![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Astrocyte Functions
|
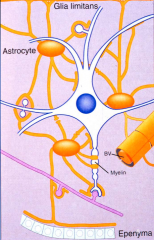
Marked by GFAP (glial fibrullary astrocyte protein)
1. Only neuronal cell that store glucose. 2. They isolate synapses and the nodes of Ranvier 3. They interconnect the brain surface (glial limitans), epnedymal lining the ventricles, synapses and blood vessels. 4. They form desmosomal (tight) junctions, permitting cell to cell transfer of small molecules. 5. They surround foreign bodies and form a scar. 6. They induce brain endothelial cells to form the blood brain barrier. 7. Consume excess extracellular potassium to prevent excessively depolarized neurons. 8. Gaba and Glutamate update / degradation from synaptic cleft via EAAT (excitatory amino acid transporters). 9. They provide extracellular matrix. |
|
|
Reperfusion Injury (as a result of astrocyte malfunction):
|
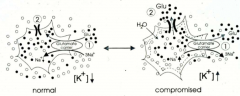
Astrocytes absorb Glutamate from the synaptic cleft and convert it to Glutamine (via glutamine synthatase). The glutamate transporter in this process is a secondary active (co-) transporter that uses Na+ concentration gradient to pull Glutamate into the astrocyte. If astrocytes are depolarized, then the transporters will reverse and glutamate will spill back into the synaptic cleft.
|
|
|
Oligodendrocytes staining and function:
|
Marked by glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase & 2'-3' cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (CNPase).
1. Function to make myelin in the CNS. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the myelin NoGo protein?
|
This protein prevents growth cones within the axon and prevents it from growing out of the myelin. In spinal cord crush injury, antibodies or gene mutations can effect this protein and enhance axon elongation.
|
|
|
Microglia functions:
|
Marked by complement receptor 3 and MHC-II.
1. Major representative of the immune system in CNS 2. In severe conditions they can round out and become macrophages. |

