![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Remote Sensing? |
The science of acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually being in contact with it. This is done by sensing and recording reflected or emitted energy and processing, analyzing and applying that information. |
|
|
What is Electromagnetic Energy? |
Energy propagated through space or through material media in the form of an interaction between electric and magnetic fields, moving at the velocity of light. |
|
|
Name the forms of Electromagnetic Energy. |
*Visible light *Radio waves *Heat *Ultraviolet rays *X-rays |
|
|
Name the two components/waves which comprise Electromagnetic Radiation. |
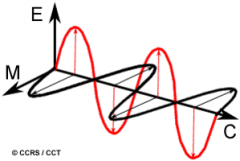
1. An electrical field (E) which varies in magnitude in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the radiation is traveling. 2. A magnetic field (M)oriented at right angles to the electrical field. Both these fields travel at the speed of light (c). |
|
|
Electromagnetic (EM) energy displays 3 properties. Name them and give their units. |
*Wavelength (lambda) in micrometer *Frequency (v) in hertz (Hz) *Amplitude in W.m^2.micrometer (Watt per SM) |
|
|
Show the relationship between short wavelength, long wavelength, low frequency & high frequency. |
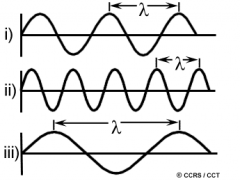
ii) short wavelength and high frequency iii) long wavelength and low frequency |
|
|
What is the formula relating wavelength & frequency? |

|
|
|
What does the wave theory say about EMR? |
The wave theory describes electromagnetic energy as travelling in a harmonic, sinusoidal fashion at the velocity of light c, (3x10^8m/sec). |
|
|
Define wavelength. |
The distance from one wave peak to the next. |
|
|
Define frequency. |
The number of peaks passing a fixed point in space per unit time.
|

