![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
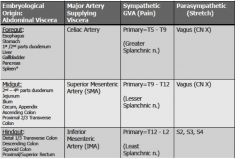
Name the three divisions of abdominal viscera?
|
1. foregut
2. midgut 3. hindgut |
|
|
For parietal peritoneum, pain is usually well localized except
for the diaphragm... what nerve roots innervate it and to where is pain referred? |
C3,C4, C5 (keeps the diaphargm alive) irritation referred to dermatomes over the shoulder
|
|
|
What part of the embryological gut becomes pharynx to ~1/2 the duodenum (and some accessory structures)?
|
foregut
|
|
|
What part of the embryological gut becomes duodenum to transverse colon (~2/3)?
|
midgut
|
|
|
What part of the embryological gut becomes distal transverse colon to rectum?
|
hindgut
|
|
|
1. What blood vessels supply foregut structures?
2. What BV's supply midgut structures? 3. What BV's supply hindgut structures? |
1. celiac trunk
2. superior mesenteric artery 3. Inferior mesenteric structures |
|
|
Relationships with Abdominal Aorta...
a. begin b. position c. relationship/termination |
a. T12
b. retroperitoneal, anterior to vertebral bodies c. relates to L1-4 and aorta terminates at L4 where it divides L/R common iliac artery |
|
|
|
|
|
-Most common type of aneurysm?
How it is diagnosed? |
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
-Primary location: between renal and common iliac arteries Clinical Dx: AAA 1. Pulsatile abdominal mass >2 inches wide 2. Mid/low back pain 3. Abdominal Bruit |
|
|
-Clinical Dx: Ruptured AAA
|
-Clinical Dx: Ruptured AAA
1. Abrupt onset Left flank pain AAA Ultrasound Stent Graft 2. Hypotension (rupture is into left retroperitoneal potential space) |
|
|
What is the 3 major branchces of the ciliac trunk of the abdominal aorta?
|
1. left gastric a (superior)
2. common hepatic (right) 3. splenic (left) |
|
|
Gastro omental goes to what curvature
|
the greater curvature
|
|
|
Describe a major difference between parasympathetic fibers?
|
Parasympathetic fibers
from the posterior trunk of the Vagus do NOT synapse, just pass through the celiac plexus follow blood vessels (branches of the celiac artery) to the target organ synapse in the walls of the organ |
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
45 y.o. Caucasion female, BMI=30, presents to the emergency room with chief complaint of acute abdominal pain. Further questioning reveals the patient is also experiencing pain in her right shoulder and just below her scapula.
a. why shoulder pain? b. what organ? c. why pain inferior to scapula? d. organ? Diagnosis? |
A. via C3,4,5 to dermatome
b. diaphragm c. via T7-9 dermatome d. gallbladder - acute cholecystitis with diaphragmatic involvement |
|
|
A 67 y.o. male presents to the emergency department with chief complaint: acute abdominal pain. Surgical service is called for consult. Further questioning reveals diffuse pain in the region of the umbilicus.
A. dermatome for umbilical pain? B. Organ |
a. T10 to dermatome
b. appendix acute appendicitis, early/initial stage |
|
|
What is McBurney's point?
|
A point 2/3rds the distance from the umbilicus to the right ASIS (McBurney’s Point) indicating involvement of the Parietal peritoneum
|
|
|
Name the Dermatome / Area of Skin Experiencing Pain, Sympathetic Afferent Innervation with the following visceral structure...
a. diaphragm b. esophagus c. stomach |
a. Diaphragm - C3-C5 / Skin of ipsilateral neck, shoulder Phrenic n.
b. Esophagus T5-T6 Celiac plexus c. Stomach T6-T9 / Skin of chest and substernal region, Celiac plexus |
|
|
Name the Dermatome / Area of Skin Experiencing Pain, Sympathetic Afferent Innervation with the following visceral structure...
a. liver b. gallbladder |
a. Liver T7-T9, Celiac plexus
b. Gallbladder T7-T9/ on right, inferior to scapula, Celiac plexus |
|
|
Name the Dermatome / Area of Skin Experiencing Pain, Sympathetic Afferent Innervation with the following visceral structure...
a. pancreas b. small intestine |
a. Pancreas T6-T10 Celiac plexus /Superior mesenteric plexus
b. Small Intestine T9-T10 (lateral), Superior mesenteric plexus |
|
|
Name the Dermatome / Area of Skin Experiencing Pain, Sympathetic Afferent Innervation with the following visceral structure...
a. appendix b. large intestine proximal to splenic flexure |
a. Appendix T10, Superior mesenteric plexus
b. Large Intestine proximal to splenic flexure T11-T12 Superior mesenteric plexus/ Inferior mesenteric plexus |
|
|
Name the Dermatome / Area of Skin Experiencing Pain, Sympathetic Afferent Innervation with the following visceral structure...
Descending Colon, Sigmoid Colon, Rectum |
S2-S4 / low sacral back and sciatic pain
in upper posterior thigh and/or calf, Sacral plexus |

