![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the five categories of wellbeing? |
Social, Political, Technological, Economic and Environmental |
|
|
Social Indicator does what? |
Measures population growth, literacy and life expectancy |
|
|
Political Indicator does what? |
Measure governmance, work safety, female parlimentarians |
|
|
Technological Indicator does what? |
Measures access to electricity and the internet |
|
|
Economic indicator does what? |
Measures income, employment and Gross National income |
|
|
Environmental indicator does what? |
Assess access to natural and man made environmental resources such as water and Co2 emissions |
|
|
Qualitative Indicator |
Analyses features that are not easily calculated or measured such as freedom and security. |
|
|
Quantitative Indicator |
Easily measured and can be stated in numbers such as annual income or how many doctors there are in a country. |
|
|
Classify the following as either quantitative or qualitative? 1.Motor Vehicles 2.Unemployment 3.Power Consumption 4.Obesity 5.Quality of Teaching 6.How much you trust neighbours 7.Access to public transport
|
1. Quantitative 2. Quantitative 3. Quantitative 4. Quantitative 5. Qualitative 6. Qualitative 7. Qualitative
|
|
|
Define Wellbeing? |
A good or satisfactory condition of existence, a state characterised by health, happiness, prosperity and welfare |
|
|
What is poverty? |
A denial of choices and opportunities, a violation of human dignity . |
|
|
What examples does the United Nations give to explain poverty? |
Not having enough to feed or clothe your family Not having a school or clinic to go to Not having land to grow ones food Not having a job to earn ones living Susceptibility to violence Implies living in marginal or fragile environments No access to clean water or sanitation
|
|
|
Map First and Third World |
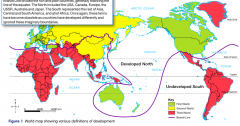
|
|
|
Characteristics of LEDC (Less Economically Developed Country) |
- A third world country - Over population - Poor economy - Little or no access to education - Little or no access to medical facilities - Widespread malnutrition - High Infant mortality rate (babies don't live long) - Low life expectancy - Unstable government - Contaminated water |
|
|
Characteristics Of MEDC (More Economically Developed Country) |
- A first world country - Access to basic needs(food,water,shelter) - Access to wants (phones, cars) - Access to Primary, Secondary and University education - Government and private medical facilities - Stable economy and government - Welfare - Low birth and death rate - No internal conflicts |
|
|
Africa |
Sudan South Africa Kenya
|
|
|
South America |
Brazil Argentina Peru
|
|
|
North America |
Canada United States Mexico |
|
|
Europe |
France Sweden Turkey |
|
|
Asia |
India Thialand Malaysia |
|
|
Oceiana |
Australia Fiji Pupa New Guinea |
|
|
Human Development Index |
Measures the standard of living and wellbeing by measuring life expectancy, education, literacy and income. |
|
|
Three types of aid? |
Bilateral aid Multilateral aid NGO/Charity aid
|
|
|
Positive and Negative of Bilateral aid? |
Positive - Helps expand infrastructure Negative - Tied aid has to be spent on goods and services from donor country |
|
|
Positive and Negative of Multilateral aid? |
Positive- Clear aims around what trying to achieve Negative - Sometimes directed towards specific areas leaving many without any benefits |
|
|
Positive and Negative of NGO/charity aid? |
Positive - targeted at long term development within county Negative - Up to 30% of donations may be eaten up by administration costs. |
|
|
Difference between the types of aid? |
Bilateral aid is given by governments to donor countries where Multilateral aid is provided through international institutions such as UNICEF and Non government organisations (NGOs) is voluntary or private individual donations collected by organisations such as the Red Cross. |
|
|
Negative impact of aid |
- dependency on donor countries - sometimes not a gift but loan - may be used to place political or economic pressure on a country - corruption among politicians - it it does not provide and empower citizens, wellbeing will not be improved. |
|
|
Population distribution |
the spread of people across the globe. |
|
|
Population density |
the number of people within a given area, usually per square kilometer. |
|
|
What effects human distribution? |
Physical factors - freshwater, fertile soil, moderate climate and sea ports
Human factors - urban environments with availability of employment, government policies such as migration
|
|
|
Regions with high population density? |
Clustered in Europe, East and South East Asia and Eastern half of United States
Example: Germany 233 people per square kilometer |
|
|
Regions with low population density? |
Inland of central Asia and Australia.
Example: Australia has population density of 2.9 people per square kilometer |

