolism
|
-produces pancreatic amylases and bicarbonate to aid with carb digestion
-produces two key hormones: Insulin from B-cells Glucagon from a-cells |
|
|
What type of hormones are Glucagon, insulin and adrenaline
|
Peptide hormones
|
|
|
What does Glucagon do
|
Increases blood glucose by stimulating glycogenolysis
|
|
|
What hormone plays a supporting role in the increase of glucose
|
ADRENALINE
|
|
|
What is the effect of high insulin in the body on:
Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Glycogenolysis Glycogenesis |
1. Decreases Gluconeogenesis- don't need to make more glucose
2. Increases glycolysis- excess glucose needs to be broken down and stored 3. Glycogenolysis- decrease because sugar is not needed 4. Glycogenesis- increase because sugar needs to be stored |
|
|
Glucagon effect on
Glycolysis Glycogenolysis Glycogenesis Gluconeogenesis |
1. Glycolysis- Decreases stop storing sugar
2. Glycogenolysis- Increases needed for glucose 3 . Glycogenesis- Decreases can't be making glycogen because sugar is needed 4 .Gluconeogenesis- increases sugar needs to be made |
|
|
-How many steps of glycolysis are irreversible
-what are they -why |
- 3
-step 1: G to G-6-P by hexokinase Step 3: F-6-P to F-1,6-B by PFKs Step 10: Phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate -because of input of ATP |
|
|
Key enzymes of glycolysis
|
Hexokinase, PFK and pyruvate kinase
|
|
|
In what ways are the key enzymes of glycolysis regulated
|
1 Allosteric effects of metabolites
(build up of AMP or product) 2 Hormonal action:- a) Enzyme modification usually phosphorylation (short term) b) Induction/repression of enzyme synthesis (longer term) |
|
|
PFK 1 ALLOSTERIC REGULATION
|

|
|
|
PEP Allosteric regulations
|

|

